Summary
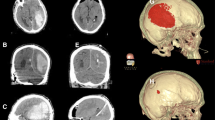
The autors present a serie of 37 traumatic intracerebral haematomas (ICH) evacuated by a simplified stereotatic surgical procedure.
The mortality rate was 80% in patients with Glasgow coma scale (G.C.S.) scores of 3–5 and 25% in patients with scores of 6–7. There were no deaths in patients with G.C.S. of 8 or more. With the exception of the first group of patients, the results were better than those archieved by wide craniotomy. The importance of reduced operative trauma in patients with ICH, which often are associated with multifocal or diffuse brain injuries, are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH, Graham DI, Scott G, Parker LS (1980) Brain damage in fatal non-missile head injury. J Clin Pathol 33: 1132–1145
Andrews BT, Chiles BW, Olsen WL, Pitts LH (1988) The effect of intracerebral haematoma location on the risk of brain-stem compression and on clinical outcome. J Neurosurg 69: 518–522
Auer LM, Deinsberger W, Niederkorn K,et al (1989) Endoscopic surgery versus medical treatment for spontaneus intracerebral haematoma. A randomized study. J Neurosurg 70: 530–535
Backlund EO, Holst H (1978) Controlled subtotal evacuation of intracerebral haematomas by stereotaxic technique. Surg Neurol 9: 99–101
Bruce DA, Alavi A, Bilaniuk L, Dolinskas C, Obrist W, Uzzel B (1981) Diffuse cerebral swelling following head injuries in children: the syndrome of malignant brain edema. J Neurosurg 54: 170–178
Bullock R, Golek J, Blake G (1989) Traumatic intracerebral haematoma Which patients should undergo surgical evacuation? CT scan features and ICP monitoring as a basis for decision making. Surg Neurol 32: 181–187
Cooper PR, Rovit RL, Ransohoff J (1976) Hemicraniectomy in the treatment of acute subdural haematoma. A reappraisal. Surg Neurol 5: 25–28
Cooper PR, Hagler H, Clark WK, Barnett P (1979) Enhancement of experimental cerebral edema after decompressive craniectomy: implications for the management of severe head injuries. Neurosurgery 4: 296–300
Cooper PR (1985) Traumatic intracranial haematomas. In: Wilkins RH, Reganchary SS (eds) Neurosurgery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1657–1665
Coraddu M, Nurchi GC, Floris F, Meleddu V (1990) Considerations about the surgical indication of the spontaneous cerebral haematomas. J Neurosurg Sci 34: 35–39
Coraddu M, Mascia MP, Nurchi GC, Pelaghi AE (1988) Ricostruzione sullo scalpo di lesioni intracraniche da immagini T.C. Nota tecnica. Ricerca Neurochirgica II: 335–340
Enevoldsen EM, Cold G, Jensen FT, et al (1976) Dynamic changes in regional CBF, intraventricular pressure, CSF pH and lactate levels during the acute phase of head injury. J Neurosurg 44: 191–214
Gade GF, Becker DP (1988) Surgical management of acute head injuries. In: Schmidek HH, Sweet WH (eds) Operative neurosurgical techniques. Grune-Stratton, New York, pp 19–31
Galbraith SL, Teasdale GM (1981) Predicting the need for operation in a patient with on occult traumatic intracranial haematoma. J Neurosug 55: 75–81
Gennarelli TA, Spielman GM, Langfitt TW, Gildemberg PL, Harrington T, Jane JA (1982) Influence of the type of lesion on outcome from severe head injury. A multicenter study using a new classification system. J Neurosurg 56: 26–32
Hirschberg H (1981) Localization of brain tumors with a simple scalp mounted fiducial device. Technical note. J Neurosurg 20: 255–256
Ito U, Tomita H, Yemazaki Sh, Takeda Y, Inaba Y (1988) Brain swelling and brain oedema in acute head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 79: 120–124
Jayakumar PN, Kolluri Sastry VR, Baavakumar DG, Subbakrishna DK, Arya BYT, Das BS (1991) Prognosis in contre-coup intracerebral haematomas. A clinical and radiological study of 63 patients. Acta Neurochir 108: 30–33
Kandel EI, Peresedol W (1985) Stereotaxic evacuation of spontaneous intracerebral haematomas. J Neurosurg 62: 206–213
