Summary
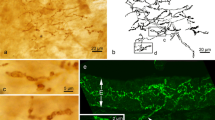
Immunoreactivity of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, neuropeptide Y, and galanin is localized in nerve fibres distributed in the fungiform and filiform papillae of the tongue of the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana. A combination of indirect double immunofluorescence labelling and a multiple dye filter system clearly demonstrated that all substance P fibres in the connective tissue core of the fungiform and filiform papillae, and within the rim of ciliated cells located on the top of the fungiform papillae showed coexistence with calcitonin gene-related peptide. A few fibres in the epithelial discs, which are located in the centre of the top of the fungiform papillae, showed the immunoreactivity of calcitonin gene-related peptide alone. There were no substance P fibres which showed coexistence with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, galanin, and neuropeptide Y. In high magnification images, substance P and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, and substance P and galanin fibres were recognized as two interwined fibres within the same thin nerve bundle. No immunoreactivity of leucine- and methionine-enkephalins can be detected.
These findings suggest that the chemoreceptor function of the bullfrog gustatory organ may be under the control of complicated peptidergic innervation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baecker, B., Yanaihara, N. &Forssmann, W.G. (1983) VIP innervation of the tongue in vertebrates.Anat. Embryol. 167, 173–89.
Dehan, R.S. &Graziadei, P.P.C. (1971) Functional anatomy of frog's taste organs.Experientia 27, 823–6.
Finger, T. E. (1986) Peptide immunohistochemistry demonstrates multiple classes of perigemmal nerve fibers in the circumvallata papilla of the rat.Chem. Senses. 11, 135–44.
Graziadei, P. P. C. &Dehan, R. S. (1971) The ultrastructure of frog's taste organs.Acta Anat. 80, 563–603.
Hirata, K. &Kanaseki, T. (1987) Substance P-like immunoreactive fibers in the frog taste organs.Experientia 43, 386–9.
Ichikawa, H., Nishikawa, S., Wakisaka, S., Matsuo, S., Takano, Y. &Akai, Y. (1988) Coexistence of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-and substance P-like immunoreactivities in the tongue of the guinea pig.Neurosci. Lett. 89, 283–5.
Jaeger, C.B. &Hillman, D.E. (1976) Morphology of gustatory organs. InFrog Neurobiology (edited by R. Llians & W. Precht) pp. 587–606. Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Kawakami, T., Kusakabe, T. &Takenaka, T. (1995) Distribution of immunoreactive neuropeptides in the pancreas of the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana, demonstrated by immunofluorescence.Cell Tissue Res. 280, 307–11.
Kinnman, E. &Aldskogius, H. (1991) The role of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide containing nerve fibers in maintaining fungiform taste buds in the rat after a chronic chorda tympani nerve injury.Exp. Neurol. 113, 85–91.
Kline, L.W., Kaneko, T., Chiu, K.W., Harvey, S. &Pang, P.T.K. (1988) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana: Localization and vascular actions.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 72, 123–9.
Kuramoto, H. (1988) An immunohistochemical study of cellular and nervous elements in the taste organ of the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana.Arch Histol. Cytol. 51, 205–21.
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T., Hori, H., Bandou, Y. &Takenaka, T. (1993a) Immunohistochemical coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in the nerve fibers of the internal gills of bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) larvae.Neurosci. Lett. 158, 59–62.
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T., Tanabe, Y., Fujii, S., Bandou, Y. &Takenaka, T. (1993b) Coexistence of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in the nerve fibers of the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana.Brain Res. 603, 153–6.
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T. &Takenaka, T. (1994a) Coexistence of substance P, neuropeptide Y, VIP, and CGRP in the nerve fibers of the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog,Rana catebeiana: a double-labelling immunofluorescence study in combination with alternate consecutive sections.Cell Tissue Res. 276, 91–7.
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T. &Takenaka, T. (1994b) Localization of immunoreactive neuropeptides in the kidney of the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana, by immunofluorescence.Cell Tissue Res. 278, 41–4.
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T. &Takenaka, T. (1995a) Peptidergic innervation in the amphibian carotid labyrinth.Histol. Histopathol. 10, 185–202.
