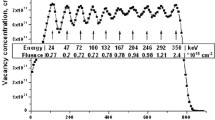
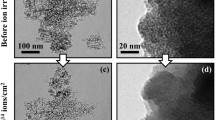
Abstract
We give a brief overview of the results of investigations that gave birth to new trends in radiospectroscopy, physics of interactions of atomic particles with condensed materials, and solid-state physics, especially, physics of superhard materials. The main factors that provided the basis for these trends are as follows.
-
1.
High-energy ion implantation into solids plays a constructive role with respect to the solid matrix. A modified structure composed of matrix atoms and characterized by both short-range and long-range orders different from the initial one is formed as a result of this implantation. Low-dimension systems of a new class, whose properties are described in the present work, were produced in diamonds. A distinguishing feature of this new class of elements is that one-dimensional elements possesing their own spatial ordering of atoms constitute a volume superlattice composed of the same atoms in a three-dimensional crystalline matrix.
-
2.
Radiospectroscopy methods can be used to identify formations with sizes greater than 0.1 μm in one dimension (along with traditional objects with sizes within the nanorange in three dimensions) and study their properties. These objects are characterized by a number of essentially new radiospectroscopic properties: superlinear kinetics of resonance absorption, an additional nonzero phase angle in the recorded absorption signal relative to the hf modulation field in the absence of saturation, (“phase angle”), an anomalous increase in the intensity of absorption with an increase in the modulation frequency of the static field (in the absence of saturation), and a super-Lorentizian shape of the resonance absorption line. These properties provide a basis for radiospectroscopic identification of mobile quasiparticles with nonzero spin (like to solitons) in solids.
-
3.
A system of “channels” with high electroconductivity (in the microwave range) can be produced in dielectric solids, specifically in superhard materials. Individual channels can have cross-sectional sizes of up to sizes of the nanorange. This can serve as a basis for the development of electronic devices with elements having cross-sectional sizes that are significantly smaller than those of elements of traditional microelectronics as small as the sizes of elements of nanotechnology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. P. Erchak, N. M. Penina, V. F. Stelmakh, V. P. Tolstykh, and A. M. Zaitsev, in: Abstracts of Reports to the 7th International Conference on Ion Beam Modification of Materials, Knoxville, USA (1990), p. 313.
V. G. Efimov, D. F. Ertchak, R. B. Gelfand, N. M. Penina, V. F. Stelmakh, V. S. Varichenko, A. G. Ulyashin, and A. M. Zaitsev, in: Abstracts of Reports to the E-MRS-90 Fall Meeting, Strasburg, France (1990), C.-V/P12.
D. P. Erchak, V. G. Efimov, A. M. Zaitsev, V. F. Stelmakh, N. M. Penina, V. S. Varichenko, and V. P. Tolstykh, Nucl. Instrum. Methods,B69, 443–451 (1992).
P. R. Brosious, J. W. Corbett, and J. C. Bourgoin, Physica Status Solidi (a),21, 677 (1974).
P. R. Brosious, Y. H. Lee, J. W. Corbett, and L. J. Cheng, Physica Status Solidi (a),25, 541 (1974).
Y. H. Lee, P. R. Brosious, and J. W. Corbett, Physica Status Solidi, (a)50, 237 (1978).
D. P. Erchak, R. B. Gelfand, N. M. Penina, V. F. Stelmakh, V. P. Tolstykh, A. G. Ulyashin, V. S. Varichenko, and A. M. Zaitsev, Physica Status Solidi (a),121, 63–72 (1990).
V. S. Varichenko, A. Yu. Didyk, V. A. Martinovich, D. P. Ertchak, N. M. Penina A. M. Zaitsev, V. F. Stel’makh, and W. R. Fahrener, Paramagneti Properties of Diamond Modified by High-energy Ion Irradiation [in Russian], Preprint of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences, P14-95-181, Dubna (1995).
D. P. Erchak, V. A. Martinovich, V. S. Varichenko, N. M. Penina, V. G. Efimov, A. M. Zaitsev, S. A. Fedotov, W. R. Fahrner, and V. F. Stelmakh, in Abstracts of Reports to the International Conference on Ion Beam Modification of Materials, Australia (1995).
