Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this case–control study was to investigate whether polymorphisms and gene–gene interactions of the two type I interferon (IFN) genes (IRF5 and TYK2) are the susceptible factors of systemic Lupus erythematosus (SLE) in the Han Chinese population.
Methods
The four variants [rs2004640, rs2070197, rs10954213 and exon6 insertion/deletion (in/de)] of IRF5 gene and five single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (rs280500, rs280519, rs2304256, rs8108236, rs12720270) of TYK2 gene were examined in a cohort of 642 SLE patients and 642 healthy controls. Genotyping was conducted using polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR–RFLP) and confirmed by direct sequencing in 10 % sample randomly.
Results
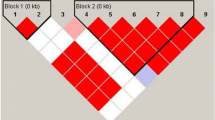
Rs2070197 was not polymorphic in this study, and was excluded in further analysis. Significant association was found for loci on IRF5 (rs2004640: p = 0.0003, p corr = 0.0012) and TYK2 (rs280500: p = 8.83 × 10−6, p corr = 4.41 × 10−5; rs2304256: p = 3.71 × 10−6, p corr = 1.85 × 10−5; rs8108236: p = 0.0004, p corr = 0.002), but not for other SNPs. Significant association was also observed for genotypes of IRF5 (rs2004640, p = 0.0009, p corr = 0.0036) and TYK2 SNPs (rs280500: p = 5.21 × 10−5, p corr = 2.61 × 10−4; rs2304256: p = 7.72 × 10−6, p corr = 3.86 × 10−5; rs8108236: p = 0.002, p corr = 0.01). Nevertheless, two haplotypes based on the 3 variants [exon6(in/de), rs10954213, rs2004640] of IRF5 (DAG and IAT) could define protective or susceptibility haplotype in SLE. Similarly, three haplotypes containing 5 SNPs (rs280500, rs280519, rs2304256, rs8108236, rs12720270) of TYK2 (GATAT, AGGAT and GAGGT) may also be associated with SLE in Han Chinese. Additionally, the gene–gene interaction analysis was conducted on the IRF5 and TYK2 SNPs. And a three-way interaction between TYK2 rs280500, rs2304256 and IRF5 rs10954213 and SLE was found (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Genetic associations and gene–gene interactions of IRF5 and TYK2 were significantly detected in Han Chinese with SLE. Our results had important implications for future research on the role of type I IFN function in SLE susceptibility.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gregersen PK, Behrens TW. Genetics of autoimmune diseases disorders of immune homeostasis. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:917–28.
Sigurdsson S, Nordmark G, Göring HH, Lindroos K, Wiman AC, Sturfelt G, et al. Polymorphisms in the tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 genes are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76:528–37.
Cui Y, Sheng YJ, Zhang XJ. Genetic susceptibility to SLE: recent progress from GWAS. J Autoimmun. 2013;41:25–33.
Kyogoku C, Tsuchiya N. A compass that points to lupus: genetic studies on type I interferon pathway. Genes Immun. 2007;8:445–55.
Graham RR, Kozyrev SV, Baechler EC, Reddy MV, Plenge RM, Bauer JW, et al. A common haplotype of interferon regulatoryfactor 5 (IRF5) regulates splicing and expression and is associated with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2006;38:550–5.
Remmers EF, Plenge RM, Lee AT, Graham RR, Hom G, Behrens TW, et al. STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:977–86.
Jarvinen TM, Hellquist A, Koskenmies S, Einarsdottir E, Koskinen LL, Jeskanen L, et al. Tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 polymorphisms are associated with discoid and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Exp Dermatol. 2010;19:123–31. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.00982.x.
Cunninghame Graham DS, Morris DL, Bhangale TR, Criswell LA, Syvanen AC, Ronnblom L, et al. Association of NCF2, IKZF1, IRF8, IFIH1, and TYK2 with systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002341.
Ishizaki M, Akimoto T, Muromoto R, Yokoyama M, Ohshiro Y, Sekine Y, et al. Involvement of tyrosine kinase-2 in both the IL-12/Th1 and IL-23/Th17 axesin vivo. J Immunol. 2011;187:181–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003244.
Tao JH, Zou YF, Feng XL, Li J, Wang F, Pan FM, et al. Meta-analysis of TYK2 gene polymorphisms association with susceptibility to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38:4663–72. doi:10.1007/s11033-010-0601-5.
Löfgren SE, Yin H, Delgado-Vega AM, Sanchez E, Lewén S, Pons-Estel BA, et al. Promoter insertion/deletion in the IRF5 gene is highly associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in distinct populations, but exerts a modest effect on gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:574–8.
Kelly JA, Kelley JM, Kaufman KM, Kilpatrick J, Bruner GR, Merrill JT, et al. Interferon regulatory factor-5 is genetically associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in African Americans. Genes Immun. 2008;9:187–94.
Shin HD, Sung YK, Choi CB, Lee SO, Lee HW, Bae SC, et al. Replication of genetic effects of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) on systemic lupus erythematosus in a Korean population. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9:R32.
Kawasaki A, Kyogoku C, Ohashi J, Miyashita R, Hikami K, Kusaoi M, et al. Association of IRF5 polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population: support for a crucial role of intron 1 polymorphisms. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:826–34.
