Abstract
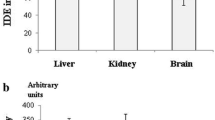
Enzymes that degrade the amyloid β-peptide (Aβ) are important regulators of cerebral Aβ levels. High level of Aβ was found in the brain of diabetic patients and diabetic animals. Aim of the study was to investigate whether activities of Aβ-degrading enzymes neprilysin (NEP), endothelin-converting enzyme 1 (ECE-1) and insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) were impaired in the brain of diabetic rats. Diabetes was induced in rats by ip administration of 65 mg/kg streptozotocin. The temporal cortex and hippocampus were obtained for activity and mRNA level assays of the three enzymes on the 35th day after induction. ECE-1 activity was significantly decreased both in the hippocampus and cortex of diabetic rats, while for IDE significantly lower activity occurred only in the cortex. NEP activity was slightly decreased in both brain regions. The hippocampus of diabetic rats showed significant decrease in mRNA levels of NEP and ECE-1 and moderate increase in IDE mRNA level. The cortex of diabetic rats showed slight decrease in mRNA levels of the three enzymes. The results indicated that the three Aβ-degrading enzymes were damaged to different extents in the brain of diabetic rats, and impairment of ECE-1 and IDE partly contributed to the elevated Aβ(1–40) levels in brain of diabetic rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saido TC. Alzheimer’s disease as proteolytic disorders: anabolism and catabolism of beta-amyloid. Neurobiol Aging 1998, 19 (1 Suppl): S69–75.
Miners JS, Baig S, Palmer J, Palmer LE, Kehoe PG, Love S. Abeta-degrading enzymes in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol 2008, 18: 240–52.
Nalivaeva NN, Fisk LR, Belyaev ND, Turner AJ. Amyloid-degrading enzymes as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2008, 5: 212–24.
Tanzi RE, Moir RD, Wagner SL Clearance of Alzheimer’s Abeta peptide: the many roads to perdition. Neuron 2004, 43: 605–8.
Wang YJ, Zhou HD, Zhou XF. Clearance of amyloid-beta in Alzheimer’s disease: progress, problems and perspectives. Drug Discov Today 2006, 11: 931–8.
Caccamo A, Oddo S, Sugarman MC, Akbari Y, LaFerla FM. Age-and region-dependent alterations in Abeta-degrading enzymes: implications for Abeta-induced disorders. Neurobiol Aging 2005, 26: 645–54.
Cook DG, Leverenz JB, McMillan PJ, et al. Reduced hippocampal insulin-degrading enzyme in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease is associated with the apolipoprotein E-epsilon4 allele. Am J Pathol 2003, 162: 313–9.
Farris W, Mansourian S, Leissring MA, et al. Partial loss-of-function mutations in insulin-degrading enzyme that induce diabetes also impair degradation of amyloid beta-protein. Am J Pathol 2004, 164: 1425–34.
Funalot B, Ouimet T, Claperon A, et al. Endothelin-converting en-zyme-1 is expressed in human cerebral cortex and protects against Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Psychiatry 2004, 9: 1122–8, 1059.
Mouri A, Zou LB, Iwata N, et al. Inhibition of neprilysin by thiorphan (i.c.v.) causes an accumulation of amyloid beta and impairment of learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 2006, 168: 83–91.
Newell AJ, Sue LI, Scott S, et al. Thiorphan-induced neprilysin inhibition raises amyloid beta levels in rabbit cortex and cere-brospinal fluid. Neurosci Lett 2003, 350: 178–80.
Rempel HC, Pulliam L. HIV-1 Tat inhibits neprilysin and elevates amyloid beta. AIDS 2005, 19: 127–35.
Eckman EA, Adams SK, Troendle FJ, et al. Regulation of steady-state beta-amyloid levels in the brain by neprilysin and endothelin-converting enzyme but not angiotensin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 2006, 281: 30471–8.
Iwata N, Tsubuki S, Takaki Y, et al. Metabolic regulation of brain Abeta by neprilysin. Science 2001, 292: 1550–2.
Eckman EA, Watson M, Marlow L, Sambamurti K, Eckman CB. Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptide is increased in mice deficient in endothelin-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem 2003, 278: 2081–4.
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, et al. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003, 100: 4162–7.
Miller BC, Eckman EA, Sambamurti K, et al. Amyloid-beta peptide levels in brain are inversely correlated with insulysin activity levels in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003, 100: 6221–6.
