Abstract
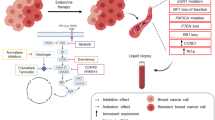
Endocrine therapy represents a mainstay adjuvant treatment of estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer in clinical practice with an overall survival (OS) benefit. However, the emergence of resistance is inevitable over time and is present in one-third of the ER+ breast tumors. Several mechanisms of endocrine resistance in ER+/HER2− advanced breast cancers, through ERα itself, receptor tyrosine signaling, or cell cycle pathway, have been identified to be pivotal in endocrine therapy. The epigenetic alterations also contribute to ensuring tumor cells’ escape from endocrine therapies. The strategy of combined hormone therapy with targeted pharmaceutical compounds has shown an improvement of progression-free survival or OS in clinical practice, including three different classes of drugs: CDK4/6 inhibitors, selective inhibitor of PI3Kα and mTOR inhibitors. Many therapeutic targets of cell cycle pathway and cell signaling and their combination strategies have recently entered clinical trials. This review focuses on Cyclin D–CDK4/6–RB axis, PI3K pathway and HDACs. Additionally, genomic evolution is complex in tumors exposed to hormonal therapy. We highlight the genomic alterations present in ESR1 and PIK3CA genes to elucidate adaptive mechanisms of endocrine resistance, and discuss how these mutations may inform novel combinations to improve clinical outcomes in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AIs:
-
Aromatase inhibitors
- CDK4:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4
- CDK6:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 6
- DNMT:
-
DNA methyltransferase
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- ETs:
-
Endocrine therapies
- HAT:
-
Histone acetyltransferase
- HDAC:
-
Histone deacetylase
- HR:
-
Hormone receptor-positive
- KDM:
-
Histone demethylase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- NCoR:
-
Nuclear corepressor
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3 kinase
- RB:
-
Retinoblastoma protein
- RTKs:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases
- SMRT:
-
Silencing mediator for retinoid or thyroid hormone receptors
- TET:
-
Ten–eleven translocation
References
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G (2005) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 365(9472):1687–1717. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(05)66544-0
Chen WY, Colditz GA (2007) Risk factors and hormone-receptor status: epidemiology, risk-prediction models and treatment implications for breast cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4(7):415–423. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncponc0851
Bernstein L, Lacey JV Jr (2011) Receptors, associations, and risk factor differences by breast cancer subtypes: positive or negative? J Natl Cancer Inst 103(6):451–453. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djr046
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G (2015) Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen in early breast cancer: patient-level meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Lancet 386(10001):1341–1352. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(15)61074-1
Pan H, Gray R, Braybrooke J, Davies C, Taylor C, McGale P, Peto R, Pritchard KI, Bergh J, Dowsett M, Hayes DF, Ebctcg (2017) 20-year risks of breast-cancer recurrence after stopping endocrine therapy at 5 years. N Engl J Med 377(19):1836–1846. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1701830
Dowsett M, Cuzick J, Ingle J, Coates A, Forbes J, Bliss J, Buyse M, Baum M, Buzdar A, Colleoni M, Coombes C, Snowdon C, Gnant M, Jakesz R, Kaufmann M, Boccardo F, Godwin J, Davies C, Peto R (2010) Meta-analysis of breast cancer outcomes in adjuvant trials of aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen. J Clin Oncol 28(3):509–518. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2009.23.1274
Razavi P, Chang MT, Xu G, Bandlamudi C, Ross DS, Vasan N, Cai Y, Bielski CM, Donoghue MTA, Jonsson P, Penson A, Shen R, Pareja F, Kundra R, Middha S, Cheng ML, Zehir A, Kandoth C, Patel R, Huberman K, Smyth LM, Jhaveri K, Modi S, Traina TA, Dang C, Zhang W, Weigelt B, Li BT, Ladanyi M, Hyman DM, Schultz N, Robson ME, Hudis C, Brogi E, Viale A, Norton L, Dickler MN, Berger MF, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Chandarlapaty S, Scaltriti M, Reis-Filho JS, Solit DB, Taylor BS, Baselga J (2018) The genomic landscape of endocrine-resistant advanced breast cancers. Cancer Cell 34(3):427–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.08.008
Jordan VC, O’Malley BW (2007) Selective estrogen-receptor modulators and antihormonal resistance in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(36):5815–5824. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2007.11.3886
Perissi V, Rosenfeld MG (2005) Controlling nuclear receptors: the circular logic of cofactor cycles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6(7):542–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1682
Lannigan DA (2003) Estrogen receptor phosphorylation. Steroids 68(1):1–9
Ellis MJ, Llombart-Cussac A, Feltl D, Dewar JA, Jasiowka M, Hewson N, Rukazenkov Y, Robertson JF (2015) Fulvestrant 500 mg versus anastrozole 1 mg for the first-line treatment of advanced breast cancer: overall survival analysis from the phase II FIRST Study. J Clin Oncol 33(32):3781–3787. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2015.61.5831
Zhang J, Zhou C, Jiang H, Liang L, Shi W, Zhang Q, Sun P, Xiang R, Wang Y, Yang S (2017) ZEB1 induces ER-alpha promoter hypermethylation and confers antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis 8(4):e2732. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.154
Clarke R, Liu MC, Bouker KB, Gu Z, Lee RY, Zhu Y, Skaar TC, Gomez B, O’Brien K, Wang Y, Hilakivi-Clarke LA (2003) Antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer and the role of estrogen receptor signaling. Oncogene 22(47):7316–7339. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206937
Hartmaier RJ, Trabucco SE, Priedigkeit N, Chung JH, Parachoniak CA, Vanden Borre P, Morley S, Rosenzweig M, Gay LM, Goldberg ME, Suh J, Ali SM, Ross J, Leyland-Jones B, Young B, Williams C, Park B, Tsai M, Haley B, Peguero J, Callahan RD, Sachelarie I, Cho J, Atkinson JM, Bahreini A, Nagle AM, Puhalla SL, Watters RJ, Erdogan-Yildirim Z, Cao L, Oesterreich S, Mathew A, Lucas PC, Davidson NE, Brufsky AM, Frampton GM, Stephens PJ, Chmielecki J, Lee AV (2018) Recurrent hyperactive ESR1 fusion proteins in endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer. Ann Oncol 29(4):872–880. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdy025
