Abstract.
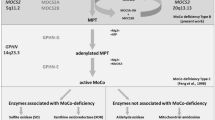
The molybdenum cofactor (Moco) forms the active site of all molybdenum (Mo) enzymes, except nitrogenase. Mo enzymes catalyze important redox reactions in global metabolic cycles. Moco consists of Mo covalently bound to one or two dithiolates attached to a unique tricyclic pterin moiety commonly referred to as molybdopterin (MPT). Moco is synthesized by an ancient and conserved biosynthetic pathway that can be divided into four steps, according to the biosynthetic intermediates precursor Z (cyclic pyranopterin monophosphate), MPT and adenylated MPT. In a fifth step modifications such as attachment of nucleotides, sulfuration or bond formation between Mo and the protein result in different catalytic Mo centers. A defect in any of the steps of Moco biosynthesis results in the pleiotropic loss of all Mo enzyme activities. Human Moco deficiency is a hereditary metabolic disorder characterized by severe neurodegeneration resulting in early childhood death. Recently, a first substitution therapy was established.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 17 June 2005; received after revision 18 August 2005; accepted 1 September 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, G. Molybdenum cofactor biosynthesis and deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 2792–2810 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5269-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5269-y