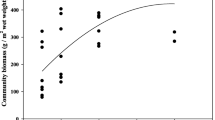
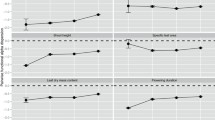
Abstract
Biodiversity is declining globally at a rapid rate nowadays as a result of a variety of global changes, and estimating how biodiversity loss affects ecosystem process (e.g., productivity) is critical. However, little is known about the relationship of macrophyte community productivity to trait-based biodiversity nor the comparative strength of trait-based biodiversity relative to species diversity in relation to productivity. Here, we investigated how multifaceted biodiversity indices were related with macrophyte community productivity using the data collected from a survey of 78 macrophyte plots in Liangzi lake, a shallow freshwater lake in China. We found that functional evenness and community-weighted mean traits had close association with community productivity, while species diversity, functional richness and divergence, and functional group richness were not significantly correlated with productivity. The connection between characteristics of dominant species and community productivity depended on the given trait. The significant correlation between community-level photosynthetic traits (Fv/Fm and chlorophyll content) and productivity revealed the importance of taking photosynthetic traits into account when exploring the mechanism behind the biodiversity–productivity relationship. Moreover, our results showed the redundancy and complementarity of the biodiversity indices in predicting community productivity. Overall, our results suggested that both mass ratio hypothesis and niche complementarity hypothesis can operate on community productivity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alahuhta J, Toivanen M, Hjort J, Ecke F, Johnson LB, Sass L, Heino J (2017) Species richness and taxonomic distinctness of lake macrophytes along environmental gradients in two continents. Freshwat Biol 62:1194–1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12936
Amoros G, Bornette C (1991) Aquatic vegetation and hydrology of a braided river floodplain. J Veg Sci 2:497–512
Balvanera P, Pfisterer AB, Buchmann N, He J-S, Nakashizuka T, Raffaelli D, Schmid B (2006) Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services. Ecol Lett 9:1146–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00963.x
Binzer T, Sand-Jensen K, Middelboe A-L (2006) Community photosynthesis of aquatic macrophytes. Limnol Oceanogr 51:2722–2733. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.6.2722
Bolpagni R (2021) Towards global dominance of invasive alien plants in freshwater ecosystems: the dawn of the Exocene? Hydrobiologia 848:2259–2279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04490-w
Bouchard V, Frey SD, Gilbert JM, Reed SE (2007) Effects of macrophyte functional group richness on emergent freshwater wetland functions. Ecology 88:2903–2914
Cadotte MW (2017) Functional traits explain ecosystem function through opposing mechanisms. Ecol Lett 20:989–996. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12796
Cadotte MW, Carscadden K, Mirotchnick N (2011) Beyond species: functional diversity and the maintenance of ecological processes and services. J Appl Ecol 48:1079–1087. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2011.02048.x
Cardinale BJ, Ives AR, Inchausti P (2004) Effects of species diversity on the primary productivity of ecosystems: extending our spatial and temporal scales of inference. Oikos 104:437–450. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2004.13254.x
Chambers PA, Lacoul P, Murphy KJ, Thomaz SM (2008) Global diversity of aquatic macrophytes in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:9–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-9154-6
Chmara R, Szmeja J, Robionek A (2019) Leaf traits of macrophytes in lakes: interspecific, plant group and community patterns. Limnologica 77:125691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2019.125691
Croft H, Chen JM, Froelich N, Chen B, Staebler RM (2015) Seasonal controls of canopy chlorophyll content on forest carbon uptake: implications for GPP modeling. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 120:1576–1586. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JG002980
Croft H, Chen JM, Luo X, Bartlett P, Chen B, Staebler RM (2017) Leaf chlorophyll content as a proxy for leaf photosynthetic capacity. Global Change Biol 23:3513–3524. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13599
Dalla Vecchia A, Villa P, Bolpagni R (2020) Functional traits in macrophyte studies: current trends and future research agenda. Aquat Bot 167:103290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2020.103290
Díaz S, Lavorel S, de Bello F, Quétier F, Grigulis K, Robson TM (2007) Incorporating plant functional diversity effects in ecosystem service assessments. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:20684–20689. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704716104
