Abstract
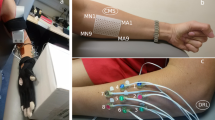
A four-channel impedance measurement system, including a two-channel goniometer, to analyse human arm movement, was constructed. Impedances and joint angles were simultaneously measured for wrist and elbow movements. As the impedance changes resulting from wrist and elbow movements depended heavily on electrode placement, the optimum electrode configurations for those movements were determined by searching for high correlation coefficients, large impedance changes and minimum interferences in ten subjects (age: 29±6 years). The optimum electrode configurations showed very strong relationships between the wrist joint elbow joint angle and upper arm impedance (correlation coefficient=−0.97±0.03). Although the measured impedance changes of the wrist (1.1±1.5Ω) and elbow (−5.0±2.9Ω) varied between individuals, the reproducibilities of wrist and elbow impedance changes of five subjects were 5.8±1.8% and 4.6±1.4% for the optimum electrode pairs, respectively. It is proposed that this optimum electrode configuration would be useful for future studies involving the accurate measurement of arm movements by the impedance method.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, M. J., andCooper, J. M. (1994): ‘Biomechanics of human movement, 2nd edn’ (McGraw-Hill, Boston, 1994), pp. 43–48
Cornish, B. H., andFallah, S. (2001): ‘The application of bioelectrical impedance to monitor muscular activity’. Proc. XII Int. Conf. Elect. Bio-Imp., Oslo, Norway, pp. 637–640
Cornish, B. H., Jacobs, A., Thomas, B. J., andWard, L. C. (1999): ‘Optimizing electrode sites for segmental bioimpedance measurements’,Physiol. Meas.,20, pp. 241–250
Gray, H., Bannister, L. H., Berry, M. M., andWilliams, P. L. (1995): ‘Glay's anatomy: the anatomical basis of medicine & surgery, 38th edn’ (Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1995), pp. 1923–1929
Geddes, L. A., andBaker, L. E. (1989): ‘Principles of applied biomedical instrumentation, 3rd edn’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1989), pp. 539–546
Hall, S. J. (1995): ‘Basic biomechanics, 2nd edn, (Mosby, St. Louis, 1995)
Kim, S. C., Nam, K. C., Kim, D. W., Jeong, Y. K., Kim, K. Y., andKim, K. H. (2001): ‘Human arm motion detection system for robotic teleoperation using electrical bio-impedance method’. Proc. XII Int. Conf. Elect. Bio-Imp., Oslo, Norway, pp. 615–618
Koike, Y., andKawato, M. (1996): ‘Human interface using surface EMG signals’,Trans. Inst. Electron. Inf. Commun. Eng.,2, pp. 363–370
Nakamura, T., Yamamoto, Y., Yamamoto, T., andTsuji, H. (1992): ‘Fundamental characteristics of human limb electrical impedance for biodynamic analysis’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,30, pp. 465–472
Nakamura, T., Kusuhara, T., andYamamoto, Y. (2001): Impedance characteristics and data processing for analysis of human movement’. Proc. XII Int. Conf. Elect. Bio-Imp., Oslo, Norway, pp. 641–644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.C., Nam, K.C., Kim, D.W. et al. Optimum electrode configuration for detection of arm movement using bio-impedance. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 41, 141–145 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344881
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344881