Abstract
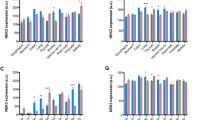
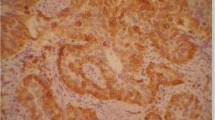
Bcl-2 and Bax proteins, which are involved in repressing and promoting programmed cell death, respectively, have been investigated immunohistochemically and by Western blot analysis in a series of thyroid tumours. Three immunostaining patterns were identified. Benign lesions and well-differentiated thyroid carcinomas displayed a profile similar to that of normal follicular epithelium, in which Bcl-2 immunostaining was predominant. Thyroid carcinomas associated with an aggressive behaviour, such as the tall-cell variant of papillary carcinoma and the poorly differentiated carcinomas, co-expressed both proteins. Finally, anaplastic carcinomas expressed only the Bax protein. Western blot analyses revealed that the anti-Bcl-2 antibody recognized two bands, of molecular weights 21 kDa and 25 kDa. This was only seen in the tall-cell papillary carcinomas and in the anaplastic carcinomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barinaga M (1994) Cell suicide by ice, not fire. Science 263:754–756
Bosman FT, Visser BC, Oeveren J van (1996) Apoptosis: pathophysiology of programmed cell death. Pathol Res Pract 192:676–683
Branet F, Brousset P, Krajewski S, Schlaifer D, Selves J, Reed JC, Caron P (1996) Expression of the cell death-inducing gene bax in carcinomas developed from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:2726–2730
Doglioni C, Dei-Tos AP, Laurino L, Chiarelli C, Barbareschi M, Viale C (1994) The prevalence of Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in breast carcinoma and its clinicopathological correlates, with particular references to oestrogen receptor status. Virchows Arch 424:47–51
Hockenbery DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ (1991) Bcl-2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6961–6965
Korsmeyer SJ (1992) Bcl-2 initiates a new category of oncogenes: regulators of cell death. Blood 80:879–886
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Miyashita T, Wang HG, Reed J (1994) Immunohistochemical determination of in vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bel-2. Am J Pathol 145:1323–1336
Laemmli UK (1997) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Lu Q-L, Abel P, Foster CF, Lalani E-N (1996) Bcl-2: role in the epithelial differentiation and oncogenesis. Hum Pathol 27:102–110
Munakata S, Hendricks JB (1993) Effect of fixation time and microwave oven heating time on retrieval of the Ki-67 antigen from paraffin-embedded tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 41:1241–1246
Ngan BY, Chen-Levy Z, Weiss LM, Warnke RA, Cleary ML (1988) Expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the Bcl-2 protein associated with the t(14;18) translocation. N Engl J Med 318:1638–1644
Oltvai Z, Milliman C, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74:609–619
Pezzella F, Morrison H, Jones M, Garter KC, Lane D, Harris AL, Mason DY (1993) Immunohistochemical detection of p53 and Bel-2 proteins in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Histopathology 22:39–44
Pezzella F, Turley H, Kuzu I, Tungekar MF, Pierce CB, Harris A, Garter KC, Mason DY (1993) Bcl-2 protein in non-small cell lung carcinoma. N Engl J Med 329:690–694
Pilotti S, Collini P, Rilke F, Cattoretti G, Del Bo R, Pierotti MA (1994f) Bcl-2 protein expression in carcinomas originating from the follicular epithelium of the thyroid gland. J Pathol (Lond) 172:337–342
Reed JC (1994) Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 124:1–6
Sobrino-Simoes M (1995) Tumours of thyroid: a brief overview with emphasis on the most controversial issues. Curr Diagn Pathol 2:15–22
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Vaux DL (1993) Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:786–789
Viale G, Roncalli M, Grimelius L, Graziani D, Wilander E, Johansson H, Bergholm U, Coggi G (1995) Prognostic value of bcl-2 immunoreactivity in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Hum Pathol 26:945–950
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manetto, V., Lorenzini, R., Cordon-Cardo, C. et al. Bcl-2 and Bax expression in thyroid tumours An immunohistochemical and Western blot analysis. Virchows Archiv 430, 125–130 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01008033
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01008033