Wang Q, Jiang J, Ying G, Xie XQ, Zhang X, Xu W, Zhang X, Song E, Bu H, Ping YF, Yao XH, Wang B, Xu S, Yan ZX, Tai Y, Hu B, Qi X, Wang YX, He ZC, Wang Y, Wang JM, Cui YH, Chen F, Meng K, Wang Z, Bian XW (2018) Tamoxifen enhances stemness and promotes metastasis of ERalpha36(+) breast cancer by upregulating ALDH1A1 in cancer cells. Cell Res 28(3):336–358. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2018.15
Shi L, Dong B, Li Z, Lu Y, Ouyang T, Li J, Wang T, Fan Z, Fan T, Lin B, Wang Z, Xie Y (2009) Expression of ER-{alpha}36, a novel variant of estrogen receptor {alpha}, and resistance to tamoxifen treatment in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(21):3423–3429. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2008.17.2254
Zheng XQ, Guo JP, Yang H, Kanai M, He LL, Li YY, Koomen JM, Minton S, Gao M, Ren XB, Coppola D, Cheng JQ (2014) Aurora-A is a determinant of tamoxifen sensitivity through phosphorylation of ERalpha in breast cancer. Oncogene 33(42):4985–4996. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.444
Holz MK (2012) The role of S6K1 in ER-positive breast cancer. Cell Cycle 11(17):3159–3165. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.21194
Campbell RA, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Patel NM, Constantinidou D, Ali S, Nakshatri H (2001) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor alpha: a new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 276(13):9817–9824. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m010840200
Cui Y, Zhang M, Pestell R, Curran EM, Welshons WV, Fuqua SA (2004) Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha blocks its acetylation and regulates estrogen sensitivity. Can Res 64(24):9199–9208. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-2126
Yu L, Liang Y, Cao X, Wang X, Gao H, Lin SY, Schiff R, Wang XS, Li K (2017) Identification of MYST3 as a novel epigenetic activator of ERalpha frequently amplified in breast cancer. Oncogene 36(20):2910–2918. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.433
Jia X, Li C, Li L, Liu X, Zhou L, Zhang W, Ni S, Lu Y, Chen L, Jeong LS, Yu J, Zhang Y, Zhang J, He S, Hu X, Sun H, Yu K, Liu G, Zhao H, Zhang Y, Jia L, Shao ZM (2019) Neddylation inactivation facilitates FOXO3a nuclear export to suppress estrogen receptor transcription and improve fulvestrant sensitivity. Clin Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-2434
Jin K, Park S, Teo WW, Korangath P, Cho SS, Yoshida T, Gyorffy B, Goswami CP, Nakshatri H, Cruz LA, Zhou W, Ji H, Su Y, Ekram M, Wu Z, Zhu T, Polyak K, Sukumar S (2015) HOXB7 is an ERalpha cofactor in the activation of HER2 and multiple ER target genes leading to endocrine resistance. Cancer Discov 5(9):944–959. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-15-0090
Patten DK, Corleone G, Gyorffy B, Perone Y, Slaven N, Barozzi I, Erdos E, Saiakhova A, Goddard K, Vingiani A, Shousha S, Pongor LS, Hadjiminas DJ, Schiavon G, Barry P, Palmieri C, Coombes RC, Scacheri P, Pruneri G, Magnani L (2018) Enhancer mapping uncovers phenotypic heterogeneity and evolution in patients with luminal breast cancer. Nat Med 24(9):1469–1480. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0091-x
Sherr CJ (1996) Cancer cell cycles. Science 274(5293):1672–1677
Hay N (2005) The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell 8(3):179–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.08.008
Steelman LS, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Libra M, Nicoletti F, Abrams SL, McCubrey JA (2016) The therapeutic potential of mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer. Br J Clin Pharmacol 82(5):1189–1212. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12958
Toska E, Osmanbeyoglu HU, Castel P, Chan C, Hendrickson RC, Elkabets M, Dickler MN, Scaltriti M, Leslie CS, Armstrong SA, Baselga J (2017) PI3K pathway regulates ER-dependent transcription in breast cancer through the epigenetic regulator KMT2D. Science 355(6331):1324–1330. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah6893
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2009) Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9(9):631–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2713
Liu CY, Wu CY, Petrossian K, Huang TT, Tseng LM, Chen S (2017) Treatment for the endocrine resistant breast cancer: current options and future perspectives. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 172:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.07.001
Ellis MJ, Tao Y, Luo J, A’Hern R, Evans DB, Bhatnagar AS, Chaudri Ross HA, von Kameke A, Miller WR, Smith I, Eiermann W, Dowsett M (2008) Outcome prediction for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer based on postneoadjuvant endocrine therapy tumor characteristics. J Natl Cancer Inst 100(19):1380–1388. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djn309
Sighoko D, Liu J, Hou N, Gustafson P, Huo D (2014) Discordance in hormone receptor status among primary, metastatic, and second primary breast cancers: biological difference or misclassification? Oncologist 19(6):592–601. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2013-0427
Toy W, Shen Y, Won H, Green B, Sakr RA, Will M, Li Z, Gala K, Fanning S, King TA, Hudis C, Chen D, Taran T, Hortobagyi G, Greene G, Berger M, Baselga J, Chandarlapaty S (2013) ESR1 ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer. Nat Genet 45(12):1439–1445. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2822
Robinson DR, Wu YM, Vats P, Su F, Lonigro RJ, Cao X, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Wang R, Ning Y, Hodges L, Gursky A, Siddiqui J, Tomlins SA, Roychowdhury S, Pienta KJ, Kim SY, Roberts JS, Rae JM, Van Poznak CH, Hayes DF, Chugh R, Kunju LP, Talpaz M, Schott AF, Chinnaiyan AM (2013) Activating ESR1 mutations in hormone-resistant metastatic breast cancer. Nat Genet 45(12):1446–1451. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2823
Merenbakh-Lamin K, Ben-Baruch N, Yeheskel A, Dvir A, Soussan-Gutman L, Jeselsohn R, Yelensky R, Brown M, Miller VA, Sarid D, Rizel S, Klein B, Rubinek T, Wolf I (2013) D538G mutation in estrogen receptor-alpha: a novel mechanism for acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Can Res 73(23):6856–6864. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-13-1197