Duffy JE, Godwin CM, Cardinale BJ (2017) Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity. Nature 549:261–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23886
Engelhardt KAM, Ritchie ME (2001) Effects of macrophyte species richness on wetland ecosystem functioning and services. Nature 411:687–689. https://doi.org/10.1038/35079573
Engelhardt KA, Ritchie ME (2002) The effect of aquatic plant species richness on wetland ecosystem processes. Ecology 83:2911–2924
Fang J et al (2006) Biodiversity changes in the lakes of the Central Yangtze. Front Ecol Environ 4:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1890/1540-9295(2006)004[0369:BCITLO]2.0.CO;2
Fu H, Zhong J, Yuan G, Ni L, Xie P, Cao T (2014) Functional traits composition predict macrophytes community productivity along a water depth gradient in a freshwater lake. Ecol Evol 4:1516–1523. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1022
Gagic V et al (2015) Functional identity and diversity of animals predict ecosystem functioning better than species-based indices. Proc Roy Soc B 282:20142620. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.2620
Gallardo B, Gascón S, Quintana X, Comín FA (2011) How to choose a biodiversity indicator–redundancy and complementarity of biodiversity metrics in a freshwater ecosystem. Ecol Indicators 11:1177–1184
García-Girón J, Fernández-Aláez M, Fernández-Aláez C (2019) Redundant or complementary? Evaluation of different metrics as surrogates of macrophyte biodiversity patterns in Mediterranean ponds. Ecol Indicators 101:614–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.01.062
Garnier E et al (2004) Plant functional markers capture ecosystem properties during secondary succession. Ecology 85:2630–2637. https://doi.org/10.1890/03-0799
Gascón S, Boix D, Sala J (2009) Are different biodiversity metrics related to the same factors? A case study from Mediterranean wetlands. Biol Conserv 142:2602–2612
Gitelson AA et al (2006) Relationship between gross primary production and chlorophyll content in crops: implications for the synoptic monitoring of vegetation productivity. J Geophys Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005jd006017
Grime J (1998) Benefits of plant diversity to ecosystems: immediate, filter and founder effects. J Ecol 86:902–910
Gustafsson C, Boström C (2011) Biodiversity influences ecosystem functioning in aquatic angiosperm communities. Oikos 120:1037–1046. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2010.19008.x
Gustafsson C, Norkko A, Austin A (2019) Quantifying the importance of functional traits for primary production in aquatic plant communities. J Ecol 107:154–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.13011
Hillebrand H, Cardinale BJ (2010) A critique for meta-analyses and the productivity–diversity relationship. Ecology 91:2545–2549
Hodapp D, Hillebrand H, Blasius B, Ryabov AB (2016) Environmental and trait variability constrain community structure and the biodiversity-productivity relationship. Ecology 97:1463–1474. https://doi.org/10.1890/15-0730.1
Ibaraki Y, Murakami J (2007) Distribution of chlorophyll fluorescence parameter Fv/Fm within individual plants under various stress conditions. In: Cantliffe DJ (ed) Proceedings of the International Symposium on Advances in Environmental Control, Automation and Cultivation Systems for Sustainable, High-Quality Crop Production under Protected Cultivation. Acta Horticulturae, vol 761. Int Soc Horticultural Science, Leuven 1, pp 255–260. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2007.761.33
Jing G, Cheng J, Su J, Wei L, Hu T, Li W (2019) Community-weighted mean traits play crucial roles in driving ecosystem functioning along long-term grassland restoration gradient on the Loess Plateau of China. J Arid Environ 165:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2019.01.018
Kalaji HM, Carpentier R, Allakhverdiev SI, Bosa K (2012) Fluorescence parameters as early indicators of light stress in barley. J Photochem Photobiol B 112:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2012.03.009
Korol AR, Ahn C (2016) Dominance by an obligate annual affects the morphological characteristics and biomass production of a planted wetland macrophyte community. J Plant Ecol 9:187–200. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtv041
Laliberté E, Legendre P, Shipley B, Laliberté ME (2014) Package ‘FD’ Measuring functional diversity from multiple traits, and other tools for functional ecology. R package version 1.0-12
Lanta V, Lepš J (2006) Effect of functional group richness and species richness in manipulated productivity–diversity studies: a glasshouse pot experiment. Acta Oecol 29:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actao.2005.08.003
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Portland Press Ltd
