Abstract
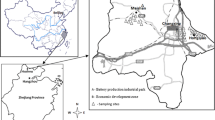
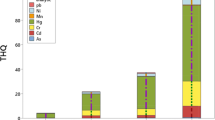
Trace elements contents in Tricholoma matsutake (T. matsutake) and its corresponding soil substrates from Yunnan province of China were determined. Samples were collected from seven different locations in Yunnan province, and the contents of arsenic (As), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd) and chromium (Cr) were analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The results demonstrated that the average contents of As, Pb, Hg, Cd, and Cr in T. matsutake were 0.82–5.62, 0.34–0.82, 0.03–0.11, 0.24–2.84, and 0.13–0.62 mg/kg dry weight (DW), respectively. The results show that the contents of potentially toxic trace elements (As and Cd) exceeded statutory standard limits of China (1.0 mg/kg for As and 0.2 mg/kg for Cd) in most cases. Differences among trace elements contents from all sampling sites were found to be statistically significant (p < 0.05). Bioconcentration factor (BCF) illustrated that Cd was easily bioaccumulated by T. matsutake. Human health risks of these trace elements were assessed based on target hazard quotient (THQ). The estimated weekly intake of trace elements was estimated and compared with the Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake (PTWI) recommended by the FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. The results indicate that As and Cd in T. matsutake may pose a potential health risk for human beings. The estimated weekly intake of Pb, Hg, and Cr from consuming T. matsutake were lower than the PTWI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amde M, Yin Y, Zhang D, Liu J (2016) Methods and recent advances in speciation analysis of mercury chemical species in environmental samples: a review. Chem Spec Bioavailab 28:51–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/09542299.2016.1164019
Arora M, Kiran B, Rani S, Rani A, Kaur B, Mittal N (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in vegetables irrigated with water from different sources. Food Chem 111:811–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.04.049
Árvay J, Tomáš J, Hauptvogl M, Massányi P, Harangozo Ľ, Tóth T, Stanovič R, Bryndzová Š, Bumbalová M (2015) Human exposure to heavy metals and possible public health risks via consumption of wild edible mushrooms from Slovak Paradise National Park, Slovakia. J Environ Sci Heal B 50:833–843. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2015.1058107
Árvay J, Demková L, Hauptvogl M, Michalko M, Bajčan D, Stanovič R, Tomáš J, Hrstková M, Trebichalský P (2017) Assessment of environmental and health risks in former polymetallic ore mining and smelting area, Slovakia: Spatial distribution and accumulation of mercury in four different ecosystems. Ecotox Environ Safe 144:236–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.06.020
Bastami KD, Afkhami M, Mohammadizadeh M, Ehsanpour M, Chambari S, Aghaei S, Esmaeilzadeh M, Neyestani MR, Lagzaee F, Baniamam M (2015) Bioaccumulation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediments and mullet Liza klunzingeri in the northern part of the Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 94:329–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.01.019
Chudzyński K, Jarzyńska G, Stefańska A, Falandysz J (2011) Mercury contents and bio-concentration potential of Slippery Jack, Suillus luteus, mushroom. Food Chem 125:986–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.102
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112301
Dimitrijevi MV, Mitic VD, Cvetkovic JS, Jovanovic VP, Mutic JJ, Mandic SDN (2016) Update on element contents profiles in eleven wild edible mushrooms from family Boletaceae. Eur Food Res Technol 242:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-015-2512-0
Ding X, Hou YL (2012) Identification of genetic characterization and volatile compounds of Tricholoma matsutake from different geographical origins. Biochem Syst Ecol 44:233–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2012.06.003
Endo N, Dokmai P, Suwannasai N, Phosri C, Horimai Y, Hirai N, Fukuda M, Yamada A (2015) Ectomycorrhization of Tricholoma matsutake with Abies veitchii and Tsuga diversifolia in the subalpine forests of Japan. Mycoscience 56:402–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.myc.2014.12.004
Falandysz J, Borovička J (2013) Macro and trace mineral constituents and radionuclides in mushrooms: health benefits and risks. Appl Microbiol Biot 97:477–501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4552-8
Falandysz J, Rizal LM (2016) Arsenic and its compounds in mushrooms: a review. J Environ Sci Heal C 34:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2016.1235935
Falandysz J, Krasińska G, Pankavec S, Nnorom IC (2014) Mercury in certain boletus mushrooms from Poland and Belarus. J Environ Sci Heal B 49:690–695. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2014.922853