Jeselsohn R, Yelensky R, Buchwalter G, Frampton G, Meric-Bernstam F, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Ferrer-Lozano J, Perez-Fidalgo JA, Cristofanilli M, Gomez H, Arteaga CL, Giltnane J, Balko JM, Cronin MT, Jarosz M, Sun J, Hawryluk M, Lipson D, Otto G, Ross JS, Dvir A, Soussan-Gutman L, Wolf I, Rubinek T, Gilmore L, Schnitt S, Come SE, Pusztai L, Stephens P, Brown M, Miller VA (2014) Emergence of constitutively active estrogen receptor-alpha mutations in pretreated advanced estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 20(7):1757–1767. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-13-2332
Yates LR, Knappskog S, Wedge D, Farmery JHR, Gonzalez S, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB, Van Loo P, Haugland HK, Lilleng PK, Gundem G, Gerstung M, Pappaemmanuil E, Gazinska P, Bhosle SG, Jones D, Raine K, Mudie L, Latimer C, Sawyer E, Desmedt C, Sotiriou C, Stratton MR, Sieuwerts AM, Lynch AG, Martens JW, Richardson AL, Tutt A, Lonning PE, Campbell PJ (2017) Genomic evolution of breast cancer metastasis and relapse. Cancer Cell 32(2):169–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.07.005
McDonnell DP, Norris JD, Chang CY (2018) Neomorphic ERalpha mutations drive progression in breast cancer and present a challenge for new drug discovery. Cancer Cell 33(2):153–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.01.014
Harrod A, Fulton J, Nguyen VTM, Periyasamy M, Ramos-Garcia L, Lai CF, Metodieva G, de Giorgio A, Williams RL, Santos DB, Gomez PJ, Lin ML, Metodiev MV, Stebbing J, Castellano L, Magnani L, Coombes RC, Buluwela L, Ali S (2017) Genomic modelling of the ESR1 Y537S mutation for evaluating function and new therapeutic approaches for metastatic breast cancer. Oncogene 36(16):2286–2296. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.382
Jeselsohn R, Bergholz JS, Pun M, Cornwell M, Liu W, Nardone A, Xiao T, Li W, Qiu X, Buchwalter G, Feiglin A, Abell-Hart K, Fei T, Rao P, Long H, Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Gray N, Melchers D, Houtman R, Liu XS, Cohen O, Wagle N, Winer EP, Zhao J, Brown M (2018) Allele-specific chromatin recruitment and therapeutic vulnerabilities of ESR1 activating mutations. Cancer Cell 33(2):173–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.01.004
Spoerke JM, Gendreau S, Walter K, Qiu J, Wilson TR, Savage H, Aimi J, Derynck MK, Chen M, Chan IT, Amler LC, Hampton GM, Johnston S, Krop I, Schmid P, Lackner MR (2016) Heterogeneity and clinical significance of ESR1 mutations in ER-positive metastatic breast cancer patients receiving fulvestrant. Nat Commun 7:11579. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11579
Jeselsohn R, Buchwalter G, De Angelis C, Brown M, Schiff R (2015) ESR1 mutations-a mechanism for acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 12(10):573–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.117
Fribbens C, O’Leary B, Kilburn L, Hrebien S, Garcia-Murillas I, Beaney M, Cristofanilli M, Andre F, Loi S, Loibl S, Jiang J, Bartlett CH, Koehler M, Dowsett M, Bliss JM, Johnston SR, Turner NC (2016) Plasma ESR1 mutations and the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 34(25):2961–2968. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.67.3061
Toy W, Weir H, Razavi P, Lawson M, Goeppert AU, Mazzola AM, Smith A, Wilson J, Morrow C, Wong WL, De Stanchina E, Carlson KE, Martin TS, Uddin S, Li Z, Fanning S, Katzenellenbogen JA, Greene G, Baselga J, Chandarlapaty S (2017) Activating ESR1 mutations differentially affect the efficacy of ER antagonists. Cancer Discov 7(3):277–287. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-15-1523
Martin LA, Ribas R, Simigdala N, Schuster E, Pancholi S, Tenev T, Gellert P, Buluwela L, Harrod A, Thornhill A, Nikitorowicz-Buniak J, Bhamra A, Turgeon MO, Poulogiannis G, Gao Q, Martins V, Hills M, Garcia-Murillas I, Fribbens C, Patani N, Li Z, Sikora MJ, Turner N, Zwart W, Oesterreich S, Carroll J, Ali S, Dowsett M (2017) Discovery of naturally occurring ESR1 mutations in breast cancer cell lines modelling endocrine resistance. Nat Commun 8(1):1865. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01864-y
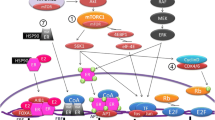
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2009) Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9(3):153–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2602
Burkhart DL, Sage J (2008) Cellular mechanisms of tumour suppression by the retinoblastoma gene. Nat Rev Cancer 8(9):671–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2399
Sherr CJ (1995) D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem Sci 20(5):187–190
Trimarchi JM, Lees JA (2002) Sibling rivalry in the E2F family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm714
Dyson N (1998) The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev 12(15):2245–2262. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.12.15.2245
Weinberg RA (1995) The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell 81(3):323–330
Zwijsen RM, Wientjens E, Klompmaker R, van der Sman J, Bernards R, Michalides RJ (1997) CDK-independent activation of estrogen receptor by cyclin D1. Cell 88(3):405–415
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1999) CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 13(12):1501–1512. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.12.1501
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL, Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK, Toogood PL (2004) Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3(11):1427–1438
Bosco EE, Knudsen ES (2007) RB in breast cancer: at the crossroads of tumorigenesis and treatment. Cell Cycle 6(6):667–671. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.6.6.3988
Arima Y, Inoue Y, Shibata T, Hayashi H, Nagano O, Saya H, Taya Y (2008) Rb depletion results in deregulation of E-cadherin and induction of cellular phenotypic changes that are characteristic of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Can Res 68(13):5104–5112. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-5680
Trere D, Brighenti E, Donati G, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Taffurelli M, Montanaro L, Derenzini M (2009) High prevalence of retinoblastoma protein loss in triple-negative breast cancers and its association with a good prognosis in patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Oncol 20(11):1818–1823. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp209
