Abstract
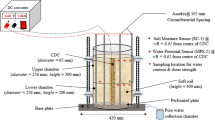
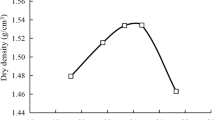
This paper describes settling process of clay particles in suspension and subsequent consolidation behaviour of Speswhite kaoli n clay under the influence of DC electric field. For comparing soil behaviour under electrokinetics with self-weight consolidation, the electrode configuration of closed anode at the base of the sample and open cathode at the top is used. The density measurements of soil are achieved by an accurate and non-destructive X-ray technique, and pore pressures are also measured during the process so that correlations between effective stress and void ratio can be identified. The testing programme has been directed towards understanding the behaviour of soft soil under electrokinetic process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Been, K. (1981). “Non-destructive soil bulk density measurement by X-ray attenuation.”Geotech. Testing J., ASTM, pp. 169–176.
Bowden, R.K. (1988). “Compression behaviour and shear strength characteristics of a natural silty clay sedimented in the laboratory.” D. Phil. Thesis, Oxford University.
Casagrande, L., Wade, N., Wakely, M., and Loughney, R. (1981). “Electro–Osmosis Project, British Columbia, Canada.”Proc. 10th ICSMFE, Stockholm, 3, pp. 607–610.
Chappell, B.A. and Burton, P.L. (1975). “Electro-osmosis applied to unstable embankment.”J. Geotech. Engng. ASCE, Vol. 101, No. 8, pp. 733–739.
Eggestad, Å. and Føyn, T. (1983). “Electro–osmotic improvement of a soft sensitive clay.”Proc. 8th ECSMFE, Helsinki, 2, pp. 597–603.
Fetzer, C. A. (1967). “Electroosmotic stabilization of west branch dam.”J. Soil Mech. Fdns. Div. ASCE, Vol. 93, No. 4, pp. 85–106.
Lee, M. (2000). “An experimental and analytical study of electrokinetic consolidation.” M. Sc. Thesis, Oxford University.
Mitchell, J.K. (1993). “Fundamentals of Soil Behavior.” Wiley Inter. Science.
Perry, W. (1963). “Electro-osmosis dewaters foundation excavation.”Constr. Methods Equip., Vol. 49, No. 9, pp. 116–119.
Wade, M. H. (1976). “Slop stability by electroosmosis.”Proc. 29th Canadian Geotechnical Conference, Vancouver, Vol. 10, pp. 44–66.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.H. Electrically induced settling and consolidation behaviour of soft soil. KSCE J Civ Eng 11, 185–191 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823983
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02823983