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T., Ono, M., Hori, H., Sawada, H. &Takenaka, T. (1995b) Distribution of galanin-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the carotid labyrinth of the bullfrog,Rana catesbeiana: comparison with substance P-immunoreactive fibers.Cell Tissue Res. 281, 63–7.
Lundberg, J.M., Hökfelt, T., Anggard, A., Pernow, B. &Emson, P. (1979) Immunohistochemical evidence for substance P immunoreactive nerve fibers in the taste buds of the cat.Acta Physiol. Scand. 107, 389–91.
Lundberg, J.M., Franco-Cereceda Hua, X., Hökfelt, T. &Fischer, A. (1985) Co-existence of substance P and calcitonin generelated peptide-like immunoreactivities in sensory nerves in relation to cardiovascular and bronchoconstrictor effects of capsaicin.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 108, 315–19.
Luts, A., Montavon, P., Lindstrand, K. &Sundler, F. (1990) Peptide-containing nerve fibers in the circumvallate papillae.Regul. Pep. 27, 209–26.
Montavon, P., Lindstrand, K., Luts, A. &Sundler, F. (1991) Peptide-containing nerve fibers in the fungiform papillae of pigs and rats.Regul. Pep. 32, 141–50.
Murray, R.G. (1973) The ultrastructure of taste buds. InThe Ultrastructure of Sensory Organs (edited by J. Friedmann) pp. 1–39. Amsterdam: North-Holland.
Nagy, J.I., Goedert, M., Hunt, A.P. &Bond A. (1982) The nature of substance P-containing nerve fibers in taste papillae of the rat tongue.Neuroscience 7, 3137–51.
Nishimoto, T., Araki, M., Inagaki, S., Shiosaka, S., Shimizu, Y., Yamamoto, K., Senba, E., Sakanaka, M., Takasuki, K., Hara, Y., Takagi, H., Matsuzaki, T. &Tohyama, M. (1982) On the distribution and origins of substance P in the papillae of the rat tongue: an experimental and immunohistochemical study.J. Comp. Neurol. 207, 85–92.
Rapuzzi, G. &Casella, C. (1965) Innervation of the fungiform papillae in the frog tongue.J. Neurophysiol. 28, 154–65.
Rosenfeld, M.G., Mermod, J.-J., Amara, S.G., Swanson, L.W., Sawchenko, P.E., Rivier, J., Vale, W.W. &Evans, R.M. (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing.Nature 304, 129–35.
Stensaas, L.J. (1971) The fine structure of fungiform papillae and epithelium of the tongue of South American toad,Calyptocephalella gayi.Am. J. Anat. 131, 443–62.
Sundler, F., Brodin, E., Ekblad, E., Hakanson, R. &Uddman, R. (1985) Sensory nerve fibers: distribution of substance P, neurokinin A and calcitonin gene-related peptide. InTachykinin Antagonists (edited by R. Håkanson & F. Sundler), pp. 3–14. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Terenghi, G., Polak, J.M., Rodrigo, J., Mulderry, P.K. &Bloom, S.R. (1986) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerves in the tongue, epiglotis and pharynx of the rat: occurrence, distribution and origin.Brain Res. 365, 1–14.
Uga, S. &Hama, K. (1967) Electron microscopic studies on the synaptic region of the taste organ of carps and frogs.J. Electronmicrosc. 16, 269–76.
Yamasaki, H., Kubota, Y., Takagi, H. &Tohyama, M. (1984) Immunoelectronmicroscopic study of the fine structure of substance P-containing fibers in the taste buds of the rat.J. Comp. Neurol. 227, 380–93.
Yamasaki, H., Kubota, Y. &Tohyama, M. (1985) Ontogeny of substance P-containing fibers in the taste buds and surrounding epithelium. I. Light microscopic analysis.Dev. Brain Res. 18, 301–5.
Zamboni, L. &Demartino, C. (1967) Buffered picric acid formaldehyde: a new rapid fixative for electron microscopy.J. Cell Biol. 35, 148A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kusakabe, T., Kawakami, T., Ono, M. et al. Distribution of peptidergic nerve fibres in bullfrog lingual papillae demonstrated by a combination of double immunofluorescence labelling and a multiple dye filter. Histochem J 28, 289–297 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02409017
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02409017