Abstract
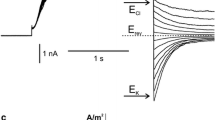
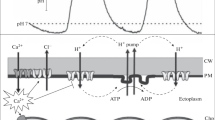
The action of a wide range of drugs effective on Ca2+ channels in animal tissues has been measured on Ca2+ channels open during the action potential of the giant-celled green alga,Chara corallina. Of the organic effectors used, only the 1,4-dihydropyridines were found to inhibit reversibly Ca2+ influx, including, unexpectedly, Bay K 8644 and both isomers of 202–791. Methoxyverapamil (D-600), diltiazem, and the diphenylbutylpiperidines, fluspirilene and pimozide were found not to affect the Ca2+ influx. Conversely, bepridil greatly and irreversibly stimulated Ca2+ influx, and with time, stopped cytoplasmic streaming (which is sensitive to increases in cytoplasmic Ca2+). By apparently altering the cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels with various drugs, it was found that (with the exception of the inorganic cation, La3+) treatments likely to lead to an increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ levels caused an increase in the rate of closure of the K+ channels. Similarly, treatments likely to lead to a decrease in cytoplasmic Ca2+ decreased the rate of K+ channel closure. The main effect of bepridil on the K+ channels was to increase the rate of voltage-dependent channel closure. The same effect was obtained upon increasing the external concentration of Ca2+, but it is likely that this was due to effects on the external face of the K+ channel. Addition of any of the 1,4-dihydropyridines had the opposite effect on the K+ channels, slowing the rate of channel closure. They sometimes also reduced K+ conductance, but this could well be a direct effect on the K+ channel; high concentrations (50 to 100 μM) of bepridil also reduced K+ conductance. No effect of photon irradiance or of abscisic acid could be consistently shown on the K+ channels. These results indicate a control of the gating of K+ channels by cytoplasmic Ca2+, with increased free Ca2+ levels leading to an increased rate of K+-channel closure. As well as inhibiting Ca2+ channels, it is suggested that La3+ acts on a Ca2+-binding site of the K+ channel, mimicking the effect of Ca2+ and increasing the rate of channel closure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APW:
-
artificial pond water
- I/V:
-
current-voltage
- PD:
-
potential difference
References
Andrejauskas, E., Hertel, R., Marmé, D. (1985) Specific binding of the calcium antagonist [3H]verapamil to membrane fractions from plants. J. Biol. Chem.260, 5411–5414
Andrejauskas, E., Hertel, R., Marmé, D. (1986) 3,4,5-triiodobenzoic acid affects [3H]verapamil binding to plant and animal membrane fractions and smooth muscle contraction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.138, 1269–1275
Armstrong, C.M., Lopez-Barneo, J. (1987) External calcium ions are required for potassium channel gating in squid neurons. Science236, 712–714
Armstrong, C.M., Matteson, D.R. (1986) The role of calcium ions in the closing of K channels. J. Gen. Physiol.87, 817–832
Azimov, R.R., Berestovsky, G.N. (1988) Multiple conductance states of a single K+ channel ofNitellopsis cells. [In Russ.] Biofizica33, 153–155
Beilby, M.J. (1984) Current-voltage characteristics of the proton pump atChara plasmalemma I. pH dependence. J. Membr. Biol.81, 113–125
Beilby, M.J. (1985) Potassium channels atChara plasmalemma. J. Exp. Bot.36, 228–239
Beilby, M.J. (1986) Factors controlling the K+ conductance inChara. J. Membr. Biol.93, 187–193
Beilby, M.J., Beilby, B.N. (1983) Potential dependence of the admittance ofChara plasmalemma. J. Membr. Biol.74, 229–245
Beilby, M.J., Blatt, M.R. (1986) Simultaneous measurements of cytoplasmic K+ concentration and the plasma membrane electrical parameters in single membrane samples ofChara corallina. Plant Physiol.82, 417–422
Beilby, M.J., Coster, H.G.L. (1979) The action potential inCharacorallina. III. The Hodgkin-Huxley parameters for the plasmalemma. Aust. J. Plant Physiol.6, 337–353
Berestovsky, G.N., Zherelova, O.M., Kataev, A.A. (1987) Ionic channels in Characean algae cells. Biophysics32, 1011–1027
