Abstract
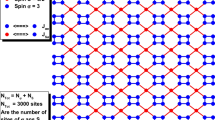
We study the finite temperature property of a model on two dimensional square lattices with two Ising spins at each lattice site by Monte Carlo simulations. When those Ising spins at a lattice site are parallel the site is said to be in the high-spin state (HS), while when they are antiparallel the site is said to be in the low-spin state (LS). Throughout the study, the energy of HS is presumed to be higher than that of LS. Two Ising spins at each site are added to form a total spin, which interacts with its nearest neighbour total spins via spin-spin couplings. The spin-phonon coupling also is introduced via harmonic springs between nearest neighbour sites with spring constants and equilibrium distances depending on the spin states of the sites involved. In this system, we investigate the feature of transitions between LS and HS (to be called low/high spin transition (LHST)) by varying the temperature. As for the ferromagnetic interaction between total spins, the second order phase transition: pure HS→mixed state of HS and LS is possible to occur in a pure spin system, as is expected from mean field calculations. The role of lattice distortions by the change of lattice spacings is shown to be essential for LHST: pure LS→(pure)HS. In the model investigated, there appears an indication of the strong first order phase transition which reveals a conspicuous hysteresis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
For a review until 1980, see Gütlich, P.: Struct. Bonding Berlin44, 83 (1981)
For works after 1981, see, for example, Kambara, T.: J. Chem. Phys.74, 4557 (1981)
Ohnishi, S., Sugano, S.: J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys.14, 39 (1981)
Köppen, H., Müller, E.W., Köhler, C.P., Spiering, H., Meissner, E., Gütlich, P., Kaji, K., Sorai, M.: Therm. Acta88, 185 (1985)
These deal with works on finite temperature and zero pressure problems. The following is an incomplete list of articles for finite pressure phenomena: Bargeron, C.B., Drickamer, H.G.: J. Chem. Phys.55, 3471 (1971)
Fisher, D.C., Drickamer, H.G.: J. Chem. Phys.54, 4825 (1971)
Slichter, C.P., Drickamer, H.G.: J. Chem. Phys.56, 2142 (1972)
Kambara, T.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.50, 2257 (1981)
Sorai, M., Seki, S.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids35, 555 (1974)
Chesnut, D.B.: J. Chem. Phys.40, 405 (1964). See also Bari, R.A., Sivardiere, J.: Phys. Rev. B5, 4466 (1972)
Zimmermann, R., König, E.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids38, 779 (1977)
Takahashi, K.: (unpublished)
Mikami, M., Konno, M., Saito, Y.: Chem. Phys. Lett.63, 566 (1979). See also Mikami-Kido, M., Saito, Y.: Acta Crystallogr. B38, 452 (1982)
Scheidt, W.R., Geiger, D.K., Haller, K.J.: J. Am. Chem. Soc.104, 495 (1982)
Kambara, T.: J. Chem. Phys.40, 4199 (1979);74, 4557 (1981)
Saito, M., Kashiwagi, H.: J. Chem. Phys.82, 3716 (1985)
Gütlich, P., Köppen, H., Link, R., Steinhauser, H.G.: J. Chem. Phys.70, 3977 (1979)
Sorai, M., Seki, S.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.33, 575 (1972). See also the review by Gütlich in [1]
Fisher, M.E.: In: Proceedings of the International School of Physics Enrico Fermi. Green, M.S. (ed.), Course LI, p. 1. London: Academic Press 1971; J. Vac. Sci. Tech.10, 665 (1973)
Suzuki, M.: Prog. Theor. Phys.58, 1 (1977)
LeGuillou, J. Zinn-Justin: Phys. Rev. B21, 3976 (1980)
Mouritsen, O.G.: J. Phys. C13, 3909 (1980)
Suzuki, M.: In: Proceedings of the International Symposium “Quantum Field Theory”. Mancini, F. (ed.). Amsterdam: North-Holland 1985
Suzuki, M., Katori, M.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.55, 1141 (1986)
Blinc, R., Zekes, B.: Adv. Phys.21, 693 (1972)
Schneider, T., Stoll, E.: Phys. Rev. Lett.31, 1254 (1973)
Krumhansl, J.A., Schrieffer, J.R.: Phys. Rev. B11, 3535 (1975)
Schneider, T., Stoll, E.: Phys. Rev. B13, 1216 (1976)
See, for instance, Shapiro, S.L., Teukolsky, S.A.: Black holes, white dwards and neutron stars: the physics of compact objects. New York: Wiley 1983
Baym, G., Pethick, C.: Ann. Rev. Nucl. Sci.25, 27 (1975)
Takatsuka, R., Tamiya, K., Tatsumi, T., Tamagaki, R.: Prog. Theor. Phys.59, 1933 (1978)
Pandharipande, V.R., Smith, R.A.: Nucl. Phys. A237, 507 (1975)
Here we refer to Bag Models of elementary particles. See, for instance: K. Johnson, Proceedings of the Seventeenth Scottish Universities Summer School in Physics, St. Andrews (1976). Barbour, I.M., Davis, A.D. (eds.); Hasenfratz, P., Kuti, J.: Phys. Reports C40, 75 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, K. Monte Carlo study of low/high spin transitions. Z. Physik B - Condensed Matter 71, 205–217 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01312791
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01312791