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (2010) RB in breast cancer: differential effects in estrogen receptor-positive and estrogen receptor-negative disease. Cell Cycle 9(23):4607. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.9.23.13889
Medema RH, Herrera RE, Lam F, Weinberg RA (1995) Growth suppression by p16ink4 requires functional retinoblastoma protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(14):6289–6293. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.14.6289
Lee JJ, Ko E, Cho J, Park HY, Lee JE, Nam SJ, Kim DH, Cho EY (2012) Methylation and immunoexpression of p16(INK4a) tumor suppressor gene in primary breast cancer tissue and Their quantitative p16(INK4a) hypermethylation in plasma by real-time PCR. Korean J Pathol 46(6):554–561. https://doi.org/10.4132/koreanjpathol.2012.46.6.554
Gao A, Sun T, Ma G, Cao J, Hu Q, Chen L, Wang Y, Wang Q, Sun J, Wu R, Wu Q, Zhou J, Liu L, Hu J, Dong JT, Zhu Z (2018) LEM4 confers tamoxifen resistance to breast cancer cells by activating cyclin D–CDK4/6–Rb and ERalpha pathway. Nat Commun 9(1):4180. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06309-8
Kenny FS, Hui R, Musgrove EA, Gee JM, Blamey RW, Nicholson RI, Sutherland RL, Robertson JF (1999) Overexpression of cyclin D1 messenger RNA predicts for poor prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 5(8):2069–2076
Gillett C, Fantl V, Smith R, Fisher C, Bartek J, Dickson C, Barnes D, Peters G (1994) Amplification and overexpression of cyclin D1 in breast cancer detected by immunohistochemical staining. Can Res 54(7):1812–1817
Buckley MF, Sweeney KJ, Hamilton JA, Sini RL, Manning DL, Nicholson RI, deFazio A, Watts CK, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (1993) Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in human breast cancer. Oncogene 8(8):2127–2133
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Muller H, Lutzhoft D, Strauss M, Bartek J (1994) Cyclin D1 protein expression and function in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 57(3):353–361
Dickson C, Fantl V, Gillett C, Brookes S, Bartek J, Smith R, Fisher C, Barnes D, Peters G (1995) Amplification of chromosome band 11q13 and a role for cyclin D1 in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 90(1):43–50
An HX, Beckmann MW, Reifenberger G, Bender HG, Niederacher D (1999) Gene amplification and overexpression of CDK4 in sporadic breast carcinomas is associated with high tumor cell proliferation. Am J Pathol 154(1):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65257-1
Cancer Genome Atlas N (2012) Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490(7418):61–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11412
Tinoco G, Warsch S, Gluck S, Avancha K, Montero AJ (2013) Treating breast cancer in the 21st century: emerging biological therapies. J Cancer 4(2):117–132. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.4925
Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, Boer K, Bondarenko IM, Kulyk SO, Ettl J, Patel R, Pinter T, Schmidt M, Shparyk Y, Thummala AR, Voytko NL, Fowst C, Huang X, Kim ST, Randolph S, Slamon DJ (2015) The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 16(1):25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(14)71159-3
Gelbert LM, Cai S, Lin X, Sanchez-Martinez C, Del Prado M, Lallena MJ, Torres R, Ajamie RT, Wishart GN, Flack RS, Neubauer BL, Young J, Chan EM, Iversen P, Cronier D, Kreklau E, de Dios A (2014) Preclinical characterization of the CDK4/6 inhibitor LY2835219: in vivo cell cycle-dependent/independent anti-tumor activities alone/in combination with gemcitabine. Invest New Drugs 32(5):825–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-014-0120-7
Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, Jones S, Im SA, Gelmon K, Harbeck N, Lipatov ON, Walshe JM, Moulder S, Gauthier E, Lu DR, Randolph S, Dieras V, Slamon DJ (2016) Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 375(20):1925–1936. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1607303
Tripathy D, Bardia A, Sellers WR (2017) Ribociclib (LEE011): mechanism of action and clinical impact of this selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor in various solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 23(13):3251–3262. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-3157
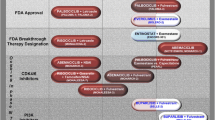
Layman RM (2019) CDK4/6 inhibitors for advanced hormone receptor-positive breast cancer, 2019 and beyond. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 17(2):190–192. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2018.7271
Eggersmann TK, Degenhardt T, Gluz O, Wuerstlein R, Harbeck N (2019) CDK4/6 inhibitors expand the therapeutic options in breast cancer: palbociclib, Ribociclib and abemaciclib. BioDrugs 33(2):125–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-019-00337-6
Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im SA, Masuda N, Colleoni M, DeMichele A, Loi S, Verma S, Iwata H, Harbeck N, Loibl S, Andre F, Puyana Theall K, Huang X, Giorgetti C, Huang Bartlett C, Cristofanilli M (2018) Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 379(20):1926–1936. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1810527
Vijayaraghavan S, Karakas C, Doostan I, Chen X, Bui T, Yi M, Raghavendra AS, Zhao Y, Bashour SI, Ibrahim NK, Karuturi M, Wang J, Winkler JD, Amaravadi RK, Hunt KK, Tripathy D, Keyomarsi K (2017) CDK4/6 and autophagy inhibitors synergistically induce senescence in Rb positive cytoplasmic cyclin E negative cancers. Nat Commun 8:15916. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15916
Yam C, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN (2018) CDK4/6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative metastatic breast cancer: are we at the finish line? Oncotarget 9(76):34193–34195. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26134
Malumbres M (2019) CDK4/6 inhibitors: what is the best cocktail? Clin Cancer Res 25(1):6–8. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-2177
Formisano L, Lu Y, Servetto A, Hanker AB, Jansen VM, Bauer JA, Sudhan DR, Guerrero-Zotano AL, Croessmann S, Guo Y, Ericsson PG, Lee KM, Nixon MJ, Schwarz LJ, Sanders ME, Dugger TC, Cruz MR, Behdad A, Cristofanilli M, Bardia A, O’Shaughnessy J, Nagy RJ, Lanman RB, Solovieff N, He W, Miller M, Su F, Shyr Y, Mayer IA, Balko JM, Arteaga CL (2019) Aberrant FGFR signaling mediates resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer. Nat Commun 10(1):1373. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09068-2