Bisson, M.A. (1984) Calcium effects on electrogenic pump and passive permeability of the plasma membrane ofChara corallina. J. Membr. Biol.81, 59–67
Brownlee, C., Pulsford, A.L. (1988) Visualization of the calcium gradient inFucus serratus rhizoids: correlation with cell ultrastructure and polarity. J. Cell Sci.91, 249–256
Clarkson, D.T., Brownlee, C., Ayling, S.M. (1988) Cytoplasmic calcium measurements in intact higher plant cells: results from fluorescence ratio imaging of fura-2. J. Cell Sci.91, 71–80
Cognard, C., Traore, F., Potreau, D., Raymond, G. (1986) Bay K 8644 enhances slow inward and outward currents in voltageclamped frog skeletal muscle fibres. Pflugers Arch.407, 677–683
Conrad, P.A., Hepler, P.K. (1988) The effect of 1,4-dihydropyridines on the initiation and development of gametophore buds in the mossFunaria. Plant Physiol.86, 684–687
Coronado, R., Affolter, H. (1986) Characterization of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from purified skeletal muscle transverse tubules. In: Ion channel reconstitution, pp. 483–505, Miller, C., ed. Plenum Press, New York
De Silva, D.L.R., Cox, R.C., Hetherington, A.M., Mansfield, T.A. (1985) Suggested involvement of calcium and calmodulin in the responses of stomata to abscisic acid. New Phytol.101, 555–563
Dolle, R. (1988) Isolation of plasma membrane and binding of the Ca2+ antagonist nimodipine inChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Physiol. Plant.73, 7–14
Dolle, R., Nutsch, W. (1988a) Effects of calcium ions and of calcium channel blockers on galvanotaxis ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bot. Acta101, 18–23
Dolle, R., Nultsch, W. (1988b) Specific binding of the calcium channel blocker [3H] verapamil to membrane fractions ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Arch. Microbiol.149, 451–458
Dolle, R., Nultsch, W. (1988c) Characterization ofd-[3H]cis-diltiazem binding to membrane fractions and specific binding of calcium channel blockers to isolated flagellar membranes ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Cell Sci.90, 457–463
Drakeford, D., Trewavas, A.J. (1986) Binding of verapamil to maize root membranes. In: Molecular and cellular aspects of calcium in plant development, p. 423, Trewavas, A., Marme, D., eds. Plenum Press, New York
Eleno, N., Botana, L., Espinosa, J. (1988) Dual effect of dihydropyridines on45Ca uptake induced by the K+-channel blocker 4-aminopyridine on mast cells. J. Cell Physiol.137, 378–383
Fabiato, A., Fabiato, F. (1979) Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J. Physiol. (Paris)75, 463–505
Findlay, G.P., Hope, A.B. (1964) Ionic relations of cells ofChara australis. VII. The separate electrical characteristics of the plasmalemma and tonoplast. Aust. J. Biol. Sci.17, 62–77
Galizzi, J.P., Fosset, M., Romey, G., Laduron, P., Lazdunski, M. (1986) Neuroleptics of the diphenylbutylpiperidine series are potent calcium channel inhibitors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA83, 7513–7517
Gamboa-Aldeco, R., Huerta, M., Stefani, E. (1988) Effect of Ca2+ channel blockers on K+ contractures in twitch fibres of the frog (Rana pipiens). J. Physiol. (Lond)397, 389–399
Gillery, M.J., Ranjeva, R. (1986) Characterization of calcium channels in carrot cells. In: Molecular and cellular aspects of calcium in plant development, pp. 421–422, Trewavas, A., Marmé, D., eds. Plenum Press, New York
Graziana, A., Fosset, M., Ranjeva, R., Hetherington, A.M., Lazdunski, M. (1988) Ca2+ channel inhibitors that bind to plant cell membranes block Ca2+ entry into protoplasts. Biochemistry27, 764–768
Hagiwara, S., Byerly, L. (1981) Calcium channel. Annu. Rev. Neurosci.4, 69–125
Hamilton, S.L., Perez, M. (1987) Toxins that affect voltage-dependent calcium channels. Biochem. Pharmacol.36, 3325–3329
Harvey, H.J., Venis, M.A., Trewavas, A.J. (1989) Partial purification of a protein from maize (Zea mays) coleoptile membranes binding the Ca2+-channel antagonist verapamil. Biochem. J.257, 95–100
Hepler, P.K. (1985) Calcium restriction prolongs metaphase in dividingTradescantia stamen hair cells. J. Cell Biol.100, 1363–1368
