Abstract
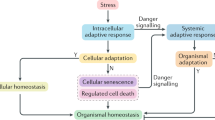
Eukaryotic cells react to potentially dangerous perturbations of the intracellular or extracellular microenvironment by activating rapid (transcription-independent) mechanisms that attempt to restore homeostasis. If such perturbations persist, cells may still try to cope with stress by activating delayed and robust (transcription-dependent) adaptive systems, or they may actively engage in cellular suicide. This regulated form of cell death can manifest with various morphological, biochemical and immunological correlates, and constitutes an ultimate attempt of stressed cells to maintain organismal homeostasis. Here, we dissect the general organization of adaptive cellular responses to stress, their intimate connection with regulated cell death, and how the latter operates for the preservation of organismal homeostasis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lombard J, Lopez-Garcia P, Moreira D (2012) The early evolution of lipid membranes and the three domains of life. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:507–515. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2815
Orgel LE (1998) The origin of life—a review of facts and speculations. Trends Biochem Sci 23:491–495
Pearl LH, Schierz AC, Ward SE, Al-Lazikani B, Pearl FM (2015) Therapeutic opportunities within the DNA damage response. Nat Rev Cancer 15:166–180. doi:10.1038/nrc3891
Kroemer G, Marino G, Levine B (2010) Autophagy and the integrated stress response. Mol Cell 40:280–293. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.023
Hetz C (2012) The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:89–102. doi:10.1038/nrm3270
Hetz C, Chevet E, Harding HP (2013) Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:703–719. doi:10.1038/nrd3976
Carmona-Gutierrez D, Eisenberg T, Buttner S, Meisinger C, Kroemer G, Madeo F (2010) Apoptosis in yeast: triggers, pathways, subroutines. Cell Death Differ 17:763–773. doi:10.1038/cdd.2009.219
Buttner S, Eisenberg T, Herker E, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Kroemer G, Madeo F (2006) Why yeast cells can undergo apoptosis: death in times of peace, love, and war. J Cell Biol 175:521–525. doi:10.1083/jcb.200608098
Madeo F, Herker E, Wissing S, Jungwirth H, Eisenberg T, Frohlich KU (2004) Apoptosis in yeast. Curr Opin Microbiol 7:655–660. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.012
Lam E (2004) Controlled cell death, plant survival and development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:305–315. doi:10.1038/nrm1358
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, El-Deiry WS, Fulda S, Gottlieb E et al (2012) Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ 19:107–120. doi:10.1038/cdd.2011.96
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P, Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS, Golstein P, Green DR, Hengartner M et al (2009) Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ 16:3–11. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.150
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L (2013) Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol 31:51–72. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100008
Kepp O, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Vacchelli E, Adjemian S, Agostinis P, Apetoh L, Aranda F, Barnaba V, Bloy N, Bracci L et al (2014) Consensus guidelines for the detection of immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology 3:e955691. doi:10.4161/21624011.2014.955691
Fuchs Y, Steller H (2011) Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 147:742–758. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.033
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Levine B, Kroemer G (2014) Metabolic control of autophagy. Cell 159:1263–1276. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.006
Green DR, Galluzzi L, Kroemer G (2014) Cell biology. Metabolic control of cell death. Science 345:1250256. doi:10.1126/science.1250256
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Kroemer G (2014) Organelle-specific initiation of cell death. Nat Cell Biol 16:728–736. doi:10.1038/ncb3005
Sica V, Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Izzo V, Maiuri MC, Kroemer G (2015) Organelle-specific initiation of autophagy. Mol Cell 59:522–539. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.07.021
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:251–262. doi:10.1038/nrm3311
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Vander Heiden MG, Kroemer G (2013) Metabolic targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:829–846. doi:10.1038/nrd4145
Avraham R, Yarden Y (2011) Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:104–117. doi:10.1038/nrm3048
Concha-Benavente F, Srivastava RM, Ferrone S, Ferris RL (2013) EGFR-mediated tumor immunoescape: the imbalance between phosphorylated STAT1 and phosphorylated STAT3. Oncoimmunology 2:e27215. doi:10.4161/onci.27215
Shiloh Y, Ziv Y (2013) The ATM protein kinase: regulating the cellular response to genotoxic stress, and more. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:197–210
Kruiswijk F, Labuschagne CF, Vousden KH (2015) p53 in survival, death and metabolic health: a lifeguard with a licence to kill. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:393–405. doi:10.1038/nrm4007
Zirngibl K, Moll UM (2013) p53 further extends its reach. Oncoimmunology 2:e24959. doi:10.4161/onci.24959
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J, Gewirtz DA, Karantza V, Kimmelman A et al (2015) Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J 34:856–880. doi:10.15252/embj.201490784
Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Malik SA, Kroemer G (2010) Autophagy regulation by p53. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:181–185. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.12.001
Bieging KT, Attardi LD (2012) Deconstructing p53 transcriptional networks in tumor suppression. Trends Cell Biol 22:97–106. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2011.10.006
