Abstract
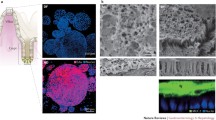
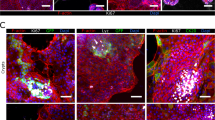
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF) is a protein growth factor whose pleiotropic effects on epithelial cells include the stimulation of motility, mitosis and tubulogenesis. These responses are mediated by the cell surface tyrosine kinase receptor c-met. Because both the cytokine and receptor are found in the gastrointestinal tract, we have studied the effects of HGF/SF on transformed gut epithelial cells which express c-met. Here we describe the response of a new transformed human jejunal epithelioid cell line (HIE-7) to HGF/SF. Morphologically HIE-7 cells are immature. Their epithelial lineage was confirmed by reactivity with the epithelial specific antibodies AE1/AE3, Cam 5.2, Ber-EP4 and anti-EMA and is consistent with their expression of c-met mRNA and protein. In addition, electron microscopic analysis revealed the presence of primitive junctions and rudimentary microvilli, but features of polarization were absent. When grown on reconstituted basement membranes, HIE-7 cells formed closely associated multicellular cord-like structures adjacent to acellular spaces. However, the cells did not mature structurally, form lumen-like structures or express disaccharidase mRNA, even in the presence of recombinant HGF (rHGF). On the other hand, rHGF induced HIE-7 cells to scatter and stimulated their rapid migration in a modified wound assay. To determine whether the motogenic effect caused by rHGF is associated with HIE-7 cell invasiveness across reconstituted basement membranes, a Boyden chamber chemoinvasion assay was performed. rHGF stimulated a 10-fold increase in the number of HIE-7 cells that crossed the basement membrane barrier, while only stimulating a small increase in chemotaxis across a collagen IV matrix, suggesting that the cytokine activates matrix penetration by these cells. rHGF also stimulated the invasion of basement membranes by an undifferentiated rat intestinal cell line (IEC-6) and by two human colon cancer cell lines which are poorly differentiated (DLD-1 and SW 948). In contrast, two moderately well differentiated colon cancer cell lines (Caco-2 and HT-29) did not manifest an invasive response when exposed to rHGF. These results suggest that HGF/SF may play a significant role in the invasive behavior of anaplastic and poorly differentiated gut epithelial tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper CS, 1992, Themet oncogene: from detection by transfection to transmembrane receptor for hepatocyte growth factor.Oncogene,7, 3–7.
Jiang WG, Lloyds D, Puntis MCA, Nakamura T and Hallett MB, 1993, Regulation of spreading and growth of colon cancer cells by hepatocyte growth factor.Clin Exp Metastasis,11, 235–42.
Weidner KM, Hartmann G, Naldini L,et al. 1993, Molecular characteristics of HGF-SF and its role in cell motility and invasion. In: Goldberg ID and Rosen EM, eds.Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Scatter Factor (HGF-SF) and the c-met Receptor. Basel: Birkhauser, 311–27.
Stoker M and Gherardi E, 1991, Regulation of cell movement: the motogenic cytokines.Biochim Biophys Acta,1072, 81–102.
Bhargawa M, Joseph A, Knesel J,et al. 1990, Scatter factor and hepatocyte growth factor: activities, properties and mechanism.Cell Growth Differentiation,3, 11–20.
Tsarfaty I, Reseau JH, Rulong S,et al. 1992, Themet proto-oncogene receptor and lumen formation.Science,257, 1258.
Quaroni A, Wands J, Trelstad RL and Isselbacher KJ, 1979, Epithelioid cell cultures from rat small intestine.J Cell Biol,80, 248–65.
Montesano R, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T and Orci L, 1991, Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor.Cell,67, 901–8.
Hsu S-M, Raine L and Fanger H, 1981, A comparative study of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase method and an avidin-biotin complex method for studying polypeptide hormones with radioimmunoassay antibodies.Am J Clin Pathol,75, 734–8.
Quaroni A and Isselbacher KJ, 1985, Study of intestinal cell differentiation with monoclonal antibodies to intestinal cell surface components.Dev Biol,111, 267–79.
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N, 1987, Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction.Analyt Biochem,162, 156–9.
Mantei N, Villa M, Enzler T,et al. 1988, Complete primary structure of human and rabbit lactasephlorizin hydrolase: implications for biosynthesis, membrane anchoring and evolution of the enzyme.EMBO J,7, 2705–13.
Gussow D, Rein R, Ginjaar I,et al. 1987, The humanΒ 2-microglobulin gene. Primary structure and definition of the transcriptional unit.J Immunol,139, 3132–8.
Park M, Dean M, Kaul K, Brau MJ and Gonda MA, 1987, Sequence of MET protooncogene cDNA has features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth-factor receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,84, 6379–83.
Boll W, Wagner P and Mantei N, 1991, Structure of the chromosomal gene and cDNAs coding for lactase-phlorizin hydrolase in humans with adult-type hypolactasia or persistence of lactase.Am J Hum Genet,48, 889–902.