Hering, S., Beech, D.J., Bolton, T.B. (1987) Voltage dependence of the actions of nifedipine and BAY K 8644 on barium currents recorded from single smooth muscle cells from the rabbit ear artery. Biomed. Biochim. Acta46, 657–661
Hess, P., Lansman, J.B., Tsien, R.W. (1984) Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature311, 538–544
Hetherington, A.M., Trewavas, A.J. (1984) Binding of nitrendipine, a calcium channel blocker, to pea shoot membranes. Plant Sci. Lett.35, 109–113
Hodick, D., Sievers, A. (1988) The action potential ofDionaea muscipula Ellis. Planta174, 8–18
Hof, R.P., Ruegg, U.T., Hof, A., Vogel, A. (1985) Stereoselectivity at the calcium channel: opposite action of the enantiomers of a 1,4-dihydropyridine. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol.7, 689–693
Hosey, M.M., Lazdunski, M. (1988) Calcium channels: molecular pharmacology, structure and regulation. J. Membr. Biol.104, 81–105
Hosoi, S., Iino, M., Shimazaki, K. (1988) Outward-rectifying K+ channels in stomatal guard cell protoplasts. Plant Cell Physiol.29, 907–911
Huddart, H., Smith, R.J., Langton, P.D., Hetherington, A.M., Mansfield, T.A. (1986) Is abscisic acid a universally active calcium agonist? New Phytol.104, 161–173
Hurwitz, L. (1986) Pharmacology of calcium channels and smooth muscle tissue. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.26, 225–258
Iijima, T., Sibaoka, T. (1985) Membrane potentials in the excitable cells ofAldrovanda vesiculosa trap-lobes. Plant Cell Physiol.26, 1–13
Kass, R.S., Tsien, R.W. (1975) Multiple effects of calcium antagonists on plateau currents in cardiac purkinje fibers. J. Gen. Physiol.66, 169–192
Kauss, H. (1987) Some aspects of calcium-dependent regulation in plant metabolism. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol.38, 47–72
Keifer, D.W., Spanswick, R.M. (1978) Activity of the electrogenic pump inChara corallina as inferred from measurements of the membrane potential, conductance, and potassium permeability. Plant Physiol.62, 653–661
Kitasato, H. (1973) K permeability ofNitella clavata in the depolarised state. J. Gen. Physiol.62, 535–549
Kloerke, D.A., Petersen, J., Jorgensen, P.L. (1987) Purification of Ca2+-activated K+ channel protein on calmodulin affinity columns after detergent solubilization of luminal membranes from outer renal medulla. FEBS Lett.216, 211–216
Kokubun, S., Reuter, H. (1984) Dihydropyridine derivatives prolong the open state of Ca channels in cultured cardiac cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA81, 4824–4827
Kokubun, S., Prod'hom, B., Becker, C., Porzig, H., Reuter, H. (1986) Studies on Ca channels in intact cardiac cells: voltage-dependent effects and cooperative interactions of dihydropyridine enantiomers. Mol. Pharmacol.30, 571–584
Krawczk, S. (1975) Current-voltage characteristics of algal membranes and calcium ions. Stud. Biophys.49, 157–159
Lee, K.S., Tsien, R.W. (1983) Mechanism of calcium channel blockade by verapamil, D600, diltiazem and nitrendipine in single dialyzed heart cells. Nature302, 790–794
Lehtonen, J. (1984) The significance of Ca2+ in the morphogenesis ofMicrasterias studied with EGTA, verapamil, LaCl3 and calcium ionophore A23187. Plant Sci. Lett.33, 53–60
Lunevsky, V.Z., Zherelova, O.M., Vostrikov, I.Y., Berestovsky, G.N. (1983) Excitation of Characeae cell membranes as a result of activation of calcium and chloride channels. J. Membr. Biol.72, 43–58
Lynch, J., Lauchli, A. (1988) Salinity affects intracellular calcium in corn root protoplasts. Plant Physiol.87, 351–356
McCleskey, E.W., Fox, A.P., Feldman, D., Tsien, R.W. (1986) Different types of calcium channels. J. Exp. Biol.124, 177–190
MacRobbie, E.A.C., (1975) Intracellular kinetics of tracer chloride and bromide inNitella translucens. J. Exp. Bot.26, 489–507
MacRobbie, E.A.C. (1989) Calcium influx at the plasmalemma of isolated guard cells ofCommelina communis. Effects of abscisic acid. Planta178, 231–241
MacRobbie, E.A.C., Banfield, J. (1988) Calcium influx at the plasmalemma ofChara corallina. Planta176, 98–108