Liu X, Wang H (2018) Contrasting patterns and drivers in taxonomic versus functional diversity, and community assembly of aquatic plants in subtropical lakes. Biodivers Conserv 27:3103–3118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-018-1590-2
Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature 412:72–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/35083573
Loreau M et al (2001) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: current knowledge and future challenges. Science 294:804–808. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064088
Loreau M, Sapijanskas J, Isbell F, Hector A (2012) Niche and fitness differences relate the maintenance of diversity to ecosystem function: comment. Ecology 93:1482–1487. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-0792.1
Ma F et al (2021) The biodiversity–biomass relationship of aquatic macrophytes Is regulated by water depth: a case study of a shallow mesotrophic lake in China. Front Ecol Evol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2021.650001
Mammola S, Carmona CP, Guillerme T, Cardoso P (2021) Concepts and applications in functional diversity. Funct Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13882
Mason NWH, Macgillivray K, Steel JB, Wilson JB (2003) An index of functional diversity. J Veg Sci 14:571–578. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1654-1103.2003.tb02184.x
Mason NWH, Mouillot D, Lee WG, Wilson JB (2005) Functional richness, functional evenness and functional divergence: the primary components of functional diversity. Oikos 111:112–118
Maturo F (2018) Unsupervised classification of ecological communities ranked according to their biodiversity patterns via a functional principal component decomposition of Hill’s numbers integral functions. Ecol Indicators 90:305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.03.013
Middleton BA, van der Valk AG, Davis CB (2015) Responses to water depth and clipping of twenty-three plant species in an Indian monsoonal wetland. Aquat Bot 126:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2015.06.004
Moi DA, Evangelista HBA, Mormul RP, Evangelista LR, Thomaz SM (2021) Ecosystem multifunctionality and stability are enhanced by macrophyte richness in mesocosms. Aquat Sci 83:1–12
Mooney E-DSaHA (1994) Ecosystem function of biodiversity: a summary Biodiversity and Ecosystem Function
Mori A (2016) Resilience in the studies of biodiversity–ecosystem functioning. Trends Ecol Evol 31:87–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.12.010
Morris EK et al (2014) Choosing and using diversity indices: insights for ecological applications from the German Biodiversity Exploratories. Ecol Evol 4:3514–3524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1155
Mouchet MA, Villéger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2010) Functional diversity measures: an overview of their redundancy and their ability to discriminate community assembly rules. Funct Ecol 24:867–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2010.01695.x
Mouillot D, Mason WN, Dumay O, Wilson JB (2005) Functional regularity: a neglected aspect of functional diversity. Oecologia 142:353–359
Mouillot D, Graham NA, Villéger S, Mason NW, Bellwood DR (2013) A functional approach reveals community responses to disturbances. Trends Ecol Evol 28:167–177
Müllerová A, Řehounková K, Prach K (2020) What is a reasonable plot size for sampling aquatic vegetation? Aquat Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-020-00743-x
Murchie EH, Lawson T (2013) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: a guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. J Exp Bot 64:3983–3998. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert208
Naeem S, Duffy JE, Zavaleta E (2012) The functions of biological diversity in an age of extinction. Science 336:1401–1406. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1215855
O’Hare MT et al (2018) Plants in aquatic ecosystems: current trends and future directions. Hydrobiologia 812:1–11
Parsons M, Mcloughlin CA, Kotschy K, Rogers KH, Rountree MW (2005) The effects of extreme floods on the biophysical heterogeneity of river landscapes. Front Ecol Environ 3:487–494
Pielou EC (1969) An introduction to mathematical ecology. Wiley, New York
Rao Q et al (2021) Stoichiometric and physiological mechanisms that link hub traits of submerged macrophytes with ecosystem structure and functioning. Water Res 202:117392
Reed S, Schnell R, Moore JM, Dunn C (2012) Chlorophyll a + b content and chlorophyll fluorescence in Avocado. J Agric Sci. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v4n4p29
Reich PB et al (2001) Do species and functional groups differ in acquisition and use of C, N and water under varying atmospheric CO2 and N availability regimes? A field test with 16 grassland species. New Phytol 150:435–448. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00114.x
