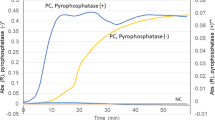
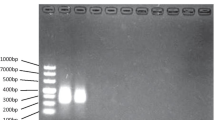
Abstract
The cryptococcal polysaccharide antigen was detected in 10 cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and 23 serum samples from cryptococcal meningitis and intestinal cryptococcosis by the cryptococcal antigen latex agglutination system (CALAS). CALAS titers in CSF and serum samples of cryptococcal meningitis ranged over 8–2048 and 32–2048, respectively, while in cases of intestinal cryptococcosis, serum titers ranged over 8-2048. The isolates of yeastCryptococcus neoformans were determined to be of serotype A or of the A/D pair. The total leukocyte count and biochemical parameters in CSF were significantly increased as indicators of microbial infection. Furthermore, thein vitro change of the teleomorph (sexual state) to the anamorph (asexual state) was also detected and the teleomorph state changedin vivo to the encapsulated anamoph state which is more virulent during infectionin vivo than the yeast-like noncapsulated form. Two primers for internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions of ribosomal DNA were used for molecular detection ofC. neoformans. After PCR amplification, a DNA band of 415 bp, visualized on agarose gel, indicated the presence ofC. neoformans cells in the tested CSF and serum samples. The primer sensitivity was also characterized using purified yeast chromosomal DNA as template; it was about 20 pg or more chromosomal DNA which represents about 10 cells ofC. neoformans. The primers were also specific for ITS regions ofC. neoformans and gave negative results withCandida albicans andE. coli chromosomal DNA templates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fatah A., Abuzeid A.: Primary cutaneous cryptococcosis in Egypt.Internat.J.Dermatol. 14, 606–608 (1976).
Arnaoot H., Mostafa W., Ekladios E.: Disseminated cryptococosis with cutaneous lesions.5th Internat. Conf. Microbiology, AIDS and Emerging Infectious Diseases, Cairo (Egypt) (1996).
Atlas R.M., Parks L.C.:Handbook of Microbiological Media, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton-New York-London-Tokyo 1997.
Casadevall A., Freundlich L., Marsh L., Scharff M.D.: Extensive allelic variation inC. neoformans.J.Clin.Microbiol. 30, 1080–1084 (1992).
Chang H.C., Leaw S.N., Huang A.H., Wu T.L., Chang T.C.: Rapid identification of yeasts in positive blood cultures by a multiplex PCR method.J.Clin.Microbiol. 39, 3466–3471 (2001).
Chen F., Currie B.P., Chen L., Spitzer S., Spitzer E., Casadevall A.: Genetic relatedness ofC. neoformans clinical isolates grouped with the repetitive DNA probe.J.Clin.Microbiol. 33, 2818–2822 (1995).
Currie B., Freundlich L., Casadevall A.: Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis ofCryptococcus neoformans isolates from environmental (pigeon excreta) and clinical sources in New York City.J.Clin.Microbiol. 32, 1188–1192 (1994).
Dorko E., Kmeťová M., Pilipčinec E., Bračoková I., Dorko F., Danko J., Švicky E., Tkáčikova L’.: Rare non-albicans Candida species detected in different clinical diagnoses.Folia Microbiol. 45, 364–368 (2000a).
Dorko E., Kmeťová M., Dorko F., Bračoková I., Danko J., Švický E., Tkáčiková L’.: Prevalence ofCryptococcus neoformans in clinical specimens.Folia Microbiol. 45, 369–374 (2000b).
Dorko E., Kmeťová M., Pilipčinec E., Dorko F., Bračokova I., Marossy A., Škardová I.: Non-albicans Candida species in cancer patients.The Sciences 1, 11–15 (2001a).
Dorko E., Pilipčinec E., Mahel’ M., Virágová S., Bračoková I., Dorko F., Švicky E., Danko J., Holoda E., Ondrašović M., Tkáčikova L’.: Yeast-like microorganisms in eye infections.Folia Microbiol. 46, 147–150 (2001b).
Dorko E., Pilipčinec E., Tkáčiková L’.: Candidal urinary tract infections caused by non-albicans Candida species.Folia Microbiol. 47, 182–184 (2002a).
Dorko E., Pilipčinec E., Tkačiková L’.: Fungal disease of the respiratory tract.Folia Microbiol. 47, 302–304 (2002b).
Dromer F., Gueho E., Ronin O., Dupont B.: Serotyping ofC. neoformans by using a monoclonal antibody specific for capsular polysaccharide.J.Clin.Microbiol. 31, 359–363 (1993).
Dromer F., Varma A., Ronin O., Mathoulin S., Dupont B.: Molecular typing ofC. neoformans serotype D clinical isolates.J.Clin. Microbiol. 32, 2364–2371 (1994).
Ellis D., Pfeiffer T.: The ecology ofCryptococcus neoformans.Eur.J.Epidemiol. 8, 321–325 (1992).
Fessel W.J.: Cryptococcal meningitis after unusual exposure to birds.N.Engl.J.Med. 328, 1354–1355 (1993).
Franzot S., Fries B., Cleare W., Casadevall A.: Genetic relationship betweenC. neoformans var.neoformans strains of serotypes A and D.J.Clin.Microbiol. 36, 2200–2204 (1998).
