Abstract
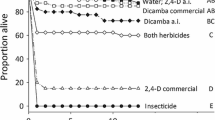
Lethal and sublethal responses to the herbicides 2,4-D, DEF®, propanil, and trifluralin of various life history stages of the Dungeness crab,Cancer magister, were examined to estimate maximum acceptable toxicant concentrations (MATC) of each compound for this species. Zoeae were found, in long term tests, to be the most sensitive stage. Based on the experiments with this stage, MATCs were concluded to be >0.95, <6.9μg for DEF, ≥26, <220μg/L for trifluralin, ≥80, < 1,700μg/L for propanil, and < 1,000μg/L for the free acid form of 2,4-D.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong, D. A., D. V. Buchanan, M. H. Mallon, R. S. Caldwell, and R. E. Millemann: Toxicity of the insecticide methoxychlor to the Dungeness crabCancer magister. Mar. Biol.38, 239 (1976).
Beaven, G. F., C. K. Rawls, and G. E. Beckett: Field observations upon estuarine animals exposed to 2,4-D. Proc. No. East. Weed Contr. Conf.16, 449 (1962).
Buchanan, D. V., R. E. Millemann, and N. E. Stewart: Effects of the insecticide Sevin on various stages of the Dungeness crab,Cancer magister. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada27, 93 (1970).
Buchanan, D. V., M. J. Myers, and R. S. Caldwell: Improved flowing water apparatus for the culture of brachyuran crab larvae. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada32, 1880 (1975).
Butler, P. A.: Effects of herbicides on estuarine fauna. Proc. So. Weed Conf.18, 576 (1965).
Butler, T. H.: Growth and age determination of the Pacific edible crabCancer magister Dana. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada18, 873 (1961).
Cope, O. B.: Some responses of freshwater fish to herbicides. Proc. So. Weed Conf.18, 439 (1965).
Crosby, D. G., and R. K. Tucker: Toxicity of aquatic herbicides toDaphnia magna. Science154, 289 (1966).
Gilderhus, P. A.: Effects of diquat on bluegills and their food organisms. Progr. Fish-Cult.29, 67 (1967).
Hilsenhoff, W.: Effects of diquat on aquatic insects and related animals. J. Econ. Entomol.59, 1520 (1966).
Hughes, J. S.: The toxicity to fish of different formulations of 2,4,5-T, 2(2,4-DP) and Silvex. Proc. So. Weed Conf.15, 265 (1962).
Hughes, J. S., and J. T. Davis: Variations in toxicity to bluegill sunfish of phenoxy herbicides. Weeds11, 50 (1963).
Liu, D. H. W., and J. M. Lee: Toxicity of selected pesticides to the bay mussel (Mytilus edulis). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Rept. EPA-660/3-75-016. Springfield, Va.: Nat. Tech. Inf. Serv. (1975).
Macek, K. J., and B. H. Sleight, III. Utility of toxicity tests with embryos and fry of fish in evaluating hazards associated with the chronic toxicity of chemicals to fishes. In F. L. Mayer and J. L. Hamelink (ed.): Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Evaluation, p. 137, Philadelphia: Am. Soc. Testing Materials (1977).
Macek, K. J., C. Hutchinson, and O. B. Cope: The effects of temperature on the susceptability of bluegills and rainbow trout to selected pesticides. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.4, 174 (1969).
Meehan, W. R., L. A. Norris, and H. S. Sears: Toxicity of various formulations of 2,4-D to salmonids in Southeast Alaska. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada31, 480 (1974).
Mount, D. I., and C. E. Stephen: A method for establishing acceptable toxicant limits for fish. Malathion and the butoxy-ethanol ester of 2,4-D. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc.96, 185 (1967).
Parka, S. J., and H. M. Worth: The effects of trifluralin to fish. Proc. So. Weed Conf.18, 469 (1965).
Rawls, C. K.: Field tests of herbicide toxicity to certain estuarine animals. Chesapeake Sci.6, 150 (1965).
Sanders, H. O.: Toxicity of pesticides to the crustacean,Gammarus lacustris. U.S. Bur. Sport Fish. Wildlife, Tech. Pap. 25. Washington, DC: Gov. Print. Off. (1969).
Sanders, H. O.: Toxicities of some herbicides to six species of freshwater crustaceans. J. Wat. Poll. Cont. Fed.42, 1544 (1970).
Sanders, H. O., and O. B. Cope: Toxicities of several pesticides to two species of cladocerans. Trans. Amer. Fish. Soc.95, 165 (1966).
—,—: The relative toxicities of several pesticides to naiads of three species of stoneflies. Limnol. Oceanogr.13, 112 (1968).
Walsh, G. E.: Effects of herbicides on photosynthesis and growth of marine unicellular algae. Hyacinth Control J.10, 45 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Technical Paper No. 4819, Oregon Agricultural Experiment Station
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caldwell, R.S., Buchanan, D.V., Armstrong, D.A. et al. Toxicity of the herbicides 2,4-D, DEF, propanil and trifluralin to the Dungeness crab,Cancer magister . Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 8, 383–396 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056345
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01056345