Daniell KM, Bardia A, Sun F, Roberts SA, Brunelle CL, Gillespie TC, Sayegh HE, Naoum GE, Juric D, Isakoff SJ, Fitzgerald DM, Taghian AG (2019) Incidence of peripheral edema in patients receiving PI3K/mTOR/CDK4/6 inhibitors for metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 175(3):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-019-05206-y
Sherr CJ, Beach D, Shapiro GI (2016) Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: from discovery to therapy. Cancer Discov 6(4):353–367. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-15-0894
Klein ME, Kovatcheva M, Davis LE, Tap WD, Koff A (2018) CDK4/6 inhibitors: the mechanism of action may not be as simple as once Thought. Cancer Cell 34(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.03.023
Goel S, DeCristo MJ, Watt AC, BrinJones H, Sceneay J, Li BB, Khan N, Ubellacker JM, Xie S, Metzger-Filho O, Hoog J, Ellis MJ, Ma CX, Ramm S, Krop IE, Winer EP, Roberts TM, Kim HJ, McAllister SS, Zhao JJ (2017) CDK4/6 inhibition triggers anti-tumour immunity. Nature 548(7668):471–475. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23465
Kish JK, Ward MA, Garofalo D, Ahmed HV, McRoy L, Laney J, Zanotti G, Braverman J, Yu H, Feinberg BA (2018) Real-world evidence analysis of palbociclib prescribing patterns for patients with advanced/metastatic breast cancer treated in community oncology practice in the USA one year post approval. Breast Cancer Res 20(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-018-0958-2
Xi J, Oza A, Thomas S, Ademuyiwa F, Weilbaecher K, Suresh R, Bose R, Cherian M, Hernandez-Aya L, Frith A, Peterson L, Luo J, Krishnamurthy J, Ma CX (2019) Retrospective analysis of treatment patterns and effectiveness of palbociclib and subsequent regimens in metastatic breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 17(2):141–147. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2018.7094
Herrera-Abreu M, Palafox M, Asghar U (2016) Early adaptation and acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibition in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Can Res 76:2301–2313. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-15-0728
Yang C, Li Z, Bhatt T (2017) Acquired CDK6 amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene 36:2255–2264. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.379
Formisano L, Lu Y, Jansen V (2017) Abstract 1008: gain-of-function kinase library screen identifies FGFR1 amplification as a mechanism of resistance to antiestrogens and CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer [abstract]. Can Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.am2017-1008
Li Z, Razavi P, Li Q, Toy W, Liu B, Ping C, Hsieh W, Sanchez-Vega F, Brown DN, Da Cruz Paula AF, Morris L, Selenica P, Eichenberger E, Shen R, Schultz N, Rosen N, Scaltriti M, Brogi E, Baselga J, Reis-Filho JS, Chandarlapaty S (2018) Loss of the FAT1 tumor suppressor promotes resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors via the Hippo pathway. Cancer Cell 34(6):893–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2018.11.006
O’Leary B, Cutts RJ, Liu Y, Hrebien S, Huang X, Fenwick K, Andre F, Loibl S, Loi S, Garcia-Murillas I, Cristofanilli M, Huang Bartlett C, Turner NC (2018) The genetic landscape and clonal evolution of breast cancer resistance to palbociclib plus fulvestrant in the PALOMA-3 trial. Cancer Discov 8(11):1390–1403. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-18-0264
Condorelli R, Spring L, O’Shaughnessy J (2018) Polyclonal RB1 mutations and acquired resistance to CDK 4/6 inhibitors in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol 29:640–645. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdx784
Miller TW, Hennessy BT, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Fox EM, Mills GB, Chen H, Higham C, Garcia-Echeverria C, Shyr Y, Arteaga CL (2010) Hyperactivation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase promotes escape from hormone dependence in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 120(7):2406–2413. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci41680
Bosch A, Li Z, Bergamaschi A, Ellis H, Toska E, Prat A, Tao JJ, Spratt DE, Viola-Villegas NT, Castel P, Minuesa G, Morse N, Rodon J, Ibrahim Y, Cortes J, Perez-Garcia J, Galvan P, Grueso J, Guzman M, Katzenellenbogen JA, Kharas M, Lewis JS, Dickler M, Serra V, Rosen N, Chandarlapaty S, Scaltriti M, Baselga J (2015) PI3K inhibition results in enhanced estrogen receptor function and dependence in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Sci Transl Med 7(283):283ra251. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa4442
Miller TW, Balko JM, Arteaga CL (2011) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and antiestrogen resistance in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(33):4452–4461. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2010.34.4879
Kang S, Bader AG, Vogt PK (2005) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mutations identified in human cancer are oncogenic. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(3):802–807. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408864102
Banerji S, Cibulskis K, Rangel-Escareno C, Brown KK, Carter SL, Frederick AM, Lawrence MS, Sivachenko AY, Sougnez C, Zou L, Cortes ML, Fernandez-Lopez JC, Peng S, Ardlie KG, Auclair D, Bautista-Pina V, Duke F, Francis J, Jung J, Maffuz-Aziz A, Onofrio RC, Parkin M, Pho NH, Quintanar-Jurado V, Ramos AH, Rebollar-Vega R, Rodriguez-Cuevas S, Romero-Cordoba SL, Schumacher SE, Stransky N, Thompson KM, Uribe-Figueroa L, Baselga J, Beroukhim R, Polyak K, Sgroi DC, Richardson AL, Jimenez-Sanchez G, Lander ES, Gabriel SB, Garraway LA, Golub TR, Melendez-Zajgla J, Toker A, Getz G, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Meyerson M (2012) Sequence analysis of mutations and translocations across breast cancer subtypes. Nature 486(7403):405–409. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11154
Sabine VS, Crozier C, Brookes CL, Drake C, Piper T, van de Velde CJ, Hasenburg A, Kieback DG, Markopoulos C, Dirix L, Seynaeve C, Rea DW, Bartlett JM (2014) Mutational analysis of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in tamoxifen exemestane adjuvant multinational pathology study. J Clin Oncol 32(27):2951–2958. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2013.53.8272
Mayer IA, Abramson VG, Formisano L, Balko JM, Estrada MV, Sanders ME, Juric D, Solit D, Berger MF, Won HH, Li Y, Cantley LC, Winer E, Arteaga CL (2017) A phase Ib study of alpelisib (BYL719), a PI3Kalpha-specific inhibitor, with letrozole in ER+/HER2− Metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23(1):26–34. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-0134