Fromtling R., Abruzzo G., Ruiz A.: Virulence and antifungal susceptibility of environmental and clinical isolates ofCryptococcus neoformans from Puerto Rico.Mycopathologia 106, 163–166 (1989).
Hosney H.Y., Refai M.K.:Fungi and the Lung: Treatise on Research. Mycology Unit, Chest Department, Ain-Shams University, Cairo (Egypt) 1986.
Ikeda R., Shinoda T., Fukazawa Y., Kaufman L.: Antigenic characterization ofC. neoformans serotypes and its application to serotyping of clinical isolates.J.Clin.Microbiol. 16, 22–29 (1982).
Ikeda R., Sugita T., Shinoda T.: Serological relationship ofCryptococcus spp.: distribution of antigenic factors inCryptococcus and interspecies diversity.J.Clin.Microbiol. 38, 4021–4025 (2000).
Kwon-Chung K., Polacheck K., Popkin T.: Improved diagnostic medium for separation ofC. neoformans var.neoformans (serotype A and D) andC. neoformans var.gattii (serotype B and C).J.Clin.Microbiol. 15, 335–337 (1982).
Kwon-Chung K., Wicker B., Stockman L., Roberts G., Ellis D., Howard D.: Virulence, serotype and molecular characteristics of environmental strains ofCryptococcus neoformans var.gattii.Infect.Immun. 60, 1869–1874 (1992).
Levitz S.M.: The ecology ofCryptococcus neoformans and the epidemiology of cryptococcosis.Rev.Infect.Dis. 13, 1163–1169 (1991).
Magee J.T., Philpot C., Yang J., Hosein I.K.: Pyrolysis typing of isolates from a recurrence of systemic cryptococcosis.J.Med. Microbiol. 40, 165–169 (1994).
Mitchell T., Freedman E., White T., Taylor J.: Unique oligonucleotide primers in PCR for identification ofC. neoformans.J.Clin. Microbiol. 32, 253–255 (1994).
Nakamura Y., Kano R., Watanabe S., Hasegawa A.: Molecular analysis ofCAP59 gene-sequencing from five serotypes ofC. neoformans.J.Clin.Microbiol. 38, 992–995 (2000).
Perfect J.R.: Cryptococcosis.Infect.Dis.Clin.N.Am. 3, 77–102 (1989).
Perfect J.R., Magee B.B., Magee P.T.: Separation of chromosomes ofC. neoformans by pulsed field gel electrophoresis.Infect. Immun. 57, 2624–2627 (1989).
Rappelli P., Are R., Casu G., Fiori P.L., Cappuccinelli P., Aceti A.: Development of a nested PCR for detection ofC. neoformans in cerebrospinal fluid.J.Clin.Microbiol. 36, 3438–3440 (1998).
Ruiz A., Formtling R.A., Bulmer G.S.: Distribution ofCryptococcus neoformans in a natural site.Infect.Immun. 31, 560–563 (1981).
Salkin I., Hurd N.: New medium for differentiation ofCryptococcus neoformans serotype pairs.J.Clin.Microbiol. 15, 169–171 (1982).
Sandhu G.S., Kline B., Stockman L., Roberts G.: Molecular probes for diagnosis of fungal infections.J.Clin.Microbiol. 33, 2913–2919 (1995).
Steenbergen N., Casadevall A.: Prevalence ofCryptococcus neoformans var.neoformans (serotype D) andCryptococcus neoformans var.grubii (serotype A) isolates in New York City.J.Clin.Microbiol. 38, 1974–1976 (2000).
Swinne D., Kayembe K., Niyimi M.: Isolation saprophyticCryptococcus neoformans var.neoformans in Kinshasa, Zaire.Ann.Soc. Belg.Med.Trop. 66, 57–61 (1986).
Tanaka K., Miyazaki T., Maesaki T., Mitsutake K., Kakeya H., Yamamoto Y., Yanagihara K., Hossain M.A., Tashiro T., Kohno S.: Detection ofC. neoformans gene with pulmonary cryptococcosis.J.Clin.Microbiol. 34, 2826–2828 (1996).
Temstet A., Roux P., Poirot J., Ronin O., Dramer F.: Evaluation of a monoclonal antibody-based latex agglutination test for diagnosis of cryptococcosis: comparison with two tests using polyclonal antibodies.J.Clin.Microbiol. 30, 2544–2550 (1992).
Tomšikova A.: Causative agents of nosocomial mycoses.Folia Microbiol. 47, 105–112 (2002).
Varma A., Kwon-Chung K.: DNA probe for strain typing ofCryptococcus neoformans.J.Clin.Microbiol. 30, 2960–2967 (1992).
Varma A., Swinne D., Staib F., Bennett J.E., Kwon-Chung J.E.: Diversity of DNA fingerprints inC. neoformans.J.Clin.Microbiol. 33, 1807–1814 (1995).
Vilgalys R., Hester M.: Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from severalCryptococcus species.J.Bacteriol. 172, 4238–4246 (1990).
Yamamoto Y., Shigeru K., Koga H., Kakeya H., Tomono K., Kaku M., Yamazaki T., Arisawa M., Hara K.: Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of clinically and environmentally isolatedC. neoformans in Nagasaki.J.Clin.Microbiol. 33, 3328–3332 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Salam, H.A. Characterization ofCryptococcus neoformans var.neoformans serotype A and A/D in samples from Egypt. Folia Microbiol 48, 261–268 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02930967
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02930967