W. P. Su, J. R. Schrieffer, and A. J. Heeger, Phys. Rew. Lett.,42, 1898 (1979).
W. P. Su, J. R. Schrieffer, and A. J. Heeger, Phys. Rev. B,22, 2099 (1980).
A. G. MacDiarmid and A. J. Heeger, in: Molecular Electronic Devices, New York and Basel (1982), pp. 259–271.
S. Kivelson and D. E. Heim, Phys. Rev. B26, 4278 (1982).
A. J. Heeger, S. Kivelson, and J. R. Schrieffer, Rev. of Mod. Phys.,60, No. 3, 781–850 (1988).
M. J. Rice, S. R. Phillpot, A. R. Bishop, and D. K. Campbell, Phys. Rev. B34, No. 6, 139–149 (1986).
D. P. Erchak, V. G. Efimov, I. I. Azarko, A. V. Denisenko, N. M. Penia, V. F. Stelmakh, V. S. Varichenko, A. M. Zaitsev, A. A. Melnikov, A. G. Ulyashin, N. V. Shlopak, L. L. Bouilov, V. P. Varnin, A. A. Botev, G. A. Sokolina, and I. G. Teremetskaya, Diamond & Related Materials,2, 1164 (1993).
D. Fink, L. T. Chadderton, F. Hosoi, H. Omichi, T. Sasuga, A. Schmoldt, L. Wang, R. Klett, and J. Hillinbround, Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research,B91, 146–150 (1994).
I. I. Azarko, V. Hnatowicz, I. P. Kozlov, E. I. Kozlova, V. B. Odzhaev, and V. N. Popok, Physica Status Solidi (a),146, 23–27 (1994).
V. B. Odzhaev, I. I. Azarko, I. A. Karpovich, I. P. Kozlov, V. N. Popok, D. V. Sviridov, V. Hnatowicz, O. N. Jankovskij, V. Rybka and V. Svorcik, Material Letters,23, 163–166 (1995).
S. Wang and P. R. Buseck, Chem. Phys. Lett.,182, 1 (1991).
J. Kastner and L. Palmetshofer, Fullerene Science & Technology,4, 179–200 (1996).
M. B. Guseva, N. F. Savchenko, and V. G. Babaev, Radiation Effects Letters,87, 215–244 (1986).
V. G. Babaev, M. B. Guseva, and V. V. Khvostov, in: Proceedings of International Conference on Ion Implantation and Ion Beam Equipment, Elenite, Bulgaria (1990), World Scientific, Singapore, New Jersey, London, Hong Kong (1991), pp. 437–457.
C. Spinella, F. Priolo, S. Lombardo, S. Campisano, and E. Rimini, in: “Ion Beam Modification of Materials,” Proceedings of 7th International Conference on IBMM, Knoxville, USA (1990), part I, ed. by S. P. Withrow and D. B. Poker, North-Holland (1991), pp. 363–371.
R. R. Hart, R. P. Vijay, and J. D. Rubio, in: “Ion Beam Modification of Materials,” Proceedings of 7th International Conference on IBMM, Knoxville, USA (1990), part I, ed. by S. P. Withrow and D. B. Poker, North-Holland (1991), pp. 427–430.
A. Golanski, W. H. Christie, M. D. Galloway, J. L. Park, S. Park, S. J. Pennycook, D. B. Poker, J. L. Moore, H. E. Harman, and C. W. White, in: “Ion Beam Modification of Materials”, Proceedings of 7th International Conference on IBMM, Knoxville, USA (1990), part I, ed. by S. P. Withron and D. B. Poker, North-Holland (1991), pp. 444–448.
T. Venkatesan, R. P. Livi, T. C. Banwell, T. A. Tombrello, M. A. Nicolet, R. Hamm, and A. E. Meixner, in: “Ion Beam Processes in Advanced Electronic Materials and Device Technology,” Proceedings of Materials Research Society Symposia,45, MRS, Pittsburgh (1985), p. 189.
M. Dobelli, T. J. Jones, A. Lee, R. P. Livi, and T. A. Tombrello, Brown Bag Preprint Series in Basic and Applied Science, BB-96, 30 (1990).
M. B. Guseva, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Fiz.,50, 459 (1986).
M. B. Guseva, V. G. Babaev, N. N. Nikiforova, and H. F. Savchenko, in: Problems of Atomic Science and Technology [in Russian], Khar’kov (1983), p. 92.
L. S. Palatnik, M. B. Guseva, V. G. Babaev, N. F. Savchenko, and I. I. Fal’ko, Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz.,87, 914 (1984).
Yu. P. Kudryavtsev, S. E. Evsyukov, M. B. Guseva, V. G. Babaev, and V. V. Khvostov, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser., Khim., No. 3, 450–463 (1993).
D. P. Erchak, V. G. Efimov, I. A. Karpovich and V. F. Stelmakh, in: Abstracts of Reports to the Conferences” ICNDST-3” and “Diamond Films-92”, Heidelberg, FRG (1992), No. 8, p. 187.
