Abstract
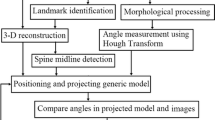
Standard 3D reconstruction of bones using stereoradiography is limited by the number of anatomical landmarks visible in more than one projection. The proposed technique enables the 3D reconstruction of additional landmarks that can be identified in only one of the radiographs. The principle of this method is the deformation of an elastic object that respects stereocorresponding and non-stereo-corresponding observations available in different projections. This technique is based on the principle that any non-stereocorresponding point belongs to a line joining the X-ray source and the projection of the point in one view. The aim is to determine the 3D position of these points on their line of projection when submitted to geometrical and topological constraints. This technique is used to obtain the 3D geometry of 18 cadaveric upper cervical vertebrae. The reconstructed geometry obtained is compared with direct measurements using a magnetic digitiser. The order of precision determined with the point-to-surface distance between the reconstruction obtained with that technique and reference measurements is about 1 mm, depending on the vertebrae studied. Comparison results indicate that the obtained reconstruction is close to the actual vertebral geometry. This method can therefore be proposed to obtain the 3D geometry of vertebrae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Aziz, Y. I., andKarara, H. M. (1971): ‘Direct linear transformation from comparator coordinates into object space coordinates in close range photogrammetry’. Proc. ASP/UI Symp. Close-Range Photogrammetry, Urbana, Illinois
André, B., Dansereau, J., andLabelle, H. (1992): ‘Effect of radiography landmark identification errors on the accuracy of three-dimensional reconstruction of the human spine’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,30, pp. 569–575
André, B., Dansereau, J., andLabelle, H. (1994): ‘Optimized vertical stereo base radiographic setup for the clinical three-dimensional reconstruction of the human spine’,J. Biomech.,27, pp. 1023–1035
Aubin, C. E., Dansereau, J., Parent, F., Labelle, H., andde, Guise, J. A. (1997): ‘Morphometric evaluations of personalised 3D reconstructions and geometric models of the human spine’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,35, pp. 611–618
Battle, X. L., Cunningham, G. S., andHanson, K. M. (1998): ‘Tomographic reconstruction using deformable models’,Investig. Radiol.,33, pp. 348–355
Berthonnaud, E., Remy, D., Moyen, B., Carrillon, Y., andDimnet, J. (1998): ‘Inferior limb stereoradiography: technique and applications in clinical pratice’,J. Biomech.,31, S1, p. 116
Dansereau, J., andStokes, I. A. F. (1988): ‘Measurements of the threedimensional shape of the rib cage’,J. Biomech.,21, pp. 893–901
De Guise J. A., andMartel, Y. (1988): ‘3D biomedical modeling: merging image processing and computer aided design’. IEEE EMBS 10th Int. Conf., New Orleans, pp. 426–427
Delorme, S. (1996): ‘Application du krigeage pour l'habillage et la personnalisation de modèle géométrique de la scoliose’. Mémoire de maîtrise, Ecole Polytechnique de Montréal
Descrimes, J. L., Aubin, C. E., Boudreault, F., Skalli, W., Zeller, R., Dansereau, J., andLavaste, F. (1995): ‘Modelling of facets joints in a global finite element model of the spine: mechanical aspects’ in ‘Three-dimensional analysis of spinal deformities, studies in health technology and informatics’ (IOS Press),15, pp. 107–112
Drerup, B. (1992): ‘3-D acquisition, reconstruction and modelling techniques applied on scoliotic deformities’. Proc. Int. Symp. 3-D Scoliotic Deformities, Montréal, Québec, Canada
Landry, C., de Guise, J. A., Dansereau, J., Labelle, H., Skalli, W., Zeller, R. B., andLavaste, F. (1997): ‘Analyse infographique des déformations tridimensionelles des vertèbres scoliotiques’,Ann. Chir. 51, pp. 868–874
Le, Borgne, P., Skalli, W., Stokes, I. A. F., Maurel, N., Duval, Beaupère, G., andLavaste, F. (1995): ‘Three-dimensional measurement of a scoliotic spine’. inD'Amico, M., Merolli, A., andSantambroglio, G. C., (Eds): ‘Three-dimensional analysis of spinal deformities’ (IOS Press)
Le, Borgne, P., Skalli, W., Dubousset, J., Zeller, R., andLavaste, F. (1998): ‘Finite element model of scoliotic spines: Mechanical personalization’. 4th Int. Symp. Three-Dimensional Scoliotic Deformities, Vermont, USA
Marzan, G. T. (1976): ‘Rational design for close-range photogrammetry’. PhD thesis, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA
Maurel, N. (1993): ‘Modelisation géometrique et mécanique tridimensionnelle par éléments finis du rachis cervical inférieur’. Thèse de doctorat en mécanique, ENSAM, Paris
Niessen, W. J., ter Haar Romeny, B. M., andViergever, M. A. (1998): ‘Geodesic deformable models for medical image analysis’,IEEE Trans. Med. Imag.,17, pp. 634–641
Nyström, L., Söderkvist, I., andWedin P. A. (1994): ‘A note on some identification problems arising in roentgen stereo photogrammetric analysis’,J. Biomech.,27, pp. 1291–1294
Panjabi, M. M., Goel, V., Oxland, T., Takata, K., Duranceau, J., Krag, M., andPrice, M. (1992): ‘Human lumbar vertebrae Quantitative three-dimensional anatomy’,Spine,17, pp. 299–306
Pearcy, M. J. (1985): ‘Stereo radiography of lumbar spine motion’,Act. Orthop. Scand. 212, pp. 1–45
Porrill, J., andIvins, J. (1994): ‘A semiautomatic tool for 3D medical image analysis using active contour models’,Med. Inform.,19, pp. 81–90
Sandor, S., andLeahy, R. (1997): ‘Surface-based labelling of cortical anatomy using deformableatlas’,IEEE Trans. Med. Imag.,16, pp. 41–54
Scoles, P. V., Linton, A. E., Latimer, E., Levy, M. E., andDigiovanni, B. F. (1988): ‘Vertebral body and posterior element morphology: The normal spine in middle life’,Spine,13, pp. 1082–1086
Stokes, I. A. F., andLaible, J. P. (1990): ‘Three-dimensional osseoligamentous model of the thorax representing initiation of scoliosis by asymmetric growth’,J. Biomech.,23, pp. 589–595
Trochu, F. (1993): ‘A contouring program based on dual kriging interpolation’,Eng. Comput.,9, pp. 160–177
Veron, S. (1997): ‘Modélisation géométrique et mécanique tridimensionelle par éléments finis du rachis cervical supérieur’. Thèse de doctorat en mécanique, ENSAM, Paris
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitton, D., Landry, C., Véron, S. et al. 3D reconstruction method from biplanar radiography using non-stereocorresponding points and elastic deformable meshes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 38, 133–139 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344767
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344767