Pirali T, Ciraolo E, Aprile S, Massarotti A, Berndt A, Griglio A, Serafini M, Mercalli V, Landoni C, Campa CC, Margaria JP, Silva RL, Grosa G, Sorba G, Williams R, Hirsch E, Tron GC (2017) Identification of a potent phosphoinositide 3-kinase pan inhibitor displaying a strategic carboxylic acid group and development of its prodrugs. ChemMedChem 12(18):1542–1554. https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.201700340
Baselga J, Im SA, Iwata H, Cortes J, De Laurentiis M, Jiang Z, Arteaga CL, Jonat W, Clemons M, Ito Y, Awada A, Chia S, Jagiello-Gruszfeld A, Pistilli B, Tseng LM, Hurvitz S, Masuda N, Takahashi M, Vuylsteke P, Hachemi S, Dharan B, Di Tomaso E, Urban P, Massacesi C, Campone M (2017) Buparlisib plus fulvestrant versus placebo plus fulvestrant in postmenopausal, hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (BELLE-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 18(7):904–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30376-5
Di Leo A, Johnston S, Lee KS, Ciruelos E, Lonning PE, Janni W, O’Regan R, Mouret-Reynier MA, Kalev D, Egle D, Csoszi T, Bordonaro R, Decker T, Tjan-Heijnen VCG, Blau S, Schirone A, Weber D, El-Hashimy M, Dharan B, Sellami D, Bachelot T (2018) Buparlisib plus fulvestrant in postmenopausal women with hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer progressing on or after mTOR inhibition (BELLE-3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 19(1):87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30688-5
Fruman DA, Rommel C (2014) PI3K and cancer: lessons, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(2):140–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4204
Fritsch C, Huang A, Chatenay-Rivauday C, Schnell C, Reddy A, Liu M, Kauffmann A, Guthy D, Erdmann D, De Pover A, Furet P, Gao H, Ferretti S, Wang Y, Trappe J, Brachmann SM, Maira SM, Wilson C, Boehm M, Garcia-Echeverria C, Chene P, Wiesmann M, Cozens R, Lehar J, Schlegel R, Caravatti G, Hofmann F, Sellers WR (2014) Characterization of the novel and specific PI3Kalpha inhibitor NVP-BYL719 and development of the patient stratification strategy for clinical trials. Mol Cancer Ther 13(5):1117–1129. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-13-0865
Juric D, Rodon J, Tabernero J, Janku F, Burris HA, Schellens JHM, Middleton MR, Berlin J, Schuler M, Gil-Martin M, Rugo HS, Seggewiss-Bernhardt R, Huang A, Bootle D, Demanse D, Blumenstein L, Coughlin C, Quadt C, Baselga J (2018) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha-selective inhibition with alpelisib (BYL719) in PIK3CA-altered solid tumors: results from the first-in-human study. J Clin Oncol 36(13):1291–1299. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2017.72.7107
Ando Y, Iwasa S, Takahashi S, Saka H, Kakizume T, Natsume K, Suenaga N, Quadt C, Yamada Y (2019) Phase I study of alpelisib (BYL719), an alpha-specific PI3K inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Sci 110(3):1021–1031. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13923
Juric D, Janku F, Rodon J, Burris HA, Mayer IA, Schuler M, Seggewiss-Bernhardt R, Gil-Martin M, Middleton MR, Baselga J, Bootle D, Demanse D, Blumenstein L, Schumacher K, Huang A, Quadt C, Rugo HS (2018) Alpelisib plus fulvestrant in PIK3CA-altered and PIK3CA-wild-type estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: a phase 1b clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4475
Andre F, Ciruelos E, Rubovszky G, Campone M, Loibl S, Rugo HS, Iwata H, Conte P, Mayer IA, Kaufman B, Yamashita T, Lu YS, Inoue K, Takahashi M, Papai Z, Longin AS, Mills D, Wilke C, Hirawat S, Juric D, Group S-S, the S-SG (2019) Alpelisib for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 380(20):1929–1940. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1813904
Guerriero JL, Sotayo A, Ponichtera HE, Castrillon JA, Pourzia AL, Schad S, Johnson SF, Carrasco RD, Lazo S, Bronson RT, Davis SP, Lobera M, Nolan MA, Letai A (2017) Class IIa HDAC inhibition reduces breast tumours and metastases through anti-tumour macrophages. Nature 543(7645):428–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21409
Jones PA, Issa JP, Baylin S (2016) Targeting the cancer epigenome for therapy. Nat Rev Genet 17(10):630–641. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2016.93
Haven B, Heilig E, Donham C, Settles M, Vasilevsky N, Owen K, Reproducibility Project: Cancer B, Reproducibility Project Cancer B (2016) Registered report: a chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Elife 5:5. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.09462
Sharma SV, Lee DY, Li B, Quinlan MP, Takahashi F, Maheswaran S, McDermott U, Azizian N, Zou L, Fischbach MA, Wong KK, Brandstetter K, Wittner B, Ramaswamy S, Classon M, Settleman J (2010) A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 141(1):69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.027
Krusche CA, Wulfing P, Kersting C, Vloet A, Bocker W, Kiesel L, Beier HM, Alfer J (2005) Histone deacetylase-1 and -3 protein expression in human breast cancer: a tissue microarray analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 90(1):15–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-004-1668-2
Muller BM, Jana L, Kasajima A, Lehmann A, Prinzler J, Budczies J, Winzer KJ, Dietel M, Weichert W, Denkert C (2013) Differential expression of histone deacetylases HDAC1, 2 and 3 in human breast cancer–overexpression of HDAC2 and HDAC3 is associated with clinicopathological indicators of disease progression. BMC Cancer 13:215. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-13-215
Legare S, Basik M (2016) Minireview: the link between eralpha corepressors and histone deacetylases in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Mol Endocrinol 30(9):965–976. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2016-1072
Li J, Wang J, Wang J, Nawaz Z, Liu JM, Qin J, Wong J (2000) Both corepressor proteins SMRT and N-CoR exist in large protein complexes containing HDAC3. EMBO J 19(16):4342–4350. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.16.4342
Smirnov DA, Hou S, Ricciardi RP (2000) Association of histone deacetylase with COUP-TF in tumorigenic Ad12-transformed cells and its potential role in shut-off of MHC class I transcription. Virology 268(2):319–328. https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.1999.0181