D. P. Ertchak, V. G. Efimov, V. F. Stelmakh, V. A. Martinovich, A. F. Alexandrov, M. B. Guseva, N. M. Penina, V. S. Varichenko, I. A. Karpovich, A. M. Zaitsev, W. R. Fahrner, and D. Fink, Physica Status Solidi, A Vol. 203, No. 2.
M. Weger, The Bell System Technical Journal, July, 1013 (1960).
C. Boivin, C. Jacolin, and J. Y. Savard, Review Scientific Instruments,44, 191 (1973).
D. P. Ertchak, I. Z. Rutkovskii, V. F. Stel’makh, and G. G. Fedoruk, in: Problems of Atomic Science and Technics [in Russian], Khar’kov (1982), 2(21), pp. 79–81.
G. G. Fedoruk, I. Z. Rutkovskii, D. P. Yerchak, and V. F. Stel’makh, Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz.,80, No. 5, 2004–2009 (1981).
C. Barklie and J. J. Guven, J. of Physics C,14, 3621 (1981).
A. Abragam. The Principles of Nuclear Magnetism, Oxford Univ. Press, London (1961).
D. P. Ertchak, V. P. Strigutskii, V. P. Tolstykh, and Chan Khong N’yung, Zh. Prikl. Spektrosk.,22, 951 (1975).
I. B. Goldberg, H. R. Crowe, P. R. Newman, A. J. Heeger, and A. G. MacDiarmid, J. of Chem. Phys.,70, 1132 (1979).
B. Kirtman, M. Hasan, and D. M. Chipman, J. of Chem. Phys.,95, No. 10, 7698–7681 (1991).
A. L. Chugreev and I. A. Misurkin, Zh. Strukt Khim.,30, 24–28 (1989).
N. Bloembergen, E. M. Purcell, and R. V. Pound, Phys. Rev., 73, 697 (1948).
B. N. Provotorov, Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz.,41, 1582 (1961).
A. F. Burenkov, F. F. Komarov, M. A. Kumakhov, and M. M. Temkin, Spatial Distribution of Energy Released in Cascades of Atomic Collisions [in Russian], Moscow (1985).
R. L. Fleischer, P. B. Price, and R. M. Walker, Nuclear Tracks in Solids, Principles and Application, California Univ. Press, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London (1975).
D. P. Ertchak, M. B. Guseva, A. F. Aleksandrov, H. Alexander, and A. Pilar von Pilchau, Pis’ma Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz.,58, No. 4, 268–271 (1993).
C. Kittel, Phys. Rev.,110, 836 (1958).
M. H. Seavey and P. E. Tannenwald, Phys. Rev. Lett.,1, 168 (1958).
D. P. Ertchak, Yu. P. Kudryavtsev, M. B. Guseva, A. F. Alexandrov, S. E. Evsyukov, V. G. Babaev, L. M. Krechko, Ju. A. Koksharov, A. N. Tichonov, L. A. Blumenfeld, and H. J. Bardeleben, Chem. Phys. Lett. (in press).
D. P. Ertchak, V. S. Varichenko, V. A. Martinovich, N. M. Penina, V. S. Kiranov, V. F. Stelmakh, and A. M. Zaitsev, in: Abstracts of Reports to the Conference “Diamond-1996”, Tours, France (1996).
D. P. Ertchak, V. G. Efimov, S. V. Varichenko, V. F. Stelmakh, A. M. Zaitsev, H. Alexander, and M. Wattenbach, in: Abstracts of Reports to the Conference “Diamond-1996”, Tours, France (1996).
D. P. Ertchak, V. S. Varichenko, A. Yu. Didyk, V. A. Martinovich, V.S. Kiranov, V. F. Stel’makh, and A. M. Zaitsev, Paramagnetic Properties of Diamond Implanted with High-Energy Ions of Nickel, Preprint of the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences, P14-96-232, Dubna (1996).
B. R. Weinberger, E. Ehrenfreund, A. Pron, A. J. Heeger, and A. G. MacDiarmid, J. of Chem. Phys.,72, 4749 (1980).
M. Nechtschein, F. Devreux, R. L. Greene, T. C. Clarke, and G. B. Street, Phys. Rev. Lett.,44, 356 (1980).
K. Holczer, J. P. Boucher, F. Derveux, and M. Nechtschein, Phys. Rev. B,23, 1051 (1981).
R. Kubo and K. Tomita, J. of Physical Society of Japan,9, 888 (1954).
M. J. Hennessy, C. D. McElwee, and P. M. Richards, Phys. Rev. B,7, No. 3, 930 (1973).
F. J. Dyson, Phys. Rev.,98, 349 (1955).
A. M. Zaitsev, S. A. Fedotov, A. A. Melnikov, F. F. Komarov, W. R. Fahrner, V. S. Varichenko, and E. H. te Kaat, Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research,B82, 421 (1993).
