Abstract
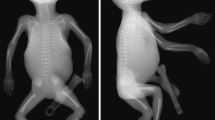
A retrospective study of 400 cases of fetal deaths has been carried out to assess the value of systematic post mortem radiological examination. Apart from general diagnosis purpose, special attention was given to the assessment of bone age and mineralization. The results were correlated with the clinical, U.S., chromosomal and pathological data. Computerized analysis of our information show the following results: (1) The radiological examination was valuable for the final diagnosis in 13.5% of cases. (2) It brings additional information in 34.5% of cases. (3) It had no diagnostic value in 52%. Furthermore, several points deserve attention such as apparition of teeth (21 weeks), calcaneum (24 weeks). Major osteoporosis was always associated with a constitutional bone disease or an infectious process. An excessive length of the upper limbs (12) was seen in 11 cases of anencephaly. We suggest that a radiological examination should not be routinely performed, when the diagnosis is otherwise obvious, but should be considered in the presence of dwarfism, or other limb abnormalities and when the gestational age is uncertain. The films provide essential information especially for further genetic counselling.
Systematic post mortem radiographic examinations are performed in all naturally aborted fetuses over 11 weeks of gestation in our institution. A retrospective study of the last 400 cases was designed in order to assess the value of this examination, with regard to overall diagnosis and assessment of bone maturation and mineralisation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Russell JGB (1981) Radiological assessment of age, retardation and death. In: Barson AJ (ed) Laboratory investigation of fetal disease. Wright, Bristol, pp 3
Cremin BJ, Draper R (1981) The value of radiography in perinatal deaths. Pediatr Radiol 11: 143
Griscom NT, Driscoll SG (1980) Radiography of stillborn fetuses and infants dying at birth. AJR 134: 485
Winter RM, Sandin BM (1984) The radiology of stillbirths and neonatal deaths. Br J Obstet Gynecol 91: 762
Seppänen U (1986) Perinatal postmortem radiography. Acta Radiol [Diagn] (Stockh) 27: 481
Foote GA, Wilson AJ, Stewart JH (1978) Perinatal post-mortem radiography — experience with 2500 cases. Br J Radiol 51: 351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Presented ot the ESPR Meeting in Montreux 1988. Selected for publication by an International Group of the ESPR
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalifa, G., Barbet, J.P., Labbe, F. et al. Value of systematic post mortem radiographic examinations of fetuses - 400 cases. Pediatr Radiol 19, 111–113 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02387898
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02387898