Shi Y, Downes M, Xie W, Kao HY, Ordentlich P, Tsai CC, Hon M, Evans RM (2001) Sharp, an inducible cofactor that integrates nuclear receptor repression and activation. Genes Dev 15(9):1140–1151. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.871201
Connolly R, Stearns V (2012) Epigenetics as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 17(3–4):191–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-012-9263-3
Richon VM, Emiliani S, Verdin E, Webb Y, Breslow R, Rifkind RA, Marks PA (1998) A class of hybrid polar inducers of transformed cell differentiation inhibits histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(6):3003–3007. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.6.3003
Falkenberg KJ, Johnstone RW (2014) Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases and immune disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(9):673–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4360
Said TK, Moraes RC, Sinha R, Medina D (2001) Mechanisms of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid inhibition of mammary cell growth. Breast Cancer Res 3(2):122–133. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr284
Munster PN, Troso-Sandoval T, Rosen N, Rifkind R, Marks PA, Richon VM (2001) The histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid induces differentiation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(23):8492–8497
Torres-Adorno AM, Lee J, Kogawa T, Ordentlich P, Tripathy D, Lim B, Ueno NT (2017) Histone deacetylase inhibitor enhances the efficacy of MEK inhibitor through NOXA-mediated MCL1 degradation in triple-negative and inflammatory breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 23(16):4780–4792. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-16-2622
Ono H, Sowa Y, Horinaka M, Iizumi Y, Watanabe M, Morita M, Nishimoto E, Taguchi T, Sakai T (2018) The histone deacetylase inhibitor OBP-801 and eribulin synergistically inhibit the growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells with the suppression of survivin, Bcl-xL, and the MAPK pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat 171(1):43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-018-4815-x
Zhou Q, Shaw PG, Davidson NE (2009) Inhibition of histone deacetylase suppresses EGF signaling pathways by destabilizing EGFR mRNA in ER-negative human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 117(2):443–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-008-0148-5
Sharma D, Saxena NK, Davidson NE, Vertino PM (2006) Restoration of tamoxifen sensitivity in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells: tamoxifen-bound reactivated ER recruits distinctive corepressor complexes. Cancer Res 66(12):6370–6378. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-06-0402
Yang X, Phillips DL, Ferguson AT, Nelson WG, Herman JG, Davidson NE (2001) Synergistic activation of functional estrogen receptor (ER)-alpha by DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibition in human ER-alpha-negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(19):7025–7029
Fan J, Yin WJ, Lu JS, Wang L, Wu J, Wu FY, Di GH, Shen ZZ, Shao ZM (2008) ER alpha negative breast cancer cells restore response to endocrine therapy by combination treatment with both HDAC inhibitor and DNMT inhibitor. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 134(8):883–890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-008-0354-x
Sabnis GJ, Goloubeva O, Chumsri S, Nguyen N, Sukumar S, Brodie AM (2011) Functional activation of the estrogen receptor-alpha and aromatase by the HDAC inhibitor entinostat sensitizes ER-negative tumors to letrozole. Cancer Res 71(5):1893–1903. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-10-2458
Huang X, Wang S, Lee CK, Yang X, Liu B (2011) HDAC inhibitor SNDX-275 enhances efficacy of trastuzumab in erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells and exhibits potential to overcome trastuzumab resistance. Cancer Lett 307(1):72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2011.03.019
Lee J, Bartholomeusz C, Mansour O, Humphries J, Hortobagyi GN, Ordentlich P, Ueno NT (2014) A class I histone deacetylase inhibitor, entinostat, enhances lapatinib efficacy in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through FOXO3-mediated Bim1 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat 146(2):259–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-3014-7
Luu TH, Morgan RJ, Leong L, Lim D, McNamara M, Portnow J, Frankel P, Smith DD, Doroshow JH, Wong C, Aparicio A, Gandara DR, Somlo G (2008) A phase II trial of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) in metastatic breast cancer: a California Cancer Consortium study. Clin Cancer Res 14(21):7138–7142. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-0122
Hodges-Gallagher L, Valentine CD, Bader SE, Kushner PJ (2007) Inhibition of histone deacetylase enhances the anti-proliferative action of antiestrogens on breast cancer cells and blocks tamoxifen-induced proliferation of uterine cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 105(3):297–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9459-6
Munster PN, Thurn KT, Thomas S, Raha P, Lacevic M, Miller A, Melisko M, Ismail-Khan R, Rugo H, Moasser M, Minton SE (2011) A phase II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat combined with tamoxifen for the treatment of patients with hormone therapy-resistant breast cancer. Br J Cancer 104(12):1828–1835. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.156
Ryan QC, Headlee D, Acharya M, Sparreboom A, Trepel JB, Ye J, Figg WD, Hwang K, Chung EJ, Murgo A, Melillo G, Elsayed Y, Monga M, Kalnitskiy M, Zwiebel J, Sausville EA (2005) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of MS-275, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in patients with advanced and refractory solid tumors or lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 23(17):3912–3922. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.02.188
Kummar S, Gutierrez M, Gardner ER, Donovan E, Hwang K, Chung EJ, Lee MJ, Maynard K, Kalnitskiy M, Chen A, Melillo G, Ryan QC, Conley B, Figg WD, Trepel JB, Zwiebel J, Doroshow JH, Murgo AJ (2007) Phase I trial of MS-275, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, administered weekly in refractory solid tumors and lymphoid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 13(18 Pt 1):5411–5417. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-0791
