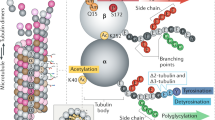
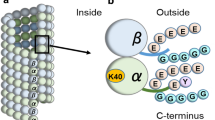
Abstract
Tubulin can be posttranslationally modified at the carboxyl terminus of the α-subunit by the addition or release of a tyrosine residue. These reactions involve two enzymes, tubulin: tyrosine ligase and tubulin carboxypeptidase. The tyrosine incorporation reaction has been described mainly in nervous tissue but it has also been found in a great variety of tissues and different species. Molecular aspects of the reactions catalyzed by these enzymes are at present well known, especially the reaction carried out by the ligase. Several lines of evidence indicate that assembled tubulin is the preferred substrate of the carboxypeptidase, whereas nonassembled tubulin is preferred by the ligase. Apparently this posttranslational modification does not affect the capacity of tubulin to form microtubules but it generates microtubules with different degrees of tyrosination. Variation in the content of the carboxyterminal tyrosine of α-tubulin as well as changes in the activity of the ligase and the carboxypeptidase are manifested during development. Changes in the cellular microtubular network modify the turnover of the carboxyterminal tyrosine of α-tubulin. Different subsets of microtubules with different degrees of tyrosination have been detected in interphase cells and during the mitotic cycle. Data from biochemical, immunological, and genetic studies have been compiled in this review; these are presented, with pertinent comments, with the hope of facilitating the comprehension of this particular aspect of the microtubule field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal H. C., Davis J. M., and Himwich W. A. (1966) Postnatal changes in free amino acid pool of rat brain.J. Neurochem. 13, 607–615.
Arce C. A., Barra H. S., Rodríguez J. A., and Caputto R. (1975a) Tentative identification of the amino acid that binds tyrosine as a single unit into a soluble brain protein.FEBS Lett. 50, 5–7.
Arce C. A., Rodríquez J. A., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1975b) Incorporation ofl-tyrosine,l-Phenylalanine andl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine as single units into rat brain tubulin.Eur. J. Biochem. 59, 145–149.
Arce C. A., Hallak M. E., Rodríguez J. A., Barra H. S., Caputto R. (1978) Capability of tubulin and microtubules to incorporate and to release tyrosine and phenylalanine and the effect of the incorporation of these amino acids on tubulin assembly.J. Neurochem. 31, 205–210.
Arce C. A. and Barra H. S. (1983) Association of tubulinyl-tyrosine carboxypeptidase with microtubules.FEBS Lett. 157, 75–78.
Arce C. A. and Barra H. S. (1985) Release of C-terminal tyrosine from tubulin and microtubules at steady state.Biochem. J. 226, 311–317.
Argaraña C. E., Arce C. A., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1977) In vivo incorporation of [14C]tyrosine into the C-terminal position of the α-subunit of tubulin.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 180, 264–268.
Argaraña C. E., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1978) Release of [14C]tyrosine from tubulinyl[14C]tyrosine by brain extract. Separation of a carboxypeptidase from tubulin:tyrosine ligase.Mol. Cell. Biochem. 19, 17–21.
Argaraña C. E., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1980) Tubulinyl-tyrosine carboxypeptidase from chicken brain: properties and partial purification.J. Neurochem. 34, 114–118.
Argaraña C. E., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1981) Inhibition of tubulinyl-tyrosine carboxypeptidase by brain soluble RNA and proteoglycan.J. Biol. Chem. 256, 827–830.
Barra H. S., Uñates L. E., Sayavedra M., and Caputto R. (1972) Capacities for binding amino acids by tRNAs from rat brain and their changes during development.J. Neurochem. 19, 2289–2297.
Barra H. S., Rodríguez J. A., Arce C. A., and Caputto R. (1973a) A soluble preparation from rat brain that incorporates into its own proteins [14C] arginine by a ribonuclease-sensitive system and [14C] tyrosine by a ribonuclease-insensitive system.J. Neurochem. 20, 97–108.
