Abstract
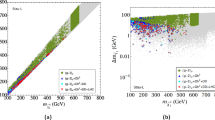
Neutralino dark matter in supersymmetric models is revisited in the presence of flavor violation in the soft supersymmetry breaking sector. We focus on flavor violation in the sleptonic sector and study the implications for the co-annihilation regions. Flavor violation is introduced by a single \( {\widetilde{\mu }_R} - {\widetilde{\tau }_R} \) insertion in the slepton mass matrix. Limits on this insertion from BR(τ → μ + γ) are weak in some regions of the parameter space where cancellations happen within the amplitudes. We look for overlaps in parameter space where both the co-annihilation condition as well as the cancellations within the amplitudes occur. In mSUGRA, such overlap regions are not existent, whereas they are present in models with non-universal Higgs boundary conditions (NUHM). The effect of flavor violation is two fold: (a) it shifts the co-annihilation regions towards lighter neutralino masses (b) the co-annihilation cross sections would be modified with the inclusion of flavor violating diagrams which can contribute significantly. Even if flavor violation is within the presently allowed limits, this is sufficient to modify the thermally averaged cross-sections by about (10-15)% in mSUGRA and (20-30)% in NUHM, depending on the parameter space. In the overlap regions, the flavor violating cross sections become comparable and in some cases even dominant to the flavor conserving ones. A comparative study of the channels is presented for mSUGRA and NUHM cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Jungman, M. Kamionkowski and K. Griest, Supersymmetric dark matter, Phys. Rept. 267 (1996)195 [hep-ph/9506380] [INSPIRE].
H. Goldberg, Constraint on the photino mass from cosmology, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50 (1983) 1419 [Erratum ibid. 103 (2009) 099905] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, J. Hagelin, D.V. Nanopoulos, K.A. Olive and M. Srednicki, Supersymmetric relics from the big bang, Nucl. Phys. B 238 (1984) 453 [INSPIRE].
P.H. Chankowski, J.R. Ellis, K.A. Olive and S. Pokorski, Cosmological fine tuning, supersymmetry and the gauge hierarchy problem, Phys. Lett. B 452 (1999) 28 [hep-ph/9811284] [INSPIRE].
D. Larson et al., Seven-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Power Spectra and WMAP-Derived Parameters, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 192 (2011) 16 [arXiv:1001.4635] [INSPIRE].
N. Arkani-Hamed, A. Delgado and G. Giudice, The Well-tempered neutralino, Nucl. Phys. B 741 (2006)108 [hep-ph/0601041] [INSPIRE].
H. Baer, C. Balázs, A. Belyaev, T. Krupovnickas and X. Tata, Updated reach of the CERN LHC and constraints from relic density, b → sγ and a(μ) in the mSUGRA model, JHEP 06 (2003)054 [hep-ph/0304303] [INSPIRE].
A. Djouadi, M. Drees and J.-L. Kneur, Updated constraints on the minimal supergravity model, JHEP 03 (2006) 033 [hep-ph/0602001] [INSPIRE].
L. Calibbi, Y. Mambrini and S. Vempati, SUSY-GUTs, SUSY-seesaw and the neutralino dark matter, JHEP 09 (2007) 081 [arXiv:0704.3518] [INSPIRE].
U. Chattopadhyay, D. Das, A. Datta and S. Poddar, Non-zero trilinear parameter in the mSUGRA model: Dark matter and collider signals at Tevatron and LHC, Phys. Rev. D 76 (2007)055008 [arXiv:0705.0921] [INSPIRE].
V. Barger, D. Marfatia and A. Mustafayev, Neutrino sector impacts SUSY dark matter, Phys. Lett. B 665 (2008) 242 [arXiv:0804.3601] [INSPIRE].
M. Gomez, S. Lola, P. Naranjo and J. Rodriguez-Quintero, WMAP Dark Matter Constraints on Yukawa Unification with Massive Neutrinos, JHEP 04 (2009) 043 [arXiv:0901.4013] [INSPIRE].
