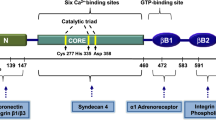
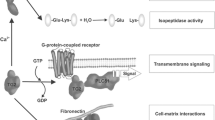
Abstract
Celiac disease is characterized by the presence of specific autoantibodies targeted against transglutaminase 2 (TG2) in untreated patients’ serum and at their production site in the small-bowel mucosa below the basement membrane and around the blood vessels. As these autoantibodies have biological activity in vitro, such as inhibition of angiogenesis, we studied if they might also modulate the endothelial barrier function. Our results show that celiac disease patient autoantibodies increase endothelial permeability for macromolecules, and enhance the binding of lymphocytes to the endothelium and their transendothelial migration when compared to control antibodies in an endothelial cell-based in vitro model. We also demonstrate that these effects are mediated by increased activities of TG2 and RhoA. Since the small bowel mucosal endothelium serves as a “gatekeeper” in inflammatory processes, the disease-specific autoantibodies targeted against TG2 could thus contribute to the pathogenic cascade of celiac disease by increasing blood vessel permeability.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korponay-Szabo IR, Laurila K, Szondy Z, Halttunen T, Szalai Z, Dahlbom I, Rantala I, Kovacs JB, Fesus L, Maki M (2003) Missing endomysial and reticulin binding of coeliac antibodies in transglutaminase 2 knockout tissues. Gut 52:199–204
Green PH, Cellier C (2007) Celiac disease. N Engl J Med 357:1731–1743
Marzari R, Sblattero D, Florian F, Tongiorgi E, Not T, Tommasini A, Ventura A, Bradbury A (2001) Molecular dissection of the tissue transglutaminase autoantibody response in celiac disease. J Immunol 166:4170–4176
Korponay-Szabo IR, Halttunen T, Szalai Z, Laurila K, Kiraly R, Kovacs JB, Fesus L, Maki M (2004) In vivo targeting of intestinal and extraintestinal transglutaminase 2 by coeliac autoantibodies. Gut 53:641–648
Salmi TT, Collin P, Korponay-Szabo IR, Laurila K, Partanen J, Huhtala H, Kiraly R, Lorand L, Reunala T, Maki M, Kaukinen K (2006) Endomysial antibody-negative coeliac disease: clinical characteristics and intestinal autoantibody deposits. Gut 55:1746–1753
Halttunen T, Maki M (1999) Serum immunoglobulin A from patients with celiac disease inhibits human T84 intestinal crypt epithelial cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 116:566–572
Barone MV, Caputo I, Ribecco MT, Maglio M, Marzari R, Sblattero D, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Esposito C (2007) Humoral immune response to tissue transglutaminase is related to epithelial cell proliferation in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 132:1245–1253
Zanoni G, Navone R, Lunardi C, Tridente G, Bason C, Sivori S, Beri R, Dolcino M, Valletta E, Corrocher R, Puccetti A (2006) In celiac disease, a subset of autoantibodies against transglutaminase binds toll-like receptor 4 and induces activation of monocytes. PLoS Med 3:e358
Cervio E, Volta U, Verri M, Boschi F, Pastoris O, Granito A, Barbara G, Parisi C, Felicani C, Tonini M, De Giorgio R (2007) Sera of patients with celiac disease and neurologic disorders evoke a mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in vitro. Gastroenterology 133:195–206
Boscolo S, Sarich A, Lorenzon A, Passoni M, Rui V, Stebel M, Sblattero D, Marzari R, Hadjivassiliou M, Tongiorgi E (2007) Gluten ataxia: passive transfer in a mouse model. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1107:319–328
Hadjivassiliou M, Maki M, Sanders DS, Williamson CA, Grunewald RA, Woodroofe NM, Korponay-Szabo IR (2006) Autoantibody targeting of brain and intestinal transglutaminase in gluten ataxia. Neurology 66:373–377
Myrsky E, Kaukinen K, Syrjanen M, Korponay-Szabo IR, Maki M, Lindfors K (2008) Coeliac disease-specific autoantibodies targeted against transglutaminase 2 disturb angiogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol 152:111–119
Cooke WT, Holmes GKT (1984) Coeliac disease. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Myrsky E, Syrjanen M, Korponay-Szabo IR, Maki M, Kaukinen K, Lindfors K (2009) Altered small-bowel mucosal vascular network in untreated coeliac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 44:162–167
Ghosh K, Thodeti CK, Dudley AC, Mammoto A, Klagsbrun M, Ingber DE (2008) Tumor-derived endothelial cells exhibit aberrant Rho-mediated mechanosensing and abnormal angiogenesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11305–11310
Janiak A, Zemskov EA, Belkin AM (2006) Cell surface transglutaminase promotes RhoA activation via integrin clustering and suppression of the Src-p190RhoGAP signaling pathway. Mol Biol Cell 17:1606–1619
Wojciak-Stothard B, Potempa S, Eichholtz T, Ridley AJ (2001) Rho and Rac but not Cdc42 regulate endothelial cell permeability. J Cell Sci 114:1343–1355
Halttunen T, Marttinen A, Rantala I, Kainulainen H, Maki M (1996) Fibroblasts and transforming growth factor beta induce organization and differentiation of T84 human epithelial cells. Gastroenterology 111:1252–1262