Barra H. S., Arce C. A., Rodríguez J. A., and Caputto R. (1973b) Incorporation of phenylalanine as single unit into rat brain protein: Reciprocal inhibition by phenylalanine and tyrosine of their respective incorporations.J. Neurochem. 21, 1241–1251.
Barra H. S., Arce C. A., Rodríguez J. A., and Caputto R. (1974) Some common properties of the protein that incorporates tyrosine as a single unit and the microtubule protein.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 60, 1384–1390.
Barra H. S., Arce C. A., and Caputto R. (1980) Total tubulin and its amonoacylated and non-amino-acylated forms during development of rat brain.Eur. J. Biochem. 109, 439–446.
Barra H. S., Argaraña Barra H. S., Argaraña C. E., and Caputto R. (1982) Enzymatic detyrosination of tubulin tyrosinated in rat brain slices and extracts.J. Neurochem. 38, 112–115.
Barra H. S. and Argaraña C. E. (1982) Activation of tubulinyl-tyrosine carboxypeptidase by spermine, spermidine, and putrescine.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 108, 654–657.
Barra H. S. and Arce C. A. (1983) State of tyrosination of soluble synaptosomal tubulin.Comun. Biolog. 1, 13–18.
Barra H. S., Modesti N. M., and Arce C. A. (1987) Tyrosination-detyrosination of thec-terminus of α-tubulin in oocytes and embryos ofBufo arenarum.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. vol. 87B,1, 151–155.
Bayer S. M. and McMurray W. C. (1967) The metabolism of amino acids in developing rat brain.J. Neurochem. 14, 695–706.
Beltramo D. M., Carabelos A. C., Arce C. A., and Barra H. S. (1986) Effect of tubulin-interacting compounds and solution variables on the release ofc-terminal tyrosine from nonassembled tubulin.An. Asoc. Quim. Argent. 74 (6), 633–642.
Beltramo D. M., Arce C. A., and Barra H. S. (1987a) Tyrosination of microtubules and nonassembled tubulin in brain slices.Eur. J. Biochem. 162, 137–141.
Beltramo D. M., Arce C. A., and Barra H. S. (1987b) Tubulin but not microtubules is the substrate for tubulin:tyrosine ligase in mature avian erythrocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 262, 15673–15677.
Bhattacharyya B. and Wolff J. (1975) Membrane bound tubulin in brain and thyroid tissue.J. Biol. Chem. 250, 7639–7646.
Borisy G. G., Olmsted J. B., Marcum J. M., and Allen C. (1974) Microtubule assembly in vitro.Fed. Proc. 33, 167–174.
Bré M. E., Kreis T. E., and Karsenti E. (1987) Control microtubule nucleation and stability in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells: The occurrence of non-centrosomal, stable detyrosinated microtubules.J. Cell Biol. 105, 1283–1296.
Bulinski J. C., Rodríquez J. A., and Borisy G. G. (1981) Test of four possible mechanisms for the temporal control of spindle and cytoplasmic microtubule assembly in HeLa cells.J. Biol. Chem. 255, 1684–1688.
Burgoyne R. D. and Norman K. M. (1986) Alpha-tubulin is not detyrosylated during axonal transport.Brain Res. 381, 113–120.
Cambray-Deakin M. A. and Burgoyne R. D. (1987) Posttranslational modifications of α-tubulin: Acetylated and detyrosinated forms in axons of rat cerebellum.J. Cell Biol. 104, 1569–1574.
Cumming R., Burgoyne R. D., and Lytton N. A. (1984) Immunocytochemical demonstration of α-tubulin modification during axonal maturation in the cerebellar cortex.J. Cell Biol. 98, 347–351.
Deanin G. G. and Gordon M. W. (1976) The distribution of tyrosyltubulin ligase in brain and other tissues.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 71, 676–683.
Deanin G. G., Thompson W. C., and Gordon M. W. (1977) Tyrosyltubulin ligase activity in brain, skeletal muscle and liver of the developing chick.Dev. Biol. 57, 230–233.
Deanin G. G., Preston S. F., and Gordon M. W. (1981) Carboxyl terminal tyrosine metabolism of alpha tubulin and changes in cell shape: Chinese hamster ovary cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 100, 1642–1650.
