Abstract
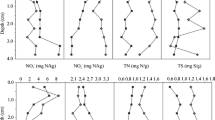
Herein presented are the researches of the past few years related to characteristics of N pollution of waterbodies and N transport from croplands to the waterbodies in Suzhou and Wuxi regions, the center of the Taihu Lake valley. Based on the types of waterbodies, concentrations of inorganic N of different forms, concentrations of, PO 3−4 , δ15NH4 values in river and lake waterbodies, the pollution sources of N in the river, lake and well waters are distinguished, and comparisons are made of trend of variation and amplitude of concentration between years, seasons and N pollutants in waterbodies. The increase in N2O concentration in different waterbodies and high δ15NO- 3 value in different waterbodies are deemed as an evidence of the existence of denitrification in the river, lake and well waters. Moreover, the role of denitrification in the waterbodies plays in stabilizing chronically concentration of N as pollutant in the waterbodies and mitigating N load in the waterbodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma Lishan, Qian Minren, Nitrate-N and nitrite-N pollution of the water environment of the Taihu Lake Valley, Environmental Science, 1987, 8(2): 60–65.
Ma Lishan, Wang Zuqiang, Zhang Shuiming et al., Agricultural non-point source pollution of the Taihu Lake water system in South Jiangsu and its control measures, Environmental Science Transaction, 1997, 17(1): 39–47.
Du Lijuan, Shi Shulian, Enrichment of nitrate-N in water systems and determination of δ15N, Soil, 1994, 26(4): 332–334.
Xu Liying, Xing Guangxi, Isolation and purification of soil fulvic acid solution with XAD series high polymer adsorbent, Soil, 1991, 23(5): 278–280.
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis, Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Publishing House, 1978, 402–411.
Sun Guoqing, Xing Guangxi, Cao Yacheng, Study on variation in 15N natural abundance, I. Characteristics of variation in15N natural abundance of forest soils, Pedosphere, 1991, 1(3): 277–281.
Terry R. E., The effect of flooding on nitrous oxide emission from an organic soil, Soil Science, 1981, 132(3): 228–232.
Kreitler, C. W., Jones, B. C., Natural soil nitrate: The cause of nitrate contamination of groundwater in runnels country, Texas Ground Water, 1975, 13(1): 53–61.
Gormly J. R., Spalding, R. F., Sources and concentrations of nitrate-nitrogen in ground water of the central platte region, Nebraska, Ground Water, 1979, 17(3): 291–301.
William, J., Flipse, Jr. K., Brian, G., Sources of Nitrate in Groundwater in a Sewered Housing Development, Central Long Island, New York, Ground Water, 1984, 22(4): 418–426.
Mariotti, A., Landreau, A., Simon, B.,15N isotope biogeochemistry and natural denitrification process in groundwater: Application to the chalk aquifer of northern France, Geochimi Cosmochimi Acta, 1988, 52: 1869–1878.
Bales, H. K., Saplding, R. F., Aquifer denitrification as interpreted from in sita microcosm experiments, J. Environ. Qual., 1998, 27:174–182.
Cao Yacheng, Sun Guoqing, Xing Guangxi et al., Natural abundance of15N in main N-containing chemical fertilizers of China, Pedosphere, 1991, 1(4): 377–382.
Shearer G-biofertilizer, B., Kohl, D. H., Commoner, B., The precision of determinations of the natural abundance of ni-trogen-15 in soils, fertilizers, and shelf-chemicals, Soil Science, 1974, 118: 308–316.
Goering, J., Marine denitrification, in Denitrification in the Nitrogen Cycle (ed. Golterman, H. L.), New York: Plenum Press, 1985, 191–124.
Jones, J. G., Determination in freshwater, in Denitrification in the Nitrogen Cycle (ed. Golterman, H. L.), New York: Plenum Press, 1985, 225–239.
Trudell, M. R., Gillham, R. W., Cherry, J. A., An in-site study of the occurrence and rate of denitrification in shallow unconfined sand aquifer, J. Hydrology, 1986, 83: 251–268.
Smith, R. L., Howes, B. L., Duff, J. H., Denitrification in nitrate-contaminated groundwater, Occurrence in steep vertical geochemical gradients, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1991, 55: 1815–1825.
Seitzinger, S. P., Denitrification in aquatic sediments, in Denitrification in Soil and Sediments (eds. Revsbech, N. P., Sφrensen, J.), New York and London: Plenum Press, 1990, 301–321.
Andersen, J., Significance of denitrification on the strategy for preserving lakes and coastal areas against eutrophication, in Denitrification in the Nitrogen Cycle (ed. Golterman, H. L.), New York: Plenum Press, 1985, 171–190.
Andersen, T. K., Jensen, M. H., Sprensen, J., Diurnal variation of nitrogen cycling in coastal marine sediments, I. Denitrification, Mar. Biol., 1984, 83: 171–176.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, G., Cao, Y., Shi, S. et al. N pollution sources and denitrification in waterbodies in Taihu Lake region. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 44, 304–314 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879621
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02879621