Birckbichler PJ, Upchurch HF, Patterson MK Jr, Conway E (1985) A monoclonal antibody to cellular transglutaminase. Hybridoma 4:179–186
Baumgartner W, Golenhofen N, Weth A, Hiiragi T, Saint R, Griffin M, Drenckhahn D (2004) Role of transglutaminase 1 in stabilisation of intercellular junctions of the vascular endothelium. Histochem Cell Biol 122:17–25
Griffin M, Mongeot A, Collighan R, Saint RE, Jones RA, Coutts IG, Rathbone DL (2008) Synthesis of potent water-soluble tissue transglutaminase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:5559–5562
Korponay-Szabo IR, Vecsei Z, Kiraly R, Dahlbom I, Chirdo F, Nemes E, Fesus L, Maki M (2008) Deamidated gliadin peptides form epitopes that transglutaminase antibodies recognize. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 46:253–261
Kiraly R, Vecsei Z, Demenyi T, Korponay-Szabo IR, Fesus L (2006) Coeliac autoantibodies can enhance transamidating and inhibit GTPase activity of tissue transglutaminase: dependence on reaction environment and enzyme fitness. J Autoimmun 26:278–287
Ensari A, Ager A, Marsh MN, Morgan S, Moriarty KJ (1993) Time-course of adhesion molecule expression in rectal mucosa of gluten-sensitive subjects after gluten challenge. Clin Exp Immunol 92:303–307
Jelinkova L, Tuckova L, Sanchez D, Krupickova S, Pozler O, Nevoral J, Kotalova R, Tlaskalova-Hogenova H (2000) Increased levels of circulating ICAM-1, E-selectin, and IL-2 receptors in celiac disease. Dig Dis Sci 45:398–402
Di Sabatino A, Rovedatti L, Rosado MM, Carsetti R, Corazza GR, MacDonald TT (2009) Increased expression of mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 in the duodenum of patients with active celiac disease is associated with depletion of integrin alpha4beta7-positive T cells in blood. Hum Pathol 40:699–704
Siegel M, Strnad P, Watts RE, Choi K, Jabri B, Omary MB, Khosla C (2008) Extracellular transglutaminase 2 is catalytically inactive, but is transiently activated upon tissue injury. PLoS ONE 3:e1861.
Dieterich W, Ehnis T, Bauer M, Donner P, Volta U, Riecken EO, Schuppan D (1997) Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat Med 3:797–801
Esposito C, Paparo F, Caputo I, Rossi M, Maglio M, Sblattero D, Not T, Porta R, Auricchio S, Marzari R, Troncone R (2002) Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies from coeliac patients inhibit transglutaminase activity both in vitro and in situ. Gut 51:177–181
Anjum N, Baker PN, Robinson NJ, Aplin JD (2009) Maternal celiac disease autoantibodies bind directly to syncytiotrophoblast and inhibit placental tissue transglutaminase activity. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 7:16
Byrne G, Ryan F, Jackson J, Feighery C, Kelly J (2007) Mutagenesis of the catalytic triad of tissue transglutaminase abrogates coeliac disease serum IgA autoantibody binding. Gut 56:336–341
Pinkas DM, Strop P, Brunger AT, Khosla C (2007) Transglutaminase 2 undergoes a large conformational change upon activation. PLoS Biol 5:e327
Noll T, Wozniak G, McCarson K, Hajimohammad A, Metzner HJ, Inserte J, Kummer W, Hehrlein FW, Piper HM (1999) Effect of factor XIII on endothelial barrier function. J Exp Med 189:1373–1382
Mehta D, Rahman A, Malik AB (2001) Protein kinase C-alpha signals rho-guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor phosphorylation and rho activation and regulates the endothelial cell barrier function. J Biol Chem 276:22614–22620
Holinstat M, Mehta D, Kozasa T, Minshall RD, Malik AB (2003) Protein kinase Calpha-induced p115RhoGEF phosphorylation signals endothelial cytoskeletal rearrangement. J Biol Chem 278:28793–28798
Singh US, Kunar MT, Kao YL, Baker KM (2001) Role of transglutaminase II in retinoic acid-induced activation of RhoA-associated kinase-2. EMBO J 20:2413–2423
Breen EC (2007) VEGF in biological control. J Cell Biochem 102:136–1358
Takahashi H, Shibuya M (2005) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond) 109:227–241
Bergamini CM, Griffin M, Pansini FS (2005) Transglutaminase and vascular biology: physiopathologic implications and perspectives for therapeutic interventions. Curr Med Chem 12:2357–2372
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Mr. Jorma Kulmala for technical assistance. The Celiac Disease Study Group has been financially supported by the Research Council for Health, the Academy of Finland, the Juselius Foundation, the Paediatric Research Foundation, the Competitive Research Funding of the Pirkanmaa Hospital District, the Research Fund of the Finnish Celiac Society, the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (OTKA K61868), and the European Commission (contract number MRTN-CT-2006-036032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myrsky, E., Caja, S., Simon-Vecsei, Z. et al. Celiac disease IgA modulates vascular permeability in vitro through the activity of transglutaminase 2 and RhoA. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 3375–3385 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0116-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0116-1