Deanin G. G., Preston S. F., and Gordon M. W. (1982) Nerve growth factor and the metabolism of the carboxyl terminal tyrosine of alpha tubulin.Develop. Neurosci. 5, 101–107.
Dentler W. L., Granett S., and Rosenbaum J. L. (1975) Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules.J. Cell Biol. 65, 237–241.
Eipper B. A. (1972) Rat brain microtubule protein: purification and determination of covalent bound phosphate and carbohydrate.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69, 2283–2287.
Feit H. and Barondes S. H. (1970) Colchicine-binding activity in particulate fractions of mouse brain.J. Neurochem. 17, 1355–1364.
Forrest G. L. and Klevecz R. R. (1978) Tyrosyltubulin ligase and colchicine binding activity in synchronized Chinese hamster cells.J. Cell Biol. 78, 441–450.
Gabius H. J., Graupner G., and Cramer F. (1983) Activity patterns of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, tRNA methylases, arginyltransferases and tubulin:tyrosine ligase during development and aging ofCaenorhabditis elegans.Eur. J. Biochem. 131, 231–234.
Gard D. L. and Kirschner M. W. (1985) A polymer-dependent increase in phosphorylation of β-tubulin accompanies differentiation of a mouse neuroblastoma cell line.J. Cell Biol. 100, 765–774.
Geuens G., Gundersen G. G., Nuydens R., Cornelissen F., Bulinski J. C., and DeBrabander M. (1986) Ultrastructural colocalization of tyrosinated and detyrosinated α-tubulin in interphase and mitotic cells.J. Cell Biol. 103, 1883–1893.
Gozes I. and Littauer U. Z. (1978) Tubulin microhetterogeneity increases with rat brain maturation.Nature 276, 411–413.
Gundersen G. G., Kalnoski M. H., and Bulinski J. C. (1984) Distinct populations of microtubules: tyrosinated and non tyrosinated alpha tubulin are distributed differentlyin vivo.Cell 38, 779–789.
Gundersen G. G. and Bulinski J. C. (1986a) Distribution of tyrosinated and non-tyrosinated α-tubulin during mitosis.J. Cell Biol. 102, 1118–1126.
Gundersen G. G. and Bulinski J. C. (1986b) Microtubule arrays in differentiated cells contain elevated levels of a posttranslationally modified form of tubulin.Eur. J. Cell Biol. 42, 288–294.
Gundersen G. G., Khawaja S., and Bulinski J. C. (1987) Postpolymerization detyrosination of α-tubulin: a mechanism for subcellular differentiation of microtubules.J. Cell Biol. 105, 251–264.
Hallak M. E., Rodríguez J. A., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1977) Release of ryrosine from tyrosinatedtubulin. Some common factors that affect this process and the assembly of tubulin.FEBS Lett. 73, 147–150.
Jacobs M. (1979) Tubulin and nucleotides,Microtubules, Roberts K. and Hyams J. S., eds., Academic Press, NY, pp. 255–277.
Johnson J. C., Gold G. J., and Clouet D. H. (1973) An improved method for the assay ofDopa.Anal. Biochem. 54, 129–136.
Kilmartin J. V., Wright B., and Milstein C. (1982) Rat monoclonal antitubulin antibodies derived by using a new nonsecreting rat cell line.J. Cell Biol. 93, 576–582.
Kobayashi T. and Flavin M. (1981) Tubulin tyrosylation in invertebrates.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 69B, 387–392.
Kobayashi T. and Matsumoto G. (1982) Cytoplasmic tubulin from squid nerve fully retains C-terminal tyrosine.J. Biochem. 92, 647–652.
Kodowaki T., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Nishida E., Takaku F., Akiyama T., Kathuria S., Akanuma Y., and Kasuga M. (1985) Phosphorylation of tubulin and microtubules associated proteins by the purified insulin receptor kinase.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 4016–4020.
Krämmer G., Singhofer-Wowra M., Seedorf K., Little M., and Schedl T. (1985) A plasmodial α-tubulin cDNA fromPhysarum polycephalum. Nucleotide sequence and comparative analysis.J. Mol. Biol. 183, 633–638.