S.K. Kang, A. Kato, T. Morozumi and N. Yokozaki, Threshold corrections to the radiative breaking of electroweak symmetry and neutralino dark matter in supersymmetric seesaw model, Phys. Rev. D 81 (2010) 016011 [arXiv:0909.2484] [INSPIRE].
C. Biggio and L. Calibbi, Phenomenology of SUSY SU(5) with type-I+III seesaw, JHEP 10 (2010)037 [arXiv:1007.3750] [INSPIRE].
J. Esteves, J. Romao, M. Hirsch, F. Staub and W. Porod, Supersymmetric type-III seesaw: lepton flavour violating decays and dark matter, Phys. Rev. D 83 (2011) 013003 [arXiv:1010.6000] [INSPIRE].
J. Ellis, A. Mustafayev and K.A. Olive, Resurrecting No-Scale Supergravity Phenomenology, Eur. Phys. J. C 69 (2010) 219 [arXiv:1004.5399] [INSPIRE].
K. Kadota, K.A. Olive and L. Velasco-Sevilla, A Sneutrino NLSP in the νCMSSM, Phys. Rev. D 79 (2009) 055018 [arXiv:0902.2510] [INSPIRE].
R. Barbieri, L.J. Hall and A. Strumia, Violations of lepton flavor and CP in supersymmetric unified theories, Nucl. Phys. B 445 (1995) 219 [hep-ph/9501334] [INSPIRE].
L. Calibbi, A. Faccia, A. Masiero and S. Vempati, Lepton flavour violation from SUSY-GUTs: Where do we stand for MEG, PRISM/PRIME and a super flavour factory, Phys. Rev. D 74 (2006) 116002 [hep-ph/0605139] [INSPIRE].
E. Dudas, S. Pokorski and C.A. Savoy, Soft scalar masses in supergravity with horizontal U(1)x gauge symmetry, Phys. Lett. B 369 (1996) 255 [hep-ph/9509410] [INSPIRE].
E. Dudas, C. Grojean, S. Pokorski and C.A. Savoy, Abelian flavor symmetries in supersymmetric models, Nucl. Phys. B 481 (1996) 85 [hep-ph/9606383] [INSPIRE].
R. Barbieri, L.J. Hall and A. Romanino, Consequences of a U(2) flavor symmetry, Phys. Lett. B 401 (1997) 47 [hep-ph/9702315] [INSPIRE].
T. Kobayashi, H. Nakano, H. Terao and K. Yoshioka, Flavor violation in supersymmetric theories with gauged flavor symmetries, Prog. Theor. Phys. 110 (2003) 247 [hep-ph/0211347] [INSPIRE].
P.H. Chankowski, K. Kowalska, S. Lavignac and S. Pokorski, Update on fermion mass models with an anomalous horizontal U(1) symmetry, Phys. Rev. D 71 (2005) 055004 [hep-ph/0501071] [INSPIRE].
S. Antusch, S.F. King, M. Malinsky and G.G. Ross, Solving the SUSY Flavour and CP Problems with Non-Abelian Family Symmetry and Supergravity, Phys. Lett. B 670 (2009) 383 [arXiv:0807.5047] [INSPIRE].
C.A. Scrucca, Soft masses in superstring models with anomalous U(1) symmetries, JHEP 12 (2007)092 [arXiv:0710.5105] [INSPIRE].
J. Esteves et al., LHC and lepton flavour violation phenomenology of a left-right extension of the MSSM, JHEP 12 (2010) 077 [arXiv:1011.0348] [INSPIRE].
J. Esteves et al., Dark matter and LHC phenomenology in a left-right supersymmetric model, JHEP 01 (2012) 095 [arXiv:1109.6478] [INSPIRE].