Riis T, Olesen A, Jensen SM, Alnoee AB, Baattrup-Pedersen A, Lauridsen TL, Sorrell BK (2018) Submerged freshwater plant communities do not show species complementarity effect in wetland mesocosms. Biol Lett 14:20180635. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2018.0635
Roscher C et al (2012) Using plant functional traits to explain diversity-productivity relationships. PLoS One 7:e36760. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036760
Rusch G, Oesterheld M (1997) Relationship between productivity, and species and functional group diversity in grazed and non-grazed pampas grassland. Oikos 78:519–526
Schleuter D, Daufresne M, Massol F, Argillier C (2010) A user’s guide to functional diversity indices. Ecol Monogr 80:469–484
Schull MA, Anderson MC, Houborg R, Gitelson A, Kustas WP (2015) Thermal-based modeling of coupled carbon, water, and energy fluxes using nominal light use efficiencies constrained by leaf chlorophyll observations. Biogeosciences 12:1511–1523. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-12-1511-2015
Shannon CE, Weaver W (1949) A mathematical model of communication. University of Illinois Press 11, Urbana
Sharma DK, Andersen SB, Ottosen CO, Rosenqvist E (2015) Wheat cultivars selected for high Fv/Fm under heat stress maintain high photosynthesis, total chlorophyll, stomatal conductance, transpiration and dry matter. Physiol Plant 153:284–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12245
Sheldon AL (1969) Equitability indices: dependence on the species count. Ecology 50:466–467. https://doi.org/10.2307/1933900
Simpson EH (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature 163:688–688. https://doi.org/10.1038/163688a0
Sparks RE, Bayley PB, Kohler SL, Osborne LL (1990) Disturbance and recovery of large floodplain rivers. Environ Manage 14:699–709
Thomas HJ et al (2019) Traditional plant functional groups explain variation in economic but not size-related traits across the tundra biome. Global Ecol Biogeogr 28:78–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12783
Tilman D, Snell-Rood EC (2014) Diversity breeds complementarity. Nature 515:44–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13929
Tilman D, Knops JMH, Wedin DA, Reich PB, Ritchie ME, Siemann E (1997) The influence of functional diversity and composition on ecosystem processes. Science 277:1300–1302. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5330.1300
Villeger S, Mason NWH, Mouillot D (2008) New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology 89:2290–2301. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-1206.1
Violle C, Navas M-L, Vile D, Kazakou E, Fortunel C, Hummel I, Garnier E (2007) Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos 116:882–892. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15559.x
Wang H, Wang Q, Bowler P, Xiong W (2016) Invasive aquatic plants in China. Aquat Invasions 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3391/ai.2016.11.1.01
Wei T, Simko V, Levy M, Xie Y, Jin Y, Zemla J (2017) Package ‘corrplot’. Statistician 56:e24
Wright JP, Naeem S, Hector A, Lehman C, Reich PB, Schmid B, Tilman D (2006) Conventional functional classification schemes underestimate the relationship with ecosystem functioning. Ecol Lett 9:111–120
Wu A-P et al (2021) The relationship between diversity and productivity from a three-dimensional space view in a natural mesotrophic lake. Ecol Indicators 121:107069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107069
Xie D, Zhou H, Zhu H, Ji H, Li N, An S (2015) Differences in the regeneration traits of Potamogeton crispus turions from macrophyte- and phytoplankton-dominated lakes. Sci Rep 5:12907. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12907
Xu Z et al (2018) Plant functional diversity modulates global environmental change effects on grassland productivity. J Ecol 106:1941–1951. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12951
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Yang Li for helpful comments. This work was financially supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2015ZX07503-005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31900281) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019M650634).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FM, LY, CHL, and DY conceived the ideas and designed study. FM, CZ, and MT contributed to and organized data collection. FM and LY analyzed the data. FM and LY drafted the manuscript with feedback from CHL and HWY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I would like to declare that no conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, F., Yang, L., Zhang, C. et al. Functional evenness and community-weighted mean traits have strong correlation with macrophyte community productivity. Aquat Sci 84, 2 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-021-00833-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-021-00833-4