Kreis, T. E. (1987) Microtubules containing detyrosinated tubulin are less dynamic.EMBO J. 6, 2597–2606.
Kumagai H. and Nishida E. (1980) The interaction between calcium-dependent regulator protein (calmodulin) and microtubule proteins. Further studies on the mechanism of microtubule assembly inhibition by calmodulin.Biomed. Res. 1, 223–229.
Kumar N. and Flavin M. (1981) Preferential action of a brain detyrosinolating carboxypeptidase on polymerized tubulin.J. Biol. Chem. 256, 7678–7680.
Kumar N. and Flavin M. (1982a) Modulation of some parameters of assembly of microtubules in vitro by tyrosination of tubulin.Eur. J. Biochem. 128, 215–222.
Kumar N. and Flavin M. (1982b) A new tubulin-binding protein.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 106, 704–710.
Lee J. C., Field D. J., George H. J., and Head J. (1986) Biochemical and chemical properties of tubulin subspecies,Dynamic Aspects of Microtubule Biology, Soifer D., ed.,Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 466, 111–128.
Lewis S. A., Lee M. G. S., and Cowan N. J. (1985) Five mouse tubulin isotypes and their regulated expression during development.J. Cell Biol. 101, 852–861.
L’Hernault S. W. and Rosenbaum J. L. (1985a) Reversal of the posttranslational modification onChlamydomonas flagellar α-tubulin occurs during flagellar resorption.J. Cell Biol. 100, 457–462.
L’Hernault S. W. and Rosenbaum J. L. (1985b) Clamydomonas α-tubulin is posttranslationally modified by acetylation on the ε-amino group of a lysine.Biochemistry 24, 473–478.
López R. A., Arce C. A., and Barra H. S. (1987) Acción de haparina sobre tubulina carboxipeptidasa. IVJornadas Científicas de la Sociedad de Biología de Córdoba. Carlos Paz (Pvcia. de Córdoba). Argentina.
Lu R. C. and Elzinga M. (1978) The primary structure of tubulin. Sequences of the carboxyl terminus and seven other cyanogen bromide peptides from the α-chain.Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 537, 320–328.
Marcum J. M., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., and Means A. (1978) Control of microtubule assembly disassembly by calcium-dependent tregulator protein.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75, 3771–3775.
Martensen T. M. (1982) Preparation of brain tyrosinotubulin carboxypeptidase.Meth. Cell Biol. 24, 265–269.
Matsumoto G., Murofushi H. Endo S., Kobayashi T., and Sakai H. (1983) Tyrosinated tubulin is necessary for maintenance of membrane excitability in squid giant axon,Structure and Function in Excitable Cells, Chang D. C., Tasaki I., Adelman W. J., Jr., and Leuchtag H. R., eds., Plenum, 471–483.
Modesti N. M., Argaraña C. E., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1984) Inhibition of brain tubulinyl-tyrosine carboxypeptidase by endogenous proteins.J. Neurosci. Research 12, 583–593.
Modesti N. M. and Barra H. S. (1986) The interaction of myelin basic protein with tubulin and the inhibition of tubulin carboxypeptidase activity.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 136, 482–489.
Monteiro M. J. and Cox R. A. (1987) Primary structure of an α-tubulin gene ofPhysarum polycephalum.J. Mol. Biol. 193, 427–438.
Murofushi H. (1980) Purification and characterization of tubulin-tyrosine ligase from porcine brain.J. Biochem. 87, 979–984.
Nath J. and Flavin M. (1979) Tubulin tyrosylationin vivo and changes accompanying differentiation of cultured neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells.J. Biol. Chem. 254, 11505–11510.
Nath J., Flavin M., and Schiffmann E. (1981) Stimulation of tubulin tyrosinolation in rabbit leukocytes evoked by the chemoattractant formyl-methionylleucyl-phenylalanine.J. Cell Biol. 91, 232–239.
Nath J., Flavin M., and Gallin J. I. (1982) Tubulin-tyrosinolation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: studies in normal subjects and in patients with the Chediak-Higashi syndrome.J. Cell Biol. 95, 519–526.