Falandysz J, Mędyk M, Treu R (2018) Bio-concentration potential and associations of heavy metals in Amanita muscaria (L.) Lam. from northern regions of Poland. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:25190–25206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2603-0
Flora G, Gupta D, Tiwari A (2012) Toxicity of lead: a review with recent updates. Interdiscip Toxicol 5:47–58. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10102-012-0009-2
Franke C (1996) How meaningful is the bioconcentration factor for risk assessment? Chemosphere 32:1897–1905. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(96)00104-X
Gaudet MM et al (2019) Blood levels of cadmium and lead in relation to breast cancer risk in three prospective cohorts. Int J Cancer 144:1010–1016. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31805
Giannaccini G, Betti L, Palego L, Mascia G, Schmid L, Lanza M, Mela A, Fabbrini L, Biondi L, Lucacchini A (2012) The trace element contents of top-soil and wild edible mushroom samples collected in Tuscany, Italy. Environ Monit Assess 184:7579–7595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2520-5
Hiatt MH (1998) Bioconcentration factors for volatile organic compounds in vegetation. Anal Chem 70:851–856. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac971167m
Huang M, Zhou S, Sun B, Zhao Q (2008) Heavy metals in wheat grain: assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Kunshan, China. Sci Total Environ 405:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.07.004
Huang Q, Jia Y, Wan Y, Li H, Jiang R (2015) Market survey and risk assessment for trace metals in edible fungi and the substrate role in accumulation of heavy metals. J Food Sci 80:H1612–H1618. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12923
Işıloğlu M, Yılmaz F, Merdivan M (2001) Concentrations of trace elements in wild edible mushrooms. Food Chem 73:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(00)00257-0
Jarzyńska G, Falandysz J (2012) Trace elements profile of Slate Bolete (Leccinum duriusculum) mushroom and associated upper soil horizon. J Geochem Explor 121:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.07.001
Kalač P (2010) Trace element contents in European species of wild growing edible mushrooms: a review for the period 2000–2009. Food Chem 122:2–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.045
Kalač P, Svoboda L (2000) A review of trace element concentrations in edible mushrooms. Food Chem 69:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00264-2
Kasemodel M, Sakamoto I, Varesche M, Rodrigues V (2019) Potentially toxic metal contamination and microbial community analysis in an abandoned Pb and Zn mining waste deposit. Sci Total Environ 675:367–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.223
Kraaij H, Connell D (1997) Bioconcentration and uptake kinetics of chlorobenzenes in soy-bean roots. Chemosphere. 34:2607–2620. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(97)00104-5
Landrigan PJ, Goldman LR (2011) Child’s vulnerability to toxic chemicals: a challenge and opportunity to strengthen health and environmental policy. Health Affair 30:842–850. https://doi.org/10.1377/hlthaff.2011.0151
Li P, Lin C, Cheng H, Duan X, Lei K (2015) Contamination and health risks of soil heavy metals around a lead/zinc smelter in southwestern China. Ecotox Environ Safe 113:391–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.12.025
Lian C, Narimatsu M, Nara K, Hogetsu T (2006) Tricholoma matsutake in a natural Pinus densiflora forest: correspondence between above- and below-ground genets, association with multiple host trees and alteration of existing ectomycorrhizal communities. New Phytol 171:825–836. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01801.x
Liu B, Huang Q, Cai H, Guo X, Wang T, Gui M (2015) Study of heavy metal concentrations in wild edible mushrooms in Yunnan Province, China. Food Chem 188:294–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.010
Mandal BK, Suzuki KT (2002) Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58:201–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-9140(02)00268-0
Melgar MJ, Alonso J, García MA (2009) Mercury in edible mushrooms and underlying soil: Bioconcentration factors and toxicological risk. Sci Total Environ 407:5328–5334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.07.001
Mleczek M, Siwulski M, Mikołajczak P, Gąsecka M, Sobieralski K, Szymańczyk M, Goliński P (2015) Contents of selected elements in Boletus badius fruiting bodies growing in extremely polluted wastes. J Environ Sci Heal A 50:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2015.1012014
Mleczek M, Niedzielski P, Kalač P, Budka A, Siwulski M, Gąsecka M, Rzymski P, Magdziak Z, Sobieralski K (2016a) Multielemental analysis of 20 mushroom species growing near a heavily trafficked road in Poland. Environ Sci Pollut R 23:16280–16295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6760-8
Mleczek M, Niedzielski P, Rzymski P, Siwulski M, Gąsecka M, Kozak L (2016b) Variations of arsenic species contents in edible Boletus badius growing at polluted sites over four years. J Environ Sci Heal B 51:469–476. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2016.1159459