J. Hisano, T. Moroi, K. Tobe, M. Yamaguchi and T. Yanagida, Lepton flavor violation in the supersymmetric standard model with seesaw induced neutrino masses, Phys. Lett. B 357 (1995)579 [hep-ph/9501407] [INSPIRE].
I. Masina and C.A. Savoy, Sleptonarium: Constraints on the CP and flavor pattern of scalar lepton masses, Nucl. Phys. B 661 (2003) 365 [hep-ph/0211283] [INSPIRE].
P. Paradisi, Constraints on SUSY lepton flavor violation by rare processes, JHEP 10 (2005) 006 [hep-ph/0505046] [INSPIRE].
J. Hisano, R. Kitano and M.M. Nojiri, Slepton oscillation at large hadron collider, Phys. Rev. D 65 (2002) 116002 [hep-ph/0202129] [INSPIRE].
J. Hisano, M.M. Nojiri and W. Sreethawong, Discriminating Electroweak-ino Parameter Ordering at the LHC and Its Impact on LFV Studies, JHEP 06 (2009) 044 [arXiv:0812.4496] [INSPIRE].
K. Griest and D. Seckel, Three exceptions in the calculation of relic abundances, Phys. Rev. D 43 (1991) 3191 [INSPIRE].
G. Bélanger et al., Indirect search for dark matter with MicrOMEGAs2.4, Comput. Phys. Commun. 182 (2011) 842 [arXiv:1004.1092] [INSPIRE].
M. Ciuchini et al., Soft SUSY breaking grand unification: Leptons versus quarks on the flavor playground, Nucl. Phys. B 783 (2007) 112 [hep-ph/0702144] [INSPIRE].
Particle Data Group collaboration, K. Nakamura et al., Review of particle physics, J. Phys. G 37 (2010) 075021 [INSPIRE].
https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/AtlasPublic, https://twiki.cern.ch/twiki/bin/view/CMSPublic/PhysicsResultsHIG.
J.R. Ellis, T. Falk, K.A. Olive and Y. Santoso, Exploration of the MSSM with nonuniversal Higgs masses, Nucl. Phys. B 652 (2003) 259 [hep-ph/0210205] [INSPIRE].
H. Baer, A. Mustafayev, S. Profumo, A. Belyaev and X. Tata, Direct, indirect and collider detection of neutralino dark matter in SUSY models with non-universal Higgs masses, JHEP 07 (2005) 065 [hep-ph/0504001] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, K.A. Olive and P. Sandick, Varying the Universality of Supersymmetry-Breaking Contributions to MSSM Higgs Boson Masses, Phys. Rev. D 78 (2008) 075012 [arXiv:0805.2343] [INSPIRE].
J.R. Ellis, S. King and J. Roberts, The Fine-Tuning Price of Neutralino Dark Matter in Models with Non-Universal Higgs Masses, JHEP 04 (2008) 099 [arXiv:0711.2741] [INSPIRE].
L. Roszkowski, R. Ruiz de Austri, R. Trotta, Y.-L.S. Tsai and T.A. Varley, Global fits of the Non-Universal Higgs Model, Phys. Rev. D 83 (2011) 015014 [arXiv:0903.1279] [INSPIRE].
D. Das, A. Goudelis and Y. Mambrini, Exploring SUSY light Higgs boson scenarios via dark matter experiments, JCAP 12 (2010) 018 [arXiv:1007.4812] [INSPIRE].
D. Chowdhury and S.K. Vempati, Flavor Effects in the Neutralino Cross-sections in the Early Universe, in preparation.
I. Hinchliffe and F. Paige, Lepton flavor violation at the CERN LHC, Phys. Rev. D 63 (2001)115006 [hep-ph/0010086] [INSPIRE].
B. Allanach, J. Conlon and C. Lester, Measuring Smuon-Selectron Mass Splitting at the CERN LHC and Patterns of Supersymmetry Breaking, Phys. Rev. D 77 (2008) 076006 [arXiv:0801.3666] [INSPIRE].