Nath J. and Flavin M. (1984) Tubulin tyrosinolatedin vivo can be different from that tyrosinolatedin vitro.Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 803, 314–322.
Nath J. and Gallin J. I. (1986) Ionic requirements and subcellular localization of tubulin tyrosinolation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.J. Immunol. 136, 628–635.
Pierce T., Hanson R. K., Deanin G. G., Gordon M. W., and Levi A. (1978) Developmental and biochemical sudies on tubulin:tyrosine ligase,Maturation of Neurotransmission, Vernadakis A., Giacobini E., and Filogamo G., eds., Karger, Basil, Switzerland, pp. 142–151.
Piperno G. and Fuller M. T. (1985) Monoclonal antibodies specific for an acetylated form of α-tubulin recognizes the antigen in cilia and flagella from a variety of organisms.J. Cell Biol. 101, 2085–2094.
Ponsting I. H., Little M., Krauhs E., and Kempf T. (1979) Carboxy-terminal amino acid sequence of α-tubulin from porcine brain.Nature 282, 423–424.
Pratt L. F., Okamura S., and Cleveland D. W. (1987) A divergent testis-specific α-tubulin isotype that does not contain a codedc-terminal tyrosine.Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 552–555.
Preston S. F., Deanin G. G., Hanson R. D., and Gordon M. W. (1979) The phylogenetic distribution of tubulin:tyrosine ligase.J. Mol. Evol. 13, 233–244.
Preston S. F., Deanin G. G., Hanson R. D., and Gordon M. W. (1981) Tubulin:tyrosine ligase in oocytes and embryos ofXenopus laevis.J. Develop. Biol. 81, 36–42.
Raybin D. and Flavin M. (1975) An enzyme tyrosylating α-tubulin and its role in microtubule assembly.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 65, 1088–1095.
Raybin D. and Flavin M. (1977a) Enzyme which specifically adds tyrosine to the α-chain of tubulin.Biochemistry 16, 2189–2194.
Raybin D. and Flavin M. (1977b) Modification of tubulin by tyrosylation in cells and extracts and its effect on assemblyin vitro.J. Cell Biol. 73, 492–504.
Roberts K. and Hyams J. (1979)Microtubules. Academic Press, NY, 1–595.
Rodríguez J. A., Arce C. A., Barra H. S., and Caputto R. (1973) Release of tyrosine incorporated as single unit into rat brain protein.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 54, 335–340.
Rodríguez J. A., Barra H. S., Arce C. A., and Hallak M. E., and Caputto R. (1975) The reciprocal exclusion byl-dopa (l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) andl tyrosine of their incorporations as single units into a soluble rat brain protein.Biochem. J. 149, 115–121.
Rodríguez J. A. and Borisy G. G. (1978) Modification of thec-terminus of brain tubulin during development.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 83, 579–586.
Rodríguez J. A. and Borisy G. G. (1979a) Tyrosination state of free tubulin subunits and tubulin disasembled from microtubules of rat brain tissue.Bichem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 89, 893–899.
Rodríguez J. A. and Borisy G. G. (1979b) Experimental phenylketonuria: replacement of carboxyl terminal tyrosine by phenylalanine in infant rat brain tubulin.Science 206, 463–465.
Rodríguez J. A. and Barra H. S. (1983) Tubulin and tubulin-colchicine complex bind to brain microsomal membranein vitro.Mol. Cell Biochem. 56, 49–53.
Schroeder H. C., Wehland J., and Weber K. (1985) Purification of brain tubulin:tyrosine ligase by biochemical and immunological methods.J. Cell Biol. 100 276–281.
Serrano L., De la Torre J., Maccioni R. B., and Avila J. (1984a) Involvement of the carboxyl-terminal domain of tubulin in the regulation of its assembly.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,81, 5989–5993.
Serrano L., Avila J., and Maccioni R. B. (1984b) Controlled proteolysis of tubulin by subtilisin: localization of the site for MAP 2 interaction.Biochemistry,23, 4675–4681.