Bishehsari F, Gach JS, Akagi N, Webber MK, Bauer J, Jung BH (2014) Anti-p21 autoantibodies detected in colorectal cancer patients: a proof of concept study. Oncoimmunology 3:e952202. doi:10.4161/21624011.2014.952202
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Ron D (1999) Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum-resident kinase. Nature 397:271–274. doi:10.1038/16729
Kepp O, Semeraro M, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Bloy N, Buque A, Huang X, Zhou H, Senovilla L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2015) eIF2alpha phosphorylation as a biomarker of immunogenic cell death. Semin Cancer Biol 33:86–92. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.004
Siekierka J, Manne V, Ochoa S (1984) Mechanism of translational control by partial phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:352–356
Sarnow P (1989) Translation of glucose-regulated protein 78/immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein mRNA is increased in poliovirus-infected cells at a time when cap-dependent translation of cellular mRNAs is inhibited. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5795–5799
Vattem KM, Wek RC (2004) Reinitiation involving upstream ORFs regulates ATF4 mRNA translation in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11269–11274. doi:10.1073/pnas.0400541101
Novoa I, Zeng H, Harding HP, Ron D (2001) Feedback inhibition of the unfolded protein response by GADD34-mediated dephosphorylation of eIF2alpha. J Cell Biol 153:1011–1022
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K, Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D, Yuan J (2005) A selective inhibitor of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 307:935–939. doi:10.1126/science.1101902
Han J, Back SH, Hur J, Lin YH, Gildersleeve R, Shan J, Yuan CL, Krokowski D, Wang S, Hatzoglou M, Kilberg MS et al (2013) ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat Cell Biol 15:481–490. doi:10.1038/ncb2738
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Vitale I, Aaronson SA, Abrams JM, Adam D, Alnemri ES, Altucci L, Andrews D, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M, Baehrecke EH et al (2015) Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ 22:58–73. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.137
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013
Le Bert N, Lam AR, Ho SS, Shen YJ, Liu MM, Gasser S (2014) STING-dependent cytosolic DNA sensor pathways regulate NKG2D ligand expression. Oncoimmunology 3:e29259. doi:10.4161/onci.29259
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2012) Mitochondria: master regulators of danger signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13:780–788. doi:10.1038/nrm3479
Vacchelli E, Aranda F, Obrist F, Eggermont A, Galon J, Cremer I, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L (2014) Trial watch: immunostimulatory cytokines in cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology 3:e29030. doi:10.4161/onci.29030
McNab F, Mayer-Barber K, Sher A, Wack A, O’Garra A (2015) Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol 15:87–103. doi:10.1038/nri3787
Schoggins JW, Wilson SJ, Panis M, Murphy MY, Jones CT, Bieniasz P, Rice CM (2011) A diverse range of gene products are effectors of the type I interferon antiviral response. Nature 472:481–485. doi:10.1038/nature09907
Galluzzi L, Brenner C, Morselli E, Touat Z, Kroemer G (2008) Viral control of mitochondrial apoptosis. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000018. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000018
Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P (2012) Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12:860–875. doi:10.1038/nrc3380
Kanegasaki S, Tsuchiya T (2014) Alarmins released during local antitumor treatments play an essential role in enhancing tumor growth inhibition at treated and non-treated sites via a derivative of CCL3. Oncoimmunology 3:e958956. doi:10.4161/21624011.2014.958956
Kaczmarek A, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV (2013) Necroptosis: the release of damage-associated molecular patterns and its physiological relevance. Immunity 38:209–223. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.02.003
Spel L, Boelens JJ, Nierkens S, Boes M (2013) Antitumor immune responses mediated by dendritic cells: how signals derived from dying cancer cells drive antigen cross-presentation. Oncoimmunology 2:e26403. doi:10.4161/onci.26403
Workenhe ST, Mossman KL (2013) Rewiring cancer cell death to enhance oncolytic viro-immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2:e27138. doi:10.4161/onci.27138
Jiang H, Fueyo J (2014) Healing after death: antitumor immunity induced by oncolytic adenoviral therapy. Oncoimmunology 3:e947872. doi:10.4161/21624011.2014.947872
Acknowledgments
The authors are supported by the Ligue contre le Cancer (équipe labellisée); Agence National de la Recherche (ANR)—Projets blancs; ANR under the frame of E-Rare-2, the ERA-Net for Research on Rare Diseases; Association pour la recherche sur le cancer (ARC); Cancéropôle Ile-de-France; Institut National du Cancer (INCa); Fondation Bettencourt-Schueller; Fondation de France; Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (FRM); the European Commission (ArtForce); the European Research Council (ERC); the LabEx Immuno-Oncology; the SIRIC Stratified Oncology Cell DNA Repair and Tumor Immune Elimination (SOCRATE); the SIRIC Cancer Research and Personalized Medicine (CARPEM); the Swiss Bridge Foundation, ISREC and the Paris Alliance of Cancer Research Institutes (PACRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
L. Galluzzi and G. Kroemer share senior co-authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galluzzi, L., Bravo-San Pedro, J.M., Kepp, O. et al. Regulated cell death and adaptive stress responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 73, 2405–2410 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2209-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2209-y