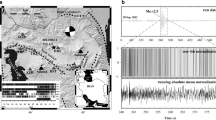
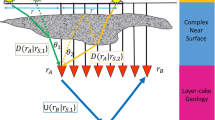
Abstract
We report the retrieval of body-wave reflections from noise records using a small-scale experiment over a mature oil field. The reflections are obtained by cross-correlation and stacking of the data. We used the stacked correlograms to create virtual source-to-receiver common shot gathers and are able to obtain body-wave reflections. Surface waves that obliterate the body-waves in our noise correlations were attenuated following a standard procedure from active source seismics. Further different strategies were employed to cross-correlate and stack the data: classical geometrical normalized cross-correlation (CCGN), phase cross-correlation (PCC), linear stacking**** and phase weighted stacking (PWS). PCC and PWS are based on the instantaneous phase coherence of analytic signals. The four approaches are independent and reveal the reflections; nevertheless, the combination of PWS and CCGN provided the best results. Our analysis is based on 2145 cross-correlations of 600 s data segments. We also compare the resulted virtual shot gathers with an active 2D seismic line near the passive experiment. It is shown that our ambient noise analysis reproduces reflections which are present in the active seismic data.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskir, E., & Weller, C. E. (1975). Sourceless reflection seismic exploration. Geophysics, 40, 158–159.
Bensen, G. D., Ritzwoller, M. H., Barmin, M. P., Levshin, A. L., Lin, F., Moschetti, M. P., et al. (2007). Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broadband surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophysical Journal International, 169, 1239–1260.
Boué, P., Poli, P., Campillo, M., & Roux, P. (2014). Reverberations, coda waves and ambient noise: Correlations at the global scale and retrieval of the deep phases. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 391, 137–145.
Claerbout, J. (1968). Synthesis of a layered medium from its acoustic transmissionresponse. Geophysics, 33, 264–269. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1439927.
Curtis, A., Gerstoft, P., Sato, H., Snieder, R., & Wapenaar, K. (2006). Seismic interferometry—turning noise into signal. The Leading Edge, 25, 1082–1092.
de Vasconcelos Lopes, A. E., & Nunes, L. C. (2010). Pitfalls of tremor-like signals for hydrocarbon exploration in producing oil fields in Potiguar Basin, northeast Brazil. The Leading Edge, 29(7), 826–830.
D’hour, V., Schimmel, M., Do Nascimento, A. F., Ferreira, J. M., & Lima Neto, H. C. (2016). Detection of subtle hydromechanical medium changes caused by a small-magnitude earthquake swarm in NE Brazil. Pure and Applied Geophysics (Printed ed.).
Dias, R. C., Julià, J., & Schimmel, M. (2015). Rayleigh-wave, group-velocity tomography of the Borborema Province, NE Brazil, from ambient seismic noise. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 171, 2863–3174.
Draganov, D., Campman, X., Thorbecke, J., Verdel, A., & Wapenaar, K. (2009). Reflection images from ambient seismic noise. Geophysics, 74, A63–A67. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.3193529.
Draganov, D., Ghose, R., Ruigrok, E., Thorbecke, J., & Wapenaar, K. (2010). Seismic interferometry, intrinsic losses and Q-estimation. Geophysical Prospecting, 58(3), 361–373.
Draganov, D., Campman, X., Thorbecke, J., Verdel, A., & Wapenaar, K. (2013). Seismic exploration-scale velocities and structure from ambient seismic noise (> 1 Hz). Journal of Geophysysical Research Solid Earth, 118, 4345–4360. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50339.
Draganov, D., Wapenaar, K., Mulder, W., Singer, J., & Verdel, A. (2007). Retrieval of reflections from seismic background-noise measurements. Geophysical Research Letters, 34, L04305. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GL028735.
Farra, V., Stutzmann, E., Gualtieri, L., Schimmel, M., & Ardhuin, F. (2016). Ray-theoretical modeling of secondary microseism P-waves. Geophysysical Journal International. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggw242.
Forghani, F., & Snieder, R. (2010). Underestimation of body waves and feasibility of surface-wave reconstruction by seismic interferometry. The Leading Edge, 29, 790–794.
Gualtieri, L., Stutzmann, E., Farra, V., Capdeville, Y., Schimmel, M., Ardhuin, F., et al. (2014). Modelling the ocean site effect on seismic noise body waves. Geophysysical Journal International, 197, 1096–1106. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggu042.
Harmon, N., Forsyth, D., & Webb, S. (2007). Using ambient seismic noise to determine short-period phase velocities and shallow shear velocities in young oceanic Lithosphere. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 97, 2024–2039.
Hanafy, S. M., AlTheyab, A., & Schuster, G. T. (2015). Controlled noise seismology: 85th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 5102–5106.
Koper, K., Seats, K., & Benz, H. (2010). On the composition of earth’s short-period seismic noise field. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 100(2), 606–617. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120090120.
Lin, F., Moschetti, M. P., & Ritzwoller, M. H. (2008). Surface wave tomography of the western United States from ambient seismic noise: Rayleigh and Love wave phase velocity maps. Geophysysical Journal International, 173, 281–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j1365-1246X.2008.03720.x.