Sherwin T., Schneider A., Sasse R., Seebeck T., and Gull K. (1987) Distinct localization and cell cycle dependence of COOH terminal tyrosinated α-tubulin in the microtubules ofTrypanosoma brucei brucei.J. Cell Biol. 104, 439–446.
Silflow C. D., Chisholm R. L., Conner T. W., and Ranum L. P. W. (1985) The two alpha-tubulin genes ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii code for slightly different proteins.Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 2389–2398.
Soifer D. (1986) Dynamic Aspects of Microtubule Biology,Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 466.
Solomon F. (1977) Binding sites for calcium on tubulin.Biochemistry 16, 358–363.
Theurkauf W. E., Baun H., Bo J., and Wensink P. C. (1986) Tissue-specific and constitutive α-tubulin genes ofDrosophila melanogaster code for structurally distinct proteins.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 8477–8481.
Thompson W. C. (1977) Posttranslational addition of tyrosine to alpha tubulin in vivo in intact brain and in myogenic cells in culture.FEBS Lett. 80, 9–13.
Thompson W. C., Deanin G. G., and Gordon M. W. (1979) Intact microtubules are required for rapid turnover of carboxyl-terminal tyrosine of α-tubulin in cell cultures.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 1318–1322.
Thompson W. C. (1982) The cyclic tyrosination/detyrosination of alpha tubulin,Methods in Cell Biology, vol. 24, part A, Wilson L., ed., Academic Press, NY, pp. 235–255.
Valenzuela P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W., and Cleveland D. W. (1981) Nucleotide and corresponding amino acid sequences encoded by α and β tubulin mRNAs.Nature 289, 650–655.
Villasante A., Wang D., Dobner P., Dolph P., Lewis S. A., and Cowan W. J. (1986) Six mouse α-tubulin mRNAs encode five distinct tubulin isotypes: testis-specific expression of two sister genes.Mol. Cell. Biol. 6, 2409–2419.
Wandosell F., Serrano L., and Avila J. (1987) Phosphorylation of α-tubulin carboxyl-terminal tyrosine prevents its incorporation into microtubules.J. Biol. Chem. 262, 8268–8273.
Wang D., Villasante A., Lewis S. A., and Cowan W. J. (1986) The mammalian tubulin repertoire, hematopoietic expression of a novel, heterologous β-tubulin isotype.J. Cell Biol. 103, 1903–1910.
Webster D. R., Gundersen G. G., Bulinski J. C., and Borisy G. G. (1987) Assembly and turnover of detyrosinated tubulinin vivo.J. Cell Biol. 105, 265–276.
Wehland J., Willingham M. C., and Sandoval I. V. (1983) A rat monoclonal antibody reacting specifically with the tyrosylated form of α-tubulin. I. Biochemical characterization, effects on microtubule polymerizationin vitro and microtubule polymerization and organizationin vivo.J. Cell Biol. 97, 1467–1475.
Wehland J. and Willingham M. C. (1983) A rat monoclonal antibody reacting specifically with the tyrosylated form of a-tubulin. II. Effects on cell movement, organization of microtubules and intermediate filaments, and arrangements of Golgi elements.J. Cell Biol. 97, 1476–1490.
Wehland J., Schroeder H. C., and Weber K. (1986) Contribution of microtubules to cellular physiology: microinjection of well-characterized monoclonal antibodies into cultured cells,Dynamic Aspects of Microtubule Biology Soifer D., ed.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 466, 609–621.
Wehland J. and Weber K. (1987a) Tubulin-tyrosine ligase has a binding site on β-tubulin: A two-domain structure of the enzyme.J. Cell Biol. 104, 1059–1067.
Wehland J. and Weber K. (1987b) Turnover of the carboxy-terminal tyrosine of α-tubulin and means of reaching elevated levels of detyrosination in living cells.J. Cell Sci. 88, 185–203.
Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S.-Y, and Kirschner, M. W. (1975) A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 72, 1858–1862.
Yanagida M. (1987) Yeast tubulin genes.Microbiol. Sci. 4, 115–118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barra, H.S., Arce, C.A. & Argaraña, C.E. Posttranslational tyrosination/detyrosination of tubulin. Mol Neurobiol 2, 133–153 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935343
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02935343