Nharingo T, Ndumo T, Moyo M (2015) Human health risks due to heavy metals through consumption of wild mushrooms from Macheke forest, Rail Block forest and Muganyi communal lands in Zimbabwe. Environ Monit Assess 187:738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4974-8
Rzymski P, Klimaszyk P (2018) Is the yellow knight mushroom edible or not? A systematic review and critical viewpoints on the toxicity of Tricholoma equestre. Compr Rev Food Sci F 17:1309–1324. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12374
Saba M, Falandysz J, Nnorom ICJES, Research P (2016) Accumulation and distribution of mercury in fruiting bodies by fungus Suillus luteus foraged in Poland, Belarus and Sweden. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:2749–2757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5513-4
Satarug S (2018) Dietary cadmium intake and its effects on kidneys. Toxics 6:15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6010015
Singh J, Kalamdhad AS (2011) Effects of heavy metals on soil, plants, human health and aquatic life. Int J Res Chem Environ 1:15–21
Singh HP, Mahajan P, Kaur S, Batish DR, Kohli RK (2013) Chromium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Environ Chem Lett 11:229–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-013-0407-5
Stihi C, Radulescu C, Busuioc G, Popescu I, Gheboianu A, Ene A (2011) Studies on accumulation of heavy metals from substrate to edible wild mushrooms. Rom J Phys 56:257–264
Streets DG, Horowitz HM, Jacob DJ, Lu Z, Levin L, Ter Schure AF, Sunderland EM (2017) Total mercury released to the environment by human activities. Environ Sci Technol 51:5969–5977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00451
Sun H, Brocato J, Costa M (2015) Oral chromium exposure and toxicity. Curr Environ Health Rep 2:295–303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40572-015-0054-z
Sun L, Liu Q, Bao C, Fan J (2017a) Comparison of free total amino acid compositions and their functional classifications in 13 wild edible mushrooms. Molecules 22:350. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030350
Sun L, Chang W, Bao C, Zhuang Y (2017b) Metal contents, bioaccumulation, and health risk assessment in wild edible Boletaceae mushrooms. J Food Sci 82:1500–1508. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13698
Su-Rui WU, Luo XL, Liu B, Gui MY (2010) Analyse and advise to research and development of wild edible fungi. Food Sci Technol 35:100–103. https://doi.org/10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2010.04.056
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. In: Luch A (ed) Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology. Experientia supplementum, vol 101. Springer, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Vetter J (2004) Arsenic contents of some edible mushroom species. Eur Food Res Technol 219:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-004-0905-6
Wang XM, Zhang J, Wu LH, Zhao YL, Li T, Li JQ, Wang YZ, Liu HG (2014) A mini-review of chemical composition and nutritional value of edible wild-grown mushroom from China. Food Chem 151:279–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.062
Wang X, Liu H, Zhang J, Li T, Wang Y (2017) Evaluation of heavy metal concentrations of edible wild-grown mushrooms from China. J Environ Sci Heal B 52:178–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2017.1261545
Wani AL, Ara A, Usmani JA (2015) Lead toxicity: a review. Interdiscip Toxicol 8:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1515/intox-2015-0009
Yang Y, Tian K, Hao J, Pei S, Yang Y (2004) Biodiversity and biodiversity conservation in Yunnan, China. Biodivers Conserv 13:813–826. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOC.0000011728.46362.3c
Yang X, Yang X, He J, Liu P, Xu JJPD, Resources (2013) Future distribution of Tuber indicum under climate change scenarios-a case study in Yunnan province. Plant Diver Resour 35:62–72
Zhang D, Zhan Y, Morawska E, Bielawski L, Krasinska G, Drewnowska M, Pankavec S, Szymanska K, Falandysz J (2013) Trace elements in Leccinum scabrum mushrooms and topsoils from Kłodzka Dale in Sudety Mountains, Poland. J Mt Sci-Engl 10:621–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2384-3
Zhao F, Ma J, Meharg A, McGrath S (2009) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in plants. New Phytol 181:777–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02716.x
Zhu F, Qu L, Fan W, Qiao M, Hao H, Wang X (2011) Assessment of heavy metals in some wild edible mushrooms collected from Yunnan Province, China. Environ Monit Assess 179:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1728-5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Hx., Chen, Y., Li, S. et al. Trace elements determination and health risk assessment of Tricholoma matsutake from Yunnan Province, China. J Consum Prot Food Saf 15, 153–162 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-019-01256-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-019-01256-y