Medeiros, W. E., Schimmel, M., & do Nascimento, A. F. (2015). How much averaging is necessary to cancel out cross-terms in noise correlation studies? Geophysical Journal International, 203(2), 1096–1100.
Obrebski, M., Ardhuin, F., Stutzmann, E., & Schimmel, M. (2013). Detection of microseismic compressional (P) body waves aided by numerical modeling of oceanic noise sources. Geophysysical Journal International, 118, 4312–4324. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrb.50233.
Olivier, G., Brenguier, F., Campillo, M., Lynch, R., & Roux, P. (2015). Body-wave reconstruction from ambient seismic noise correlations in an underground mine. Geophysics, 80(3), KS11–KS25.
Panea, I., Draganov, D., Almagro-Vidal, C., & Mocanu, V. (2014). Retrieval of reflections from ambient noise recorded in the Mizil area, Romania. Geophysics, 79(3), Q31–Q42.
Poletto, F., Malusa, M., Miranda, F., & Tinivella, U. (2004). Seismic-while-drilling by using dual sensors in drill strings. Geophysics, 69(5), 1261–1271.
Poli, P., Pedersen, H. A., Campillo, M., & The POLENET/LAPNET Working Group. (2012). Emergence of body waves from cross-correlation of short period seismic noise. Geophysysical Journal International, 188, 549–558. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246x.2011.05271.x.
Sabra, K. G., Gerstoft, P., Roux, P., Kuperman, W. A., & Fehler, M. C. (2005). Extracting time-domain Green’s function estimates from ambient seismicnoise. Geophysical Research Letters, 32, L03310-1–L03310-5. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005gl023155.
Schimmel, M. (1999). Phase cross-correlations: Design, comparisons, and applications. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 89(5), 1366–1378.
Schimmel, M., & Paulssen, H. (1997). Noise reduction and detection of weak, coherent signals through phase-weighted stacks. Geophysical Journal International, 130(2), 497–505.
Schimmel, M., & Gallart, J. (2007). Frequency-dependent phase coherence for noise suppression in seismic array data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JB004680.
Schimmel, M., Stutzmann, E., & Gallart, J. (2011). Using instantaneous phase coherence for signal extraction from ambient noise data at a local to a global scale. Geophysical Journal International, 184(1), 494–506.
Sens-Schönfelder, Snieder, & Stähler, (2015). The lack of equipartitioning in global body wave coda. Geophysical Research Letters, 42, 7483–7489. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065108.
Shapiro, N. M., & Campillo, M. (2004). Emergence of broadband Rayleighwaves from correlations of the ambient seismic noise. Geophysical Research Letters, 31, L07614. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL019491.
Telford, W. M., Geldard, L. P., & Sheriff, R. E. (1990). Applied geophysics (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Vasconcelos, & Snieder, (2008). Interferometry by deconvolution: Part 2—Theory forelastic waves and application to drill-bit seismic imaging. Geophysics, 73, S129–S141. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2904985.
Wapenaar, K., Fokkema, J., & Snieder, R. (2005). Retrieving the Green’s function in an open system by cross correlation: a comparison of approaches (L). Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 118(2), 2783–2786.
Wapenaar, K., Draganov, D., Snieder, R., Campman, X., & Verdel, A. (2010a). Tutorial on seismic interferometry: Part 1—Basic principles and applications. Geophysics, 75(5), 75A195–75A209.
Wapenaar, K., Slob, E., Snieder, R., & Curtis, A. (2010b). Tutorial on seismic interferometry: Part 2—underlying theory and new advances. Geophysics, 75(5), 75A211–75A227.
Yang, Y., Ritzwoller, M. H., Lin, F. C., Moschetti, M. P., & Shapiro, N. M. (2008). The structure of the crust and uppermost mantle beneath the western US revealed by ambient noise and earthquake tomography. Journal of Geophysysical Research, 113, B12310. https://doi.org/10.11029/12008JB005833.
Yilmaz, Ö. (2001). Seismic data analysis: Processing, inversion and interpretation, of seismic data. Society of Exploration Geophysicists.
Zhan, Z., Ni, S., Helmberger, D. V., & Clayton, R. W. (2010). Retrieval of moho-reflected shear wave arrivals from ambient seismic noise. Geophysical Journal International, 1, 408–420.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Editor, Adrien Oth, and two anonymous reviewers for the constructive comments that improved the original manuscript. We also thank Petrobras for the financial support. AFdN and MS thank CNPq for the Grant 402174/2012-7 (Science without Borders Programme), AFdN thank CNPq for Grant 303817/2014-3. OABD thanks the PRH-ANP-22 (“Programa de Formação em Geologia, Geofísica e Informática no Setor Petróleo & Gás na UFRN”) for his MSc scholarship. The authors also wish to thank the ANP (National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels) for the 2D active data used in this work. We wish to thank Flavio Santana for the discussions and his valuable help with the 2D active seismic lines visualization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dantas, O.A.B., do Nascimento, A.F. & Schimmel, M. Retrieval of Body-Wave Reflections Using Ambient Noise Interferometry Using a Small-Scale Experiment. Pure Appl. Geophys. 175, 2009–2022 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1794-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-018-1794-0