Cunninghame Graham DS, Manku H, Wagner S, Reid J, Timms K, Gutin A, et al. Association of IRF5 in UK SLE families identifies a variant involved in polyadenylation. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16:579–91.
Siu HO, Yang W, Lau CS, Chan TM, Wong RW, Wong WH, et al. Association of a haplotype of IRF5 gene with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese. J Rheumatol. 2008;35:360–2.
Song WQ, Li HH, Chen HB, Yuan JS, Yin XJ. Relationship between polymorphism sites of IRF5, TLR-9 and SLE patients in Shandong Han population. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009;89:3038–42.
Harley JB, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Criswell LA, Jacob CO, Kimberly RP, Moser KL, et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat Genet. 2008;40:204–10.
Hellquist A, Järvinen TM, Koskenmies S, Zucchelli M, Orsmark-Pietras C, Berglind L, et al. Evidence for genetic association and interaction between the TYK2 and IRF5 genes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2009;36:1631–8.
Marian SG, Manuel C, Antonio G. Lack of interaction between systemic lupus erythematosus-associated polymorphisms in TYK2 and IRF5. J Rheumatol. 2010;37:3.
Hooks JJ, Moutsopoulos HM, Geis SA, Stahl NI, Decker JL, Notkins AL, et al. Immune interferon in the circulation of patients with autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 1979;301:5–8.
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, et al. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25:1271–7.
Ronnblom L, Eloranta ML, Alm GV. The type I interferon system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:408.
Richez C, Yasuda K, Bonegio RG, Watkins AA, Aprahamian T, Busto P, et al. Ifn regulatory factor 5 is required for disease development in the fcgammariib−/−yaa and fcgammariib−/− mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunology. 2010;184:796.
Yasuda K, Richez C, Maciaszek JW, Agrawal N, Akira S, Marshak-Rothstein A, et al. Murine dendritic cell type i ifn production induced by human igg-rna immune complexes is ifn regulatory factor (irf)5 and irf7 dependent and is required for il-6 production. Journal of Immunology. 2007;178:6876.
Sigurdsson S, Göring HH, Kristjansdottir G, Milani L, Nordmark G, Sandling JK, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the genetic variants of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) reveals a novel 5 bp length polymorphism as strong risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:872–81.
Nordang GB, Viken MK, Amundsen SS, Sanchez ES, Flatø B, Førre OT, et al. Interferon regulatory factor 5 gene polymorphism confers risk to several rheumatic diseases and correlates with expression of alternative thymic transcripts. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;51:619–26.
Reddy MV, Velázquez-Cruz R, Baca V, Lima G, Granados J, Orozco L, et al. Genetic association of IRF5 with SLE in Mexicans: higher frequency of the risk haplotype and its homozygozity than Europeans. Hum Genet. 2007;121:721–7.
AlFadhli S, Jahabani I. Association of interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) markers with an increased risk of lupus and overlapping autoimmunity in a Kuwaiti population. Ann Hum Biol. 2014;41:531–9.
Kozyrev SV, Lewén S, Reddy PM, Pons-Estel B, Witte T, Argentine Collaborative Group, et al. Structural insertion/deletion variation in IRF5 is associated with a risk haplotype and defines the precise isoforms expressed in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1234–41.
Graham RR, Kyogoku C, Sigurdsson S, Vlasova IA, Davies LR, Baechler EC, et al. Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:6758–63.
Elghzaly AA, Metwally SS, El-Chennawi FA, Elgayaar MA, Mosaad YM, et al. IRF5, PTPN22, CD28, IL2RA, KIF5A, BLK and TNFAIP3 genes polymorphisms and lupus susceptibility in a cohort from the Egypt Delta; relation to other ethnic groups. Hum Immunol. 2015;76:525–31.
Leng RX, Wang W, Cen H, Zhou M, Feng CC, Zhu Y, et al. Gene–gene and gene–sex epistatic interactions of MiR146a, IRF5, IKZF1, ETS1 and IL21 in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e51090.
Lindqvist AK, Steinsson K, Johanneson B, Kristjánsdóttir H, Arnasson A, Gröndal G, et al. A susceptibility locus for human systemic lupus erythematosus (hSLE1) on chromo-some 2q. J Autoimmun. 2000;14:169–78.
Suarez-Gestal M, Calaza M, Endreffy E, Pullmann R, Ordi-Ros J, Sebastiani GD, et al. Replication of recently identified systemic lupus erythematosus genetic associations: a case–control study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R69.
Li P, Chang YK, Shek KW, Lau YL. Lack of association of TYK2 gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2011;38:177–8.
Kyogoku C, Morinobu A, Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Hashimoto H, Tokano Y, et al. Lack of association between tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to SLE in a Japanese population. Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19:401–6.
Liu J, Sun QY, Tang BS, et al. PITX3 gene polymorphism is associated with Parkinson’s disease in Chinese population. Brain Res. 2011;1392:116–20.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the SLE and RA patients and control individuals for participating in this study. This study was supported by the Foundation for Young Professors of the Education Department of Hunan (15B0146), the construct program of the key discipline in Hunan province and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2015IVA048 and 2015IB004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
L. Tang and P. Wan contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, L., Wan, P., Wang, Y. et al. Genetic association and interaction between the IRF5 and TYK2 genes and systemic lupus erythematosus in the Han Chinese population. Inflamm. Res. 64, 817–824 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0865-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0865-2