Mikkelsen, E. (1985) Comparison of effects of a new dihydropyridine, Bay K 8644, and nifedipine on spontaneous mechanical activity in rat portal vein. Br. J. Pharmacol.85, 383–385
Mikkelsen, E., Kazda, S., Nyborg, N.C.B. (1985) Effects of light and BAY K 8644, a new 1,4-dihydropyridine, on mechanical responses of rat thoracic aorta. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.56, 126–132
Miller, A.J., Sanders, D. (1987) Depletion of cytosolic free calcium induced by photosynthesis. Nature326, 397–400
Miller, C. (ed) (1986) Ion channel reconstitution. Plenum Press, New York
Miller, R.J. (1987) Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science235, 46–52
Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. (1983) Gating kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rat muscle incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. J. Gen. Physiol.82, 511–542
Mras, S., Sperelakis, N. (1981) Bepridil (CERM-1978) blockade of action potentials in cultured rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol.71, 13–19
Nawata, T. (1988) Effects of ions and membrane potential on the elongation of the unicellular green algaClosterium. Plant Cell Physiol.29, 951–959
Nultsch, W., Pfau, J., Dolle, R. (1986) Effects of calcium channel blockers on phototaxis and mobility ofChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Arch Microbiol.144, 393–397
Okazaki, Y., Tazawa, M. (1986) Ca2+ antagonist nifedipine inhibits turgor regulation upon hypotonic treatment in internodal cells ofLamprothmnium. Protoplasma134, 65–66
Okazaki, Y., Tazawa, M. (1987) Dependence of plasmalemma conductance and potential on intracellular free Ca2+ in tonoplast-removed cells of a brackish water CharaceaeLamprothamnium. Plant Cell Physiol.28, 703–708
Owen, J.H., Hetherington, A.M., Wellburn, A.R. (1987) Inhibition of respiration in protoplasts from meristematic tissues by abscisic acid in the presence of calcium ions. J. Exp. Bot.38, 498–505
Rincon, M., Hanson, J.B. (1986) Controls on calcium ion fluxes in injured or shocked corn root cells: importance of proton pumping and cell membrane potential. Physiol. Plant.67, 576–583
Robards, A.W., Robb, M.E. (1974) The entry of ions and molecules into roots: an investigation using electron-opaque tracers. Planta120, 1–12
Roblin, G., Fleurat-Lessard, P., Bonmort, J. (1989) Effects of compounds affecting calcium channels on phytochrome- and blue pigment-mediated pulvinar movements ofCassia fasciculata. Plant Physiol.90, 697–701
Sakmann, B., Neher, E. (eds) (1983) Single-channel recording. Plenum Press, New York
Sanguinetti, M.C., Krafte, D.S., Kass, R.S. (1986) Voltage-dependent modulation of Ca channel current in heart cells by Bay K8644. J. Gen. Physiol.88, 369–392
Saunders, M.J., Hepler, P.K. (1983) Calcium antagonists and calmodulin inhibitors block cytokinin-induced bud formation inFunaria. Dev. Biol.99, 41–49
Schauf, C.L., Wilson, K.J. (1987) Effects of abscisic acid on K+ channels inVicia faba guard cell protoplasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.145, 284–290
Schmidt, J.A., Eckert, R. (1976) Calcium couples flagellar reversal to photostimulation inChlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nature262, 713–715
Schramm, M., Thomas, G., Towart, R., Franckowiak, G. (1983) Novel dihydropyridines with positive ionotropic action through activation of Ca2+ channels. Nature303, 535–537
Schroeder, J.I., Hagiwara, S. (1989) Cytosolic calcium regulates ion channels in the plasma membrane ofVicia faba guard cells. Nature338, 427–430
Shiina, T., Tazawa, M. (1987) Demonstration and characterization of Ca2+ channel in tonoplast-free cells ofNitellopsis obtusa. J. Membr. Biol.96, 263–276
Smith, P.T. (1984) Electrical evidence from perfused and intact cells for voltage-dependent K+ channels in the plasmalemma ofChara australis. Aust. J. Plant Physiol.11, 303–318
Smith, J.R., Kerr, R.J. (1987) Potassium transport across the membranes ofChara. IV. Interactions with other cations. J. Exp. Bot.38, 788–799
Smith, J.R., Walker, N.A., Smith, F.A. (1987) Potassium transport across the membranes ofChara. III. Effects of pH, inhibitors and illumination. J. Exp. Bot.38, 778–787
