Abstract
Research reported in the literature on the effect of silica fume on bond-slip characterisctics of deformed bars in high performance concrete, indicates that the presence of silica fume as a replacement of part of the cement reduces the bond strength and induces a brittle mode of failure. Recently, Hamad investigated the effect of transverse reinforcement on the bond-slip behavior of tension lap splices in silica fume concrete. He recommended transverse reinforcement in order to increase the bond strength and improve the ductulity of the mode of failure.
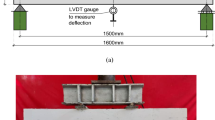
The main objective of the research program presented here was to check whether the earlier recommendation was applicable regardless of casting position, top or bottom. Twelve top cast beam specimens were tested. The beams were designed in a way that the bars would fail in bond, splitting the concrete cover in the splice region, before reaching the yield point. The variables used were the percentage replacement by mass of cement by silica fume and the amount of confinement over the splice region.
The trends of the test results were very similar to the trends of bottom cast speciments, identical except for the casting position, which were tested and analyzed earlier.
Résumé
Les recherches présentées sur l’effet de la fumée de silice sur les caractéristiques de glissement des armatures déformées d’un BHP (béton de hautes performances), indiquent que la présence de la fumée de silice comme remplaçant d’une partie du ciment réduit la force d’adhérence et induit une rupture fragile. Récemment, Hamad a examiné l’effet des armatures transversales sur les caractéristiques de glissement des longueurs de recouvrement en tension des armatures dans un béton de fumée de silice. Il a conseillé d’utiliser des armatures transversales pour augmenter la force d’adhérence et la ductilité du type de rupture.
L’objectif principal du prgramme de recherche ici presenté est de vérifier si cette demière recommandation est applicable quelque soit la position de moulage, en haut ou en bas. Douze spécimens de poutre moulés d’en haut ont été testés. Les poutres ont été étudiées de façon à présenter une rupture en adhérence, fissurant l’enrobage du béton dans la région de recouvrement, avant d’atteindre la limite de résistance. Les variables utilisées étaient le pourcentage en poids de ciment remplacé par de la fumée de silice et la zone de confinement dans la région de recouvrement.
Les tendances des résultats des essais étaient très similaires à celles des spécimens moulés d’en bas, identiques sauf pour la position de moulage. Ces spécimens ont été testés et analysés auparavant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, S., Lee, Y. and Lee, C., ‘Effect of silica fume on the splice strength of deformed bars of high-performance concrete’,ACI Structural Journal 91 (3) (1994) 294–302.
Hamad, B. and Itani M., ‘Bond strength of reinforcement in high performance concrete: Role of silica fume, casting position, and superplasticizer dosage’,ACI Materials Journal 95 (5) (1998) 499–511.
Hamad, B. and Sabbah, S., ‘Bond of reinforcement in eccentric pullout silica fume concrete specimens’,Mater. Struct. 31 (1998) 707–713.
ACI Committee 318, ‘Building Code Requirements for Reinforced Concrete and Commentary (ACI-318-95/ACI-318R-95)’, American Concrete Institute, Detroit, MI, 1995.
Azizinamini, A., Stark, M., Roller, J. J. and Ghosh, S. K., ‘Bond performance of reinforcing bars embedded in high strength concrete’,ACI Structural Journal,90 (5) (1993) 554–561.
Hamad, B. and Machaka M., ‘Effect of transverse reinforcement on bond strength of reinforcing bars in silica fume concrete’,Mater. Struct. 32 (1999) 468–476.
Orangun, O. C., Jirsa, J. O. and Breen, J. E., ‘The strength of anchored bars: A reevaluation of test data on development length and splices’,ACI Journal (March 1977) 114–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamad, B.S., Seferian, Z.S. Role of casting position on bond strength of confined tension lap splices in silica fume concrete. Mat. Struct. 33, 584–593 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480540
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02480540