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M,et al. 1989, Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor.Nature,342, 440–3.
Kleinman HK, McGarvey ML, Hassell JR,et al. 1986, Basement membrane complexes with biological activity.Biochemistry,25, 312–18.
Thompson EW, Paik S, Brunner N,et al. 1992, Association of increased basement membrane invasiveness with absence of estrogen receptor and expression of vimentin in human breast cancer cell lines.J Cell Physiol,150, 534–4.
Azumi N and Battifora H, 1987, The distribution of vimentin and keratin in epithelial and nonepithelial neoplasms.Am J Clin Pathol,88, 286–96.
Olson AD, Pysher T and Bienkowski RS, 1991, Organization of intestinal epithelial cells into multicellular structures requires laminin and functional actin microfilaments.Exp Cell Res,192, 543–9.
Pinto M, Robine-Leon S, Appay M-D,et al. 1983, Enterocyte-like differentiation and polarization of the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture.Biol Cell,47, 323–30.
Beaulieu J-F and Quaroni A, 1991, Clonal analysis of sucrase-isomaltase expression in the human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells.Biochem J,280, 599–608.
Rodrigues GA and Park M, 1993, Isoforms of themet receptor tyrosine kinase. In: Goldberg ID and Rosen EM, eds.Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Scatter Factor (HGF-SF) and the c-met Receptor. Basel: Birkhauser, pp. 167–78.
Rong S, Bodescott M, Blair D,et al. 1992, Tumorigenicity of themet proto-oncogene and the gene for hepatocyte growth factor.Mol Cell Biol,12, 5152–8.
Yagel S, Khokha R, Denhardt DT,et al. 1989, Mechanism of cellular invasiveness: A comparison of amnion invasionin vitro and metastatic behaviourin vivo.JNCI,81, 768–75.
Cohen AM, Minsky BD and Schilsky RL, 1993, Colon cancer. In: de Vita VT, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA, eds.Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. Philadelphia: Lippincott, pp. 929–77.
DiRenzo MF, Narsimhan RP, Olivero M,et al. 1991, Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues.Oncogene,4, 1997–2003.
Haffen K, Kedinger M and Simon-Assmann P, 1989, Cell contact dependent regulation of enterocytic differentiation. In: Lebenthal E, ed.Human Gastrointestinal Development. New York: Raven Press, pp. 19–39.
de Vita VT, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA, 1993,Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology, 4th edn. Philadelphia: Lippincott.
Lichtenberger LM, Lechago J and Miller TA, 1979, Cell culture of human intestinal mucosae.Gastroenterology,77, 1291–1300.
Barcellos-Hoff MH, Aggeler J, Ram TG and Bissell MJ, 1989, Functional differentiation and alveolar morphogenesis of primary mammary cultures on reconstituted basement membrane.Development,105, 223–35.
Kinsella JL, Grant DS, Weeks BS and Kleinman HK, 1992, Protein kinase C regulates endothelial cell tube formation on basement membrane matrix, Matrigel.Exp Cell Res,199, 56–62.
Neutra M and Louvard D, 1989, Differentiation of intestinal cellsin vitro. In: Matlin KS and Valentich JD, eds.Functional Epithelial Cells in Culture. New York: Alan R. Liss Inc., pp. 363–98.
Liotta LA, 1986, Tumor invasion and metastases: Role of the basement membrane.Cancer Res,46, 1–7.
Sommers CL, Thompson EW, Torri J,et al. 1991, Cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin expression in human breast cancer cell lines: relationship to morphology and invasive capacities.Cell Growth Differentiation,2, 365–72.
Wolf HK, Zarnegar R and Michaelopoulos G, 1991, Localization of hepatocyte growth factor in human and rat tissues: An immunohistochemical study.Hepatology,14, 488–94.
Stoker M, 1989, Effect of scatter factor on motility of epithelial cells and fibroblasts.J Cell Physiol,139, 565–9.
Rosen EM, Meromsky L, Setter E, Vinter DW and Goldberg ID, 1990, Purified scatter factor stimulates epithelial and vascular endothelial cell migration.Proc Soc Exp Biol Med,195, 34–43.
Giordano S, Zhen Z, Medico E,et al. 1993, Transfer of motogenic and invasive response to scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor by transfection of human MET protooncogene.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,90, 649–53.
Rutzky LP and Moyer MP, 1990, Human cell lines in colon cancer research. In: Moyer MP and Poste GH, eds.Colon Cancer Cells. New York: Academic Press, pp. 155–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Drs Sunitha and Meighen share first authorship of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunitha, I., Meighen, D.L., Hartman, D.P. et al. Hepatocyte growth factor stimulates invasion across reconstituted basement membranes by a new human small intestinal cell line. Clin Exp Metast 12, 143–154 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01753981
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01753981