E. Dartyge, J. P. Durand, Y. Langevin, and M. Maurette, Phys. Rev. B23, 5213 (1981).
T. A. Tombrello, C. R. Wie, N. Itoh, and T. Nakayama, Phys. Lett. A100, No. 1, 42–44 (1984).
V.S. Varichenko, A. Yu. Didyk, A. M. Zaitsev, A. A. Mel’nikov, V. A. Skuratov, V. F. Stel’makh, V. D. Shestakov, and V. V. Tkachev, Methods of Alloying of Solids [in Russian], Inventor’s Certificate No. 1603858 A (USSR).
A. M. Zaitsev, Materials Science and Engineering,B11, 179–190 (1992).
A. Y. Didyk and V. S. Varichenko, Radiation Measurements,25, 119–124 (1995).
V. S. Varichenko, A. M. Zaitsev, V. F. Stel’makh, V. D. Tkachev, and A. R. Chelyadinskii, High-Pressure Chamber [in Russian], Inventor’s Certificate No. 1391696 A1 (USSR).
R. Katz, Nuclear Track Detection,2, 1 (1978).
A. Hedin, P. Hacansson, P. Sundqvist, and R. E. Johnson, Phys. Rev. B,31, 1780 (1985).
A. A. Davydov and A. I. Kalinichenko, in: Problems of Atomic Science and Technology [in Russian], Khar’kov (1985), 3, No. 36, pp. 27–29.
V. S. Varichenko, A. M. Zaitsev, M. S. Rusetskii, V. F. Stelmakh, K. de Weldige, Th. Fries, K. Wandelt, A. Ju. Didyk, and V. A. Laptev, Diamond and Related Materials,3, 711–714 (1994).
V. S. Vavilov, A. B. Kiv, and O. R. Niyazova, Mechanisms of Formation and Migration of Defects in Semiconductors [in Russian], Moscow (1981).
D. P. Ertchak, N. M. Penina, A. M. Zaitsev, V. S. Varichenko, V. G. Efimov, V. F. Stel’makh, R. B. Gel’fand, and A. G. Ul’yashin, in: Technics of Communication Means, Proceedings of First International Seminar “Diamond Films”, Moscow (1991), pp 160–165.
D. P. Erchak, A. G. Ulyashin, R. B. Gelfand, N. M. Penina, A. M. Zaitsev, V. S. Varichenko, V. G. Efimov, and V. F. Stelmakh, Nucl. Instrum. Methods in Phys. Res.,B69, 271 (1992).
R. B. Heimann, Diamond & Related Materials,3, 1151–1157 (1994).
Z. Ya. Kosakovskaya, L. A. Chernozatonskii, and E. A. Fedorov, Pis’ma Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz.,56, No. 1, 26–30 (1992).
L. A. Chernosatonskii, Z. Ja. Kosakovskaja, E. A. Fedorov, et al., Phys. Lett. A,197, 40 (1995).
I. V. Stankevich and L. A. Chernozatonskii, Pis’ma Zh. Éksp. Teor. Fiz.,63, No. 8, 588–593 (1996).
M. Kosaka, T. W. Ebbesen, H. Hiura, and K. Tanigaki, Chem. Phys. Lett.,233, Nos. 1 and 2, 47–51 (1995).
J. P. Hare, K. Hsu, H. W. Kroto, A. Lappas, W. Maser, A. J. Pierik, K. Prassides, R. Taylor, M. Terrones, and D. R. M. Walton, in: Extended Abstracts of Reports to the 187th Meeting of Electrochemical Society, Reno, Nevada (1995), p. 191.
D. S. Bethune, C.-H. Kiang, W. A. Goddard III, R. Beyers, in: Extended Abstracts of Reports to the 187th Meeting of Electrochemical Sociaty, Reno, Nevada (1995), p. 190.
X. R. Wang, X. W. Lin, M. Jarrold, V. P. Dravid, J. B. Ketterson, and R. P. H. Chang, in: Extended Abstracts of Reports to the 187th Meeting of Electrochemical Society, Reno, Nevada (1995), p. 191.
Additional information
Belarusian State University, 4, F. Skorina Ave., Minsk, 220080, Belarus. Translated from Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 64, No. 4, pp. 421–449, July–August, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ertchak, D.P., Efimov, V.G. & Stelmakh, V.F. EPR spectroscopy of low-dimension structures produced in natural diamonds and synthetic diamond films by ion implantation (review). J Appl Spectrosc 64, 433–460 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02683886
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02683886