A.J. Buras, L. Calibbi and P. Paradisi, Slepton mass-splittings as a signal of LFV at the LHC, JHEP 06 (2010) 042 [arXiv:0912.1309] [INSPIRE].
A. Bartl et al., Test of lepton flavor violation at LHC, Eur. Phys. J. C 46 (2006) 783 [hep-ph/0510074] [INSPIRE].
M.M. Nojiri, Polarization of τ lepton from scalar τ decay as a probe of neutralino mixing, Phys. Rev. D 51 (1995) 6281 [hep-ph/9412374] [INSPIRE].
M.M. Nojiri, K. Fujii and T. Tsukamoto, Confronting the minimal supersymmetric standard model with the study of scalar leptons at future linear e+e− colliders, Phys. Rev. D 54 (1996) 6756 [hep-ph/9606370] [INSPIRE].
M. Guchait and D. Roy, Using τ polarization as a distinctive SUGRA signature at LHC, Phys. Lett. B 541 (2002) 356 [hep-ph/0205015] [INSPIRE].
K. Hamaguchi, Y. Kuno, T. Nakaya and M.M. Nojiri, A Study of late decaying charged particles at future colliders, Phys. Rev. D 70 (2004) 115007 [hep-ph/0409248] [INSPIRE].
R. Godbole, M. Guchait and D. Roy, Using Tau Polarization to probe the Stau Co-annihilation Region of mSUGRA Model at LHC, Phys. Rev. D 79 (2009) 095015 [arXiv:0807.2390] [INSPIRE].
A. Brignole and A. Rossi, Anatomy and phenomenology of mu-tau lepton flavor violation in the MSSM, Nucl. Phys. B 701 (2004) 3 [hep-ph/0404211] [INSPIRE].
D. Chowdhury, R. Garani and S.K. Vempati, SUSEFLAV: Program for supersymmetric mass spectra with seesaw mechanism and rare lepton flavor violating decays, arXiv:1109.3551 [INSPIRE].
D.M. Pierce, J.A. Bagger, K.T. Matchev and R.-j. Zhang, Precision corrections in the minimal supersymmetric standard model, Nucl. Phys. B 491 (1997) 3 [hep-ph/9606211] [INSPIRE].
S. Heinemeyer, W. Hollik and G. Weiglein, The Mass of the lightest MSSM Higgs boson: A Compact analytical expression at the two loop level, Phys. Lett. B 455 (1999) 179 [hep-ph/9903404] [INSPIRE].
A. Pukhov et al., CompHEP: A Package for evaluation of Feynman diagrams and integration over multiparticle phase space, hep-ph/9908288 [INSPIRE].
LEP Working Group for Higgs boson searches, ALEPH, DELPHI, L3, OPAL collaboration, R. Barate et al., Search for the standard model Higgs boson at LEP, Phys. Lett. B 565 (2003) 61 [hep-ex/0306033] [INSPIRE].
J. Frere, D. Jones and S. Raby, Fermion Masses and Induction of the Weak Scale by Supergravity, Nucl. Phys. B 222 (1983) 11 [INSPIRE].
L. Álvarez-Gaumé, J. Polchinski and M.B. Wise, Minimal Low-Energy Supergravity, Nucl. Phys. B 221 (1983) 495 [INSPIRE].
M. Claudson, L.J. Hall and I. Hinchliffe, Low-Energy Supergravity: False Vacua and Vacuous Predictions, Nucl. Phys. B 228 (1983) 501 [INSPIRE].
T. Nihei, L. Roszkowski and R. Ruiz de Austri, Exact cross-sections for the neutralino slepton coannihilation, JHEP 07 (2002) 024 [hep-ph/0206266] [INSPIRE].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
ArXiv ePrint: 1104.4467
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, D., Garani, R. & Vempati, S.K. Flavored co-annihilations. J. High Energ. Phys. 2012, 14 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP06(2012)014
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/JHEP06(2012)014