Abstract
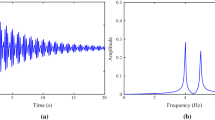
The Hilbert-based time-frequency analysis has promising capacity to reveal the time-variant behaviors of a system. To admit well-behaved Hilbert transforms, component decomposition of signals must be performed beforehand. This was first systematically implemented by the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) in the Hilbert-Huang transform, which can provide a time-frequency representation of the signals. The EMD, however, has limitations in distinguishing different components in narrowband signals commonly found in free-decay vibration signals. In this study, a technique for decomposing components in narrowband signals based on waves’ beating phenomena is proposed to improve the EMD, in which the time scale structure of the signal is unveiled by the Hilbert transform as a result of wave beating, the order of component extraction is reversed from that in the EMD and the end effect is confined. The proposed technique is verified by performing the component decomposition of a simulated signal and a free decay signal actually measured in an instrumented bridge structure. In addition, the adaptability of the technique to time-variant dynamic systems is demonstrated with a simulated time-variant MDOF system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldman M (1994a), “Non-Linear System Vibration Analysis Using Hilbert Transform-I. Free Vibration Analysis Method ‘FREEVIB’,”Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,8(2): 119–127.
Feldman M (1994b), “Non-Linear System Vibration Analysis Using Hilbert Transform-II. Forced Vibration Analysis Method ‘FORCEVIB’,”Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,8(3): 309–318.
Feldman M (1997), “Non-linear Free Vibration Identification via the Hilbert Transform,”Journal of Sound and Vibration,208(3): 475489.
Feng MQ and Kim D (2001), “Long-Term Structural Performance Monitoring of Two Highway Bridges, Phase I : Instrumentation,”Report to the California Department of Transportation RTA-59A0155.
Gröchenig K (2001),Foundations of Time-Frequency Analysis, Birkh user, Boston.
Hahn SL (1996),Hilbert Transform in Signal Processing, Artech House, Boston.
Huang NE, Shen Z and Long SR (1999), “A New View of Nonlinear Water Waves; the Hilbert Spectrum,”Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech., 1999,31: 417–457.
Huang NE, Shen Z, Long SR, Wu MC, Shih HH, Zheng Q, Yen N, Tung CC and Liu HH (1998), “The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Nonlinear and Non-stationary Time Series Analysis,”Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 454, pp. 903–995.
Ibrahim SR (1977), “Random decrement technique for modal identification of structures,”Journal of Spacecraft and Rocket, AIAA,14(11).
Mallat S (1999),A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing, Second Edition, Academic Press, San Diego.
Mathworks (1999a),Spline Toolbox User’s Guide, The Math Works Inc, Natick, MA, USA.
Mathworks (1999b),Using SIMULINK, The Math-Works Inc, Natick, MA, USA.
Pan J, Yan X, Zheng Q, Liu TW, and Klemas VV (2003), “Interpretation of Scatterometer Ocean Surface Wind Vector EOFs over the Northwestern Pacific,”Remote Sensing of Environment,84(1):53–68
Salvino LW (2000), “Empirical Mode Analysis of Structural Response and Damping,”Proceedings SPIE the International Society for Optical Engineering,1 pp. 503–509.
Yang JN and Lei Y (2000), “System Identification of Linear Structures Using Hilbert Transform and Empirical Mode Decomposition,”Proceedings SPIE the International Society for Optical Engineering,1 pp. 213–219.
Zhang RR and Ma S (2000), “HHT Analysis of Earthquake Motion Recordings and its Implications to Simulation of Ground Motion,”International Conference on Monte Carlo Simulation, Monte Carlo, June 18–21, pp. 483–490.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Feng, M.Q. A technique to improve the empirical mode decomposition in the Hilbert-Huang transform. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2, 75–85 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857540
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02857540