Kaufman HH, Moake JL, Olson JD,et al (1980) Delayed and recurrent intracranial haematomas related to disseminated intravascular clotting and fibrinolysis in head injury. Neurosurgery 7: 446–449
Langfitt TW, Tannenbaum HM, Kassell NF (1966) The etiology of acute brain swelling following experimental head injury. J Neurosurg 24: 47–56
Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Cordobes F, Alted E, Perez C, Sarabia R, Cabrera A, Diez I, Gomez P, Lamas E (1988) Acute epidural haematoma: an analysis of factors influencing the outcome of patients undergoing surgery in coma. J Neurosurg 68: 48–57
Lobato RD, Sarabia R, Cordobes F, Rivas JJ, Adrados A, Cabrera A, Gomez P, Madera A, Lamas F (1988) Posttraumatic cerebral hemispheric swelling. J Neurosurg 68: 417–423
Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Gomez PA, Castaneda M, Canizal JM, Sarabia R, Cabrera A, Munoz MJ (1991) Head injured patients who talk and deteriorate into coma. Analysis of 211 cases studied with computerized tomography. J Neurosurg 75: 256–261
McCormick WF (1985) Pathology of closed head injury. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds) Neurosurgery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1544–1570
Marshall LF, Gautille T, Kaubert MR, Eisenberg HM (1991) The outcome of severe closed head injury. J Neurosurg 75: 28–36
Obrist WD, Langfitt TW, Jaggi JL,et al (1984) Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in comatose patients with acute head injury. J Neurosurg 61: 241–253
Overgaard J, Tweed WA (1991) Cerebral circulation after head injury. J Neurosurg 59: 439–446
Patemiti S, Macri E, Marra A, Guerrera S, Cambria S (1991) Ematomi intracerebrali traumatici. Riv Neurobiologia 37: 109–115
Patil AA, Woosley RE (1986) Scalp marking of intracranial lesions using computed tomography images. A technical note. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 80: 62–64
Penning L (1987) CT localization of a convexity brain tumor on the scalp. J Neurosurg 66: 474–476
Popp AJ, Bourke RS (1985) Pathophysiology of head injury. In: Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS (eds) Neurosurgery. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1536–1543
Rivano C, Borzone M, Carta F, Michelozzi G (1980) Traumatic intracerebral haematoma: 72 cases surgically treated. J Neurosurg Sci 24: 77–84
Sahuquillo-Barris G, Lamarca-Ciuro J, Vilalta-Costan J, Subio-Garcia E, Rodriguez-Pazos M (1988) Acute subdural haematoma and diffuse axonal injury after severe head trauma. J Neurosurg 68: 894–900
Stein SC, Young GS, Talucci RC, Greenbaum ZH, Ross GE (1992) Delayed brain injury after head trauma. significance of coagulopathy. Neurosurgery 30: 160–165
Zimmermann RA, Bilaniuk LT, Gennarelli T, Bruce D, Dolinskas C, Uzzell B (1978) Cranical computed tomography in diagnosis and management of acute head trauma. AJR 131: 27–34
Warme PE, Bergstrom R, Persson L (1991) Neurosurgical intensive care improves outcome after severe head injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 110: 57–64
Wester K, Sortland O, Hauglie-Hanssen E (1981) A simple and inexpensive method for CT-guided stereotaxy. Neororadiology 20: 255–256
Wilberg JE, Harris M, Diamond DL (1991) Acute subdural haematoma: morbidity, mortality, and operative timing. J Neurosurg 74: 212–218
Yoshino E, Yamaki T, Higuchi T, Horikawa Y, Hirakawa K (1985) Acute brain edema in fatal head injury: analysis by dynamic CT scanning. J Neurosurg 63: 830–839
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coraddu, M., Floris, F., Nurchi, G. et al. Evacuation of traumatic intracerebral haematomas using a simplified stereotactic procedure. Acta neurochir 129, 6–10 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01400865
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01400865