Abstract
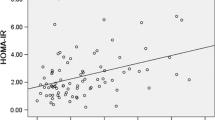
Our aim is to investigate visfatin concentration and its relationship to glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), insulin resistance, lipid parameters, and neonatal birth weight in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). In our study group, there were 47 women with GDM and 31 women with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) between 33–39 weeks of gestation. Plasma visfatin levels were significantly decreased in pregnant women with GDM compared to those with NGT (p=0.001). Homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) levels were higher in the GDM group than in the NGT group (p=0.006). In all subjects, plasma visfatin levels were negatively correlated with HOMA-IR, post-prandial blood glucose, triglycerides, and VLDL cholesterol (p<0.05). We did not observe any statistically significant correlation between the plasma visfatin levels and the selected parameters in the GDM group, but in the NGT group plasma visfatin levels were negatively correlated with HOMA-IR (r=-0.36, p=0.04). There was no correlation between visfatin concentrations and fetal birth weight in either group (p>0.05). By regression analysis, having GDM was found to be the only significant determinant (t=3.5, p=0.001) of visfatin concentration (R=0.39, r2=0.15). We conclude that women with GDM have significantly decreased visfatin concentrations in the third trimester. Future studies are required to establish the exact role of visfatin in the pathogenesis of GDM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pilz S, Mangge H, Obermayer-Pietsch B, März W. Visfatin/pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor: a protein with various suggested functions. J Endocrinol Invest 2007, 30: 138–44.
Sandeep S, Velmurugan K, Deepa R, Mohan V. Serum visfatin in relation to visceral fat, obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. Metabolism 2007, 56: 565–70.
Haider DG, Schaller G, Kapiotis S, Maier C, Luger A, Wolzt M. The release of the adipocytokine visfatin is regulated by glucose and insulin. Diabetologia 2006, 49: 1909–14.
Chen MP, Chung FM, Chang DM, et al. Elevated plasma level of visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91: 295–9.
López-Bermejo A, Chico-Julià B, Fernàndez-Balsells M, et al. Serum visfatin increases with progressive beta-cell deterioration. Diabetes 2006, 55: 2871–5.
Li L, Yang G, Li Q, et al. Changes and relations of circulating visfatin, apelin, and resistin levels in normal, impaired glucose tolerance, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2006, 114: 544–8.
Kautzky-Willer A, Bancher-Todesca D. Endocrine changes in diabetic pregnancy. In: Djelmiš J, Desoye G, Ivanišević: M eds. Diabetology of pregnancy. Frontiers in diabetes. Vol. 17. Basel: Karger 2005, 18–33.
American Diabetes Association. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2004, 27(suppl 1): S88–90.
Buchanan TA, Xiang AH. Gestational diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 2005, 115: 485–91.
Kim C, Newton KM, Knopp RH. Gestational diabetes and the incidence of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Care 2002, 25: 1862–8.
Krzyzanowska K, Krugluger W, Mittermayer F, et al. Increased visfatin concentrations in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin Sci (Lond) 2006, 110: 605–9.
Lewandowski KC, Stojanovic N, Press M, et al. Elevated serum levels of visfatin in gestational diabetes: a comparative study across various degrees of glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 2007, 50: 1033–7.
Chan TF, Chen YL, Lee CH, et al. Decreased plasma visfatin concentrations in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Soc Gynecol Investig 2006, 13: 364–7.
Haider DG, Handisurya A, Storka A, et al. Visfatin response to glucose is reduced in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2007, 30: 1889–91.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28: 412–9.
Haider DG, Schindler K, Schaller G, Prager G, Wolzt M, Ludvik B. Increased plasma visfatin concentrations in morbidly obese subjects are reduced after gastric banding. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006, 91: 1578–81.
Krzyzanowska K, Mittermayer F, Krugluger W, Kopp HP, Schernthaner G. Increase in visfatin after weight loss induced by gastroplastic surgery. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006, 14: 1886–9.
Ognjanovic S, Bryant-Greenwood GD. Pre-B-cell colony-enhancing factor, a novel cytokine of human fetal membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2002, 187: 1051–8.
Malamitsi-Puchner A, Briana DD, Gourgiotis D, Boutsikou M, Baka S, Hassiakos D. Blood visfatin concentrations in normal full-term pregnancies. Acta Paediatr 2007, 96: 526–9.
Malamitsi-Puchner A, Briana DD, Boutsikou M, Kouskouni E, Hassiakos D, Gourgiotis D. Perinatal circulating visfatin levels in intrauterine growth restriction. Pediatrics 2007, 119: e1314–8.
Kuhl C. Etiology and pathogenesis of gestational diabetes. Diabetes Care 1998, 21(Suppl 2): B19–26.
Kinoshita T, Itoh M. Longitudinal variance of fat mass deposition during pregnancy evaluated by ultrasonography: the ratio of visceral fat to subcutaneous fat in the abdomen. Gynecol Obstet Invest 2006, 61: 115–8.
Lim S, Choi SH, Park YJ, et al. Visceral fatness and insulin sensitivity in women with a previous history of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2007, 30: 348–53.
Mastorakos G, Valsamakis G, Papatheodorou DC, et al. The role of adipocytokines in insulin resistance in normal pregnancy: visfatin concentrations in early pregnancy predict insulin sensitivity. Clin Chem 2007, 53: 1477–83.
Fasshauer M, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Tönessen P, Faber R, Stepan H. Differential regulation of visfatin and adiponectin in pregnancies with normal and abnormal placental function. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2007, 66: 434–9.
Wang P, van Greevenbroek MM, Bouwman FG, et al. The circulating PBEF/NAMPT/visfatin level is associated with a beneficial blood lipid profile. Pflugers Arch 2007, 454: 971–6.
López-Bermejo A, Fernandez-Real JM, Garrido E, et al. Maternal soluble tumour necrosis factor receptor type 2 (sTNFR2) and adiponectin are both related to blood pressure during gestation and infant’s birthweight. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2004, 61: 544–52.
Briana DD, Boutsikou M, Gourgiotis D, et al. Role of visfatin, insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin in fetal growth. J Perinat Med 2007, 35: 326–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akturk, M., Altinova, A.E., Mert, I. et al. Visfatin concentration is decreased in women with gestational diabetes mellitus in the third trimester. J Endocrinol Invest 31, 610–613 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345611
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03345611