Summary
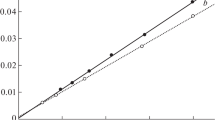
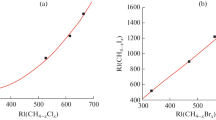
Logarithmic plots of gaschromatographic retention data for different classes of compounds on different pairs of stationary phases have been constructed. A remarkable effect was found. Isomers are spread along parallel lines in a repeated pattern, forming roofing tile series.
The scattering of points around isomer lines is real and is a consequence of detailed structure of molecules.
Alkanes have been divided into groups that have equal numbers of primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary carbon atoms. Alkanes of these groups are lying upon straight lines. Lines of all groups are parallel. Code numbers are in numerical order if attached to the position of the lines.
Zusammenfassung
Es wurden logarithmische Darstellungen gas-chromatographischer Retentionsdaten für verschiedene Substanzklassen auf verschiedenen Paaren stationärer Phasen konstruiert. Es zeigte sich ein bemerkenswerter Effekt. Isomere erscheinen in einer sich wiederholenden Abweichung entlang paralleler Linien, wobei sie eine dachziegelähnliche Serie bilden.
Die Abweichung der Punkte von den Isomerenlinien ist echt und ist auf die Detailstruktur der Moleküle zurückzuführen.
Alkane wurden in Gruppen mit gleicher Anzahl primärer, sekundärer, tertiärer und quartärer Kohlenstoffatome aufgeteilt. Alkane dieser Gruppen liegen auf geraden Linien. Die Geraden aller Gruppen sind parallel. Die Kennziffern, welche die Lage der Linien angeben, liegen in numerischer Reihenfolge.
Sommaire
On a construit des représentations graphiques à partir des logarithmes des grandeurs de rétention, obtenus en chromatographie en phase gazeuse pour différentes classes de substances sur différentes paires de phases stationnaires. Un effet remarquable se manifeste. Les isomères sont placés sur des droites parallèles à peu près équidistantes, de sorte qu'une série a l'apparence d'une rangée de tuiles.
Le décalage des droites représentant les différentes familles isomères est réel et provient de la structure de détail des molécules.
Les alcanes ont été divisé en groupes, les composés d'un même groupe ayant le même nombre d'atomes de carbone primaires, secondaires, tertiaires et quaternaires. Les points représentatifs des alcanes de chacun de ces groupes sont alignés. Les droites correspondant à ces groupes sont parallèles et placées dans le même ordre que les nombres qui caractérisent chaque groupe.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pierotti, G. J., Deal, C. H., Derr, E. L., Porter, P. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,78, 2989 (1956).
Diederen, J. M., Graduation report, Eindhoven University, Netherlands (1965).
Schomburg, G., J. Chromatog.,14 (1964) 157–77.
Ibid.,23 (1966) 18.
McReynolds, W.O., Gas Chromatographic Retention Data, Preston, Evanston, (1966), Illinois.
Cramers, C.A., Thesis, Eindhoven University, Netherlands (1967).
Tourres, D.A., J. Chromatog.,30 (1967) 357–377.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walraven, J.J., Ladon, A.W. & Keulemans, A.I.M. Chromatographic retention and structure roofing tile effect of isomeres and its fine structure. Chromatographia 1, 195–198 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02255479
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02255479