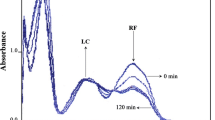
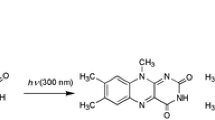
Abstract
Using time-resolved techniques of 337 and 248 nm laser flash photolysis, the photo physical and photochemical processes of riboflavin (RF, vitamin B2) were studied in detail in aqueous solution. The excited triplet state of riboflavin (3RF*) was produced with 337 nm laser, while under 248 nm irradiation, both3RF* and hydrated electron (eaq) formed from photoionization could be detected. Photobiological implications have been inferred on the basis of reactivity of3RF* including energy transfer, electron transfer and hydrogen abstraction. The RF·+ was generated by oxidation of SO4 ·-radical with the aim of confirming the results of photolysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bensasson, R. V., Land, E. J., Truscott, T. G., Flash Photolysis and Pulse Radiolysis in Biology and Medicine, 1st ed., Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1983, 140–148.
Heelis, P. F., The photophysical and photochemical properties of flavins (isoalloxazines), Chem. Soc. Rev., 1982, 11: 15.
Ito, K., Inoue, S., Yamamoto, K. et al., 8-Hydroxyguanosine formation at the 5′ site of 5′-GG-3′ sequences in double-stranded DNA by UV radiation with riboflavin, J. Biol. Chem., 1993, 268: 13221.
Frier, C., Fontecave, M., Mouscadet, J. et al., Flavin-oligonucleotide conjugates: sequence specific photocleavage of DNA, Chem. Comm., 1998: 2457.
Lu, C. Y., Wang, W. F., Lin, W. Z. et al., Generation and photosensitization properties of the oxidized radical of riboflavin: a laser flash photolysis study, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1999, 52: 111.
Jian, L., Wang, W. F., Zheng, Z. D. et al., Reactive intermediates in laser photolysis of guanosine, Res. Chem. Intermed., 1991, 15: 293.
Grodowski, M. S., Veyret, B., Weiss, K., Photochemistry of flavins, II, Photophysical properties of alloxazines and isoalloxazines, Photochem. Photobiol., 1977, 26: 341.
Land, E. J., Swallow, A. J., One-electron reactions in biochemical system as studied by pulse radiolysis, II, Riboflavin, Biochemistry, 1969, 8: 2117.
Lu, C. Y., Han, Z. H., Pan, J. X. et al., Photochemical species of riboflavin (vitamin b2): photobiological implications, J. Radiat. Res. Radiat. Process., 2000, 2: 12.
Kishore, K., Moorthy, P. N., Guha, S. N., Pulse radiolysis study of the one electron oxidation of riboflavin, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 1991, 38: 119.
Cadet, J., Berger, M., Decarroz, C. et al., Photosensitized reactions of nucletic acids, Biochimie, 1986, 68: 813.
Krishna, C. M., Uppuluri, S., Riesz, P. et al., A study of the photodynamic efficencies of some eye lens constituents, Photochem. Photobiol., 1991, 54: 51.
Fujita, S., Steenken, S., Pattern of OH radical reaction addition to uracil and methyl- and carboxyl-substituted uracils, Electron transfer of OH adducts with N, N, N’, N’-tetramethyl-p-phenylene-diamine and tetranitromethane, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1981, 103: 2540.
Lu, C. Y., Wang, W. F., Lin, W. Z. et al., Monophotonic ionization of etoposide in aqueous solution by 248 nm laser light: identification of transient intermediates, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B: Biol., 1999, 49: 61.
Lu, C. Y., Lin, W. Z., Wang, W. F. et al., Riboflavin (VB2)-sensitized photooxidation of 2′-deoxyguanosine-5′ -mono-phosphate (dGMP) in aqueous solution: a transient intermediates study, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2000, 2: 329.
Adams, G. E., Michael, B. D., Pulse radiolysis of benzoquinone and hydroquinone, semiquinone formation by water elimination from trihydroxycyclohexadienyl radicals, Trans. Faraday Soc., 1967, 63: 1171.
Takakubo, M., Faure, J., Riboflavin sensitized photoreduction of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT2+) in degassed aqueous solution, Photochem. Photobiol., 1983, 38: 137.
Heelis, P. F., Parsons, B. J., Phillips, G. O. et al., One-electron oxidation of flavins, a flash photolysis and pulse radiolysis study, J. Phys. Chem., 1986, 90: 6833.
Getoff, N., Solar, S., McCormick, D. B., Photoejection of electrons from flavins in polar media, Science, 1978, 201: 616.
Lu, C. Y., Lin, W. Z., Wang, W. F. et al., Kinetic observation of rapid electron transfer between pyrimidine electron ad-ducts and sensitizers of riboflavin, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and chloranil: a pulse radiolysis study, Radiat. Phys. Chem., 2000, 59: 61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Han, Z., Liu, G. et al. Photophysical and photochemical processes of riboflavin (vitamin B2) by means of the transient absorption spectra in aqueous solution. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 44, 39–48 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879734
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879734