Gore L, Rothenberg ML, O’Bryant CL, Schultz MK, Sandler AB, Coffin D, McCoy C, Schott A, Scholz C, Eckhardt SG (2008) A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, MS-275, in patients with refractory solid tumors and lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res 14(14):4517–4525. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-07-1461
Yardley DA, Ismail-Khan RR, Melichar B, Lichinitser M, Munster PN, Klein PM, Cruickshank S, Miller KD, Lee MJ, Trepel JB (2013) Randomized phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of exemestane with or without entinostat in postmenopausal women with locally recurrent or metastatic estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer progressing on treatment with a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor. J Clin Oncol 31(17):2128–2135. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2012.43.7251
Yeruva SLH, Zhao F, Miller KD, Tevaarwerk AJ, Wagner LI, Gray RJ, Sparano JA, Connolly RM (2018) E2112: randomized phase iii trial of endocrine therapy plus entinostat/placebo in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 4:1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41523-017-0053-3
Wander SA, Spring LM, Bardia A (2019) Genetics to epigenetics: targeting histone deacetylases in hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Lancet Oncol 20(6):746–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30279-7
Jiang Z, Li W, Hu X, Zhang Q, Sun T, Cui S, Wang S, Ouyang Q, Yin Y, Geng C, Tong Z, Cheng Y, Pan Y, Sun Y, Wang H, Ouyang T, Gu K, Feng J, Wang X, Wang S, Liu T, Gao J, Cristofanilli M, Ning Z, Lu X (2019) Tucidinostat plus exemestane for postmenopausal patients with advanced, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (ACE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20(6):806–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30164-0
Spring LM, Wander SA, Zangardi M, Bardia A (2019) CDK 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: current controversies and future directions. Curr Oncol Rep 21(3):25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-019-0769-3
Goldstein LJ, Zhao F, Wang M, Swaby RF, Sparano JA, Meropol NJ, Bhalla KN, Pellegrino CM, Katherine Alpaugh R, Falkson CI, Klein P, Sledge GW (2017) A phase I/II study of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) in combination with trastuzumab (Herceptin) in patients with advanced metastatic and/or local chest wall recurrent HER2-amplified breast cancer: a trial of the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (E1104). Breast Cancer Res Treat 165(2):375–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4310-9
Kim MS, Blake M, Baek JH, Kohlhagen G, Pommier Y, Carrier F (2003) Inhibition of histone deacetylase increases cytotoxicity to anticancer drugs targeting DNA. Cancer Res 63(21):7291–7300
Ciriello G, Gatza ML, Beck AH, Wilkerson MD, Rhie SK, Pastore A, Zhang H, McLellan M, Yau C, Kandoth C, Bowlby R, Shen H, Hayat S, Fieldhouse R, Lester SC, Tse GM, Factor RE, Collins LC, Allison KH, Chen YY, Jensen K, Johnson NB, Oesterreich S, Mills GB, Cherniack AD, Robertson G, Benz C, Sander C, Laird PW, Hoadley KA, King TA, Network TR, Perou CM (2015) Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cell 163(2):506–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.033
Gellert P, Segal CV, Gao Q, Lopez-Knowles E, Martin LA, Dodson A, Li T, Miller CA, Lu C, Mardis ER, Gillman A, Morden J, Graf M, Sidhu K, Evans A, Shere M, Holcombe C, McIntosh SA, Bundred N, Skene A, Maxwell W, Robertson J, Bliss JM, Smith I, Dowsett M, Group PTM, Trialists (2016) Impact of mutational profiles on response of primary oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancers to oestrogen deprivation. Nat Commun 7:13294. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13294
Nik-Zainal S, Davies H, Staaf J, Ramakrishna M, Glodzik D, Zou X, Martincorena I, Alexandrov LB, Martin S, Wedge DC, Van Loo P, Ju YS, Smid M, Brinkman AB, Morganella S, Aure MR, Lingjaerde OC, Langerod A, Ringner M, Ahn SM, Boyault S, Brock JE, Broeks A, Butler A, Desmedt C, Dirix L, Dronov S, Fatima A, Foekens JA, Gerstung M, Hooijer GK, Jang SJ, Jones DR, Kim HY, King TA, Krishnamurthy S, Lee HJ, Lee JY, Li Y, McLaren S, Menzies A, Mustonen V, O’Meara S, Pauporte I, Pivot X, Purdie CA, Raine K, Ramakrishnan K, Rodriguez-Gonzalez FG, Romieu G, Sieuwerts AM, Simpson PT, Shepherd R, Stebbings L, Stefansson OA, Teague J, Tommasi S, Treilleux I, Van den Eynden GG, Vermeulen P, Vincent-Salomon A, Yates L, Caldas C, van’t Veer L, Tutt A, Knappskog S, Tan BK, Jonkers J, Borg A, Ueno NT, Sotiriou C, Viari A, Futreal PA, Campbell PJ, Span PN, Van Laere S, Lakhani SR, Eyfjord JE, Thompson AM, Birney E, Stunnenberg HG, van de Vijver MJ, Martens JW, Borresen-Dale AL, Richardson AL, Kong G, Thomas G, Stratton MR (2016) Landscape of somatic mutations in 560 breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature 534(7605):47–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17676
Rheinbay E, Parasuraman P, Grimsby J, Tiao G, Engreitz JM, Kim J, Lawrence MS, Taylor-Weiner A, Rodriguez-Cuevas S, Rosenberg M, Hess J, Stewart C, Maruvka YE, Stojanov P, Cortes ML, Seepo S, Cibulskis C, Tracy A, Pugh TJ, Lee J, Zheng Z, Ellisen LW, Iafrate AJ, Boehm JS, Gabriel SB, Meyerson M, Golub TR, Baselga J, Hidalgo-Miranda A, Shioda T, Bernards A, Lander ES, Getz G (2017) Recurrent and functional regulatory mutations in breast cancer. Nature 547(7661):55–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22992
(2017) A convergence of genetics and epigenetics in cancer. Cell 168(4):561–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.035
Rizzolo P, Silvestri V, Tommasi S, Pinto R, Danza K, Falchetti M, Gulino M, Frati P, Ottini L (2013) Male breast cancer: genetics, epigenetics, and ethical aspects. Ann Oncol 24(Suppl 8):viii75–viii82. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt316
You JS, Jones PA (2012) Cancer genetics and epigenetics: two sides of the same coin? Cancer Cell 22(1):9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.06.008
Acknowledgements
The work of the authors was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 91649107), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin City of China (Grant No. 17JCYBJC24100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, Q., Wang, Q. et al. Mechanisms of resistance to estrogen receptor modulators in ER+/HER2− advanced breast cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 559–572 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03281-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03281-4