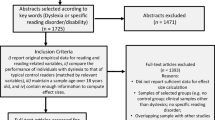
Abstract
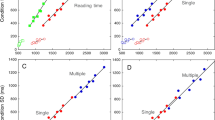
Reading performance of 46 poor readers was compared with that of 20 normal control readers. All subjects were second grade children. In Experiment 1 two matching word lists were presented under two conditions: one version of the test was read in the upright position and the other inverted. In Experiment 2 the eye movements of all subjects were recorded during reading of two meaningful sentences in the normal and inverted position. While the controls were negatively influenced by inversion of the text, the poor readers showed a variety of responses. Overall, the poor readers showed a slight tendency to be better at reading in the inverted position when the text must be scanned from right to left. An individual analysis of the data revealed that in 28.3% of the poor readers inverted reading improved performance at least 15 %, a phenomenon found in none of the controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakker, D. J. 1979. Hemispheric differences and reading strategies. Two dyslexias?Bulletin of the Orton Society 29:84–100.
Bakker, D. J., Moerland, R. and Goekoop-Koefkens, W. 1980. The effect of hemisphere-specific stimulation on reading performance of reading disabled boys: A pilot study. Paper presented at the First Symposium on Child Neuropsychology, Manhasset, New York.
Boder, E. 1973. Developmental dyslexia: a diagnostic approach based on three atypical reading-spelling patterns.Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 15:663–687.
Fried, I. 1979. Cerebral dominance and subtypes of developmental dyslexia.Bulletin of the Orton Society 29:101–112.
Keefe, B. and Swinney, D. 1979. On the relationship of hemisphere specialization and development dyslexia.Cortex 15:471–481.
Keppel, G. 1973.Design and Analysis. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Nachson, I. 1979.Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 10:231–242.
Nachson, I., Shefler, G. E. and Samocha, D. 1977. Directional scanning as a function of stimulus characteristics, reading habits, and directional set.Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 8:83–99.
Orton, S. T. 1937.Reading, Writing and Speech Problems in Children. New York: W.W. Norton and Company.
Pirozzolo, F. J. and Rayner, K. 1978. The neural control of eye movements in aquired and developmental reading disorders.Studies in Neurolinguistics 4:1–27.
Pollatsek, A., Bolozky, S., Well, A. D. and Rayner, K. 1981. Asymmetries in the perceptual span for Israeli readers.Brain and Language 14:174–180.
Rourke, B. P. 1981. Neuropsychological Assessment of Children with Learning Disabilities.In S. B. Filskov and T. J. Boll (eds.),Handbook of Clinical Neuropsychology. New York: Wiley.
Streifler, M. and Hofman, S. 1976. Sinistrad mirror writing and reading after brain concussion in a bisystemic (oriento-occidental) polyglot.Cortex 12:356–364.
Zangwill, O. L. and Blakemore, C. 1972. Dyslexia: Reversal of eye-movements during reading.Neuropsychology 10:371–373.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, S., Parlenvi, P. Patterns of inverted reading and subgroups in dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia 34, 195–203 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663620
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663620