Peila R, Rodriguez BL, Launer LJ. Type 2 diabetes, APOE gene, and the risk for dementia and related pathologies: The Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Diabetes 2002, 51: 1256–62.
Yoneda S, Hara H, Hirata A, Fukushima M, Inomata Y, Tanihara H. Vitreous fluid levels of beta-amyloid(1–42) and tau in patients with retinal diseases. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2005, 49: 106–8.
Li ZG, Zhang W, Sima AA. Alzheimer-like changes in rat models of spontaneous diabetes. Diabetes 2007, 56: 1817–24.
Liu Y, Liu H, Yang J, et al. Increased amyloid beta-peptide (1–40) level in brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neuroscience 2008, 153: 796–802.
Qiu WQ, Folstein MF. Insulin, insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease: review and hypothesis. Neurobiology of Aging 2006, 27: 190–8.
Choi DS, Wang D, Yu GQ, et al. PKCepsilon increases endothelin converting enzyme activity and reduces amyloid plaque pathology in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006, 103: 8215–20.
Zhao Z, Xiang Z, Haroutunian V, Buxbaum JD, Stetka B, Pasinetti GM. Insulin degrading enzyme activity selectively decreases in the hippocampal formation of cases at high risk to develop Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 2007, 28: 824–30.
Fernandez D, Valdivia A, Irazusta J, Ochoa C, Casis L Peptidase activities in human semen. Peptides 2002, 23: 461–8.
Lopez-Ongil S, Saura M, Zaragoza C, et al. Hydrogen peroxide regulation of bovine endothelin-converting enzyme-1. Free Radic Biol Med 2002, 32: 406–13.
Havrankova J, Roth J, Brownstein MJ. Concentrations of insulin and insulin receptors in the brain are independent of peripheral insulin levels. Studies of obese and streptozotocin-treated rodents. J Clin Invest 1979, 64: 636–42.
Ingelsson M, Fukumoto H, Newell KL, et al. Early Abeta accumulation and progressive synaptic loss, gliosis, and tangle formation in AD brain. Neurology 2004, 62: 925–31.
Taguchi K, Yamagata HD, Zhong W, et al. Identification of hippocampus-related candidate genes for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol 2005, 57: 585–8.
Turner AJ, Murphy LJ. Molecular pharmacology of endothelin converting enzymes. Biochem Pharmacol 1996, 51: 91–102.
Yasojima K, Akiyama H, McGeer EG, McGeer PL. Reduced neprilysin in high plaque areas of Alzheimer brain: a possible relationship to deficient degradation of beta-amyloid peptide. Neurosci Lett 2001, 297: 97–100.
Hellstrom-Lindahl E, Ravid R, Nordberg A. Age-dependent decline of neprilysin in Alzheimer’s disease and normal brain: inverse correlation with A beta levels. Neurobiol Aging 2008, 29: 210–21.
Pardossi-Piquard R, Petit A, Kawarai T, et al. Presenilin-dependent transcriptional control of the Abeta-degrading enzyme neprilysin by intracellular domains of betaAPP and APLP. Neuron 2005, 46: 541–54.
Russo R, Borghi R, Markesbery W, Tabaton M, Piccini A. Neprylisin decreases uniformly in Alzheimer’s disease and in normal aging. FEBS Lett 2005, 579: 6027–30.
Wang DS, Lipton RB, Katz MJ, et al. Decreased neprilysin immunoreactivity in Alzheimer disease, but not in pathological aging. J Neuropath Exp Neur 2005, 64: 378–85.
Cordes CM, Bennett RG, Siford GL, Hamel FG. Nitric oxide inhibits insulin-degrading enzyme activity and function through S-nitrosylation. Biochem Pharmacol 2009, 77: 1064–73.
Kim M, Hersh LB, Leissring MA, et al. Decreased catalytic activity of the insulin-degrading enzyme in chromosome 10-linked Alzheimer disease families. J Biol Chem 2007, 282: 7825–32.
Zhao L, Teter B, Morihara T, et al. Insulin-degrading enzyme as a downstream target of insulin receptor signaling cascade: implications for Alzheimer’s disease intervention. J Neurosci 2004, 24: 11120–6.
Hong H, Liu LP, Liao JM, et al. Downregulation of LPR1 at the blood-brain barrier in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56: 1054–9.
Liu LP, Hong H, Liao JM, et al. Upregulation of RAGE at the blood-brain barrier in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Synapse 2009, 63: 636–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF03347055.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Liu, L., Lu, S. et al. Impaired amyloid β-degrading enzymes in brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Endocrinol Invest 34, 26–31 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346691
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346691