Smith, G.N., Willmer, C.M. (1988) Effects of calcium and abscisic acid on volume changes of guard cell protoplasts ofCommelina J. Exp. Bot.39, 1529–1539
Sokolik, A.I., Yurin, V.M. (1986) Potassium channels in plasmalemma ofNitella cells at rest. J. Membr. Biol.89, 9–22
Stein, S., Hansen, U.-P. (1988) The involvement of photosynthesis in the action of temperature on plasmalemma transport inNitella. J. Membr. Biol.103, 149–158
Stenz, H.-G., Weisenseel, M.H. (1986) Phytochrome mediates a reduction of the surface charge ofMesotaenium cells. J. Plant Physiol.122, 159–168
Takagi, S., Nagai, R. (1988) Light-affected Ca2+ fluxes in protoplasts fromVallisneria mesophyll cells. Plant Physiol.88, 228–232
Tazawa, M., Shimmen, T. (1987) Cell motility and ionic relations in characean cells as revealed by internal perfusion and cell models. Int. Rev. Cytol.109, 259–312
Tester, M. (1988a) Pharmacology of K+ channels in the plasmalemma of the green alga,Chara corallina. J. Membr. Biol.103, 159–169
Tester, M. (1988b) Blockade of potassium channels in the plasmalemma ofChara corallina by tetraethylammonium, Ba2+, Na+ and Cs+. J. Membr. Biol.105, 77–85
Tester, M. (1988c) Potassium channels in the plasmalemma ofChara corallina are multi-ion pores: voltage-dependent blockade by Cs+ and anomalous permeabilities. J. Membr. Biol.105, 87–94
Tester, M. (1990) Plant ion channels: whole cell and single channel studies. New Phytol.114 (in press)
Thomas, G., Grob, R., Schramm, M., (1984) Calcium channel modulation: ability to inhibit or promote calcium influx resides in the dihydropyridine molecule. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol.6, 1170–1176
Tretyn, A. (1987) Influence of red light and acetylcholine on45Ca2+ uptake by oat coleoptile cells. Cell Biol. Int. Rep.11, 887–896
Triggle, D.J. (1981) Calcium antagonists: basic chemical and pharmacological aspects. In: New perspectives on calcium antagonists, pp. 1–18. Weiss, G.B., ed. American Physiological Society, Bethesda, Md., USA
Tsutsui, I., Ohkawa, T., Nagai, R., Kishimoto, U. (1987) Role of calcium in the excitability and electrogenic pump activity of theChara corallina membrane: I. Effects of La3+, verapamil, EGTA, W-7, and TFP on the action potential. J. Membr. Biol.96, 65–73
Tyerman, S.D., Findlay, G.P., Patterson, G.J., (1986) Inward membrane current inChara inflata: II. Effects of pH, Cl−-channel blockers and NH +4 and significance for the hyperpolarized state. J. Membr. Biol.89, 153–161
Vaughan, M.A., Mulkey, T.J., Goff, C.W. (1984) Effect of calmodulin antagonists and calcium entry blockers on ATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake in maize root microsomes. (Abstr.) Plant Physiol.75, Suppl., 2
Vergara, C., Moczydlowski, E., Latorre, R. (1984) Conduction, blockade and gating in a Ca2+-activated K+ channel incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Biophys. J.45, 73–76
von Willert, D., Kluge, M. (1973) Studies on malate fluxes in leaf slices ofBryophyllum daigremontianum: verapamil-enhanced efflux out of the vacuole. Plant Sci. Lett.1, 391–397
Williamson, R.E., Ashley, C.C. (1982) Free Ca2+ and cytoplasmic streaming in the algaChara. Nature296, 647–651
Yamamoto, D., Suzuki, N. (1987) Blockade of chloride channels by HEPES buffer. Proc. R. Soc. Lond [Biol]230, 93–100
Zherelova, O.M. (1989) Effect of calmodulin inhibitors on functioning of potential-dependent calcium channels of theNitellopsis obtusa plasmalemma. Sov. Plant Physiol.35, 499–504
Zherelova, O.M., Kataev, A.A., Berestovsky, G.N. (1985) The necessity of ATP and Mg2+ for maintenance of the functional activity of the calcium channels of Charophyta algae. Dokl. Biophys.281, 37–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tester, M., MacRobbie, E.A.C. Cytoplasmic calcium affects the gating of potassium channels in the plasma membrane ofChara corallina: a whole-cell study using calcium-channel effectors. Planta 180, 569–581 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411456
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411456