Summary
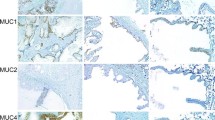
A comparative immunohistochemical study of intermediate filament expression in normal parotid glands and pleomorphic adenomas (PA) was performed using material fixed in a modified methacarn fixative. The normal myoepithelial cells of acini stained only with monoclonal antibodies 312C8-1 (cytokeratin (CK) 14) and 4.62 (CK 19) while myoepithelial/basal cells of ducts also reacted with antibodies 8.12 (CK 13, 16), 8.60 (CK 10, 11, +1), and PKK1 (CK 7, 8, 17, 18). Normal duct luminal cells showed a different CK profile, reacting consistently with ECK, a polyclonal antibody to epidermal prekeratin (CK 3,6), and monoclonal antibodies 4.62, PKK1 and 8.60. In PA, tumour cells at the periphery of ducts, in solid areas, and at the edge of myxoid regions all had CK profiles similar to normal myoepithelial/ basal cells except that antibody 4.62 was generally negative. Vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) were uniformly negative in normal parotids but showed variable (often strong) reactivity with some cells in chondroid, myxoid and solid areas of PA. A surprising feature of most PA was the variability of CK subtype expression not only from one case to another but also within morphologically similar areas of the same specimen. These results suggest that the morphology of PA is the result of diversity of tumour cell differentiation rather than the processes implicit in a reserve cell histogenetic model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batsakis JG, Kraemer B, Sciubba JJ (1983) The pathology of head and neck tumors: the myoepithelial cell and its participation in salivary gland neoplasia. Head Neck Surg 5:222–233
Caselitz J, Osborn M, Seifert G, Weber K (1981) Intermediate sized filament proteins (prekeratin, vimentin, desmin) in the normal parotid gland and parotid gland tumors: Immunofluorescence study. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat] 393:273–286
Caselitz J, Osborn M, Wustrow J, Seifert G, Weber K (1986) Immunohistochemical investigations on the epimyoepithelial islands in lymphoepithelial lesions: use of monoclonal keratin antibodies. Lab Invest 55:427–432
Cooper D, Schermer A, Sun T-T (1985) Classification of human epithelia and their neoplasms using monoclonal antibodies to keratins: Strategies, applications, and limitations. Lab Invest 52:243–256
Dairkee SH, Blayney C, Smith HS, Hackett AJ (1985) Monoclonal antibody that defines human myoepithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7409–7413
Dardick I, Nostrand van AWP, Phillips MJ (1982) Histogenesis of salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumour) with an evaluation of the role of the myoepithelial cell. Human Pathol 13:62–75
Dardick I, Nostrand van AWP, Jeans MTD, Rippstein P, Edwards V (1983) Pleomorphic adenoma: I. Ultrastructural organization of “epithelial” regions. II. Ultrastructural organization of “stromal” regions. Human Pathol 14:780–809
Dardick I, Rippstein P, Skimming L, Boivin M, Dairkee SH (1987) Immunohistochemistry and ultrastructure of myoepithelium and modified myoepithelium of the ducts of human major salivary glands: histogenetic implications for salivary gland tumors. Oral Surg 64:703–715
Dardick I, Nostrand van AWP (1985) Myoepithelial cells in salivary gland tumors - revisited. Head Neck Surg 7:395–408
Dardick I, Nostrand van AWP (1987) Morphogenesis of salivary gland tumors. A prerequisite to improving classification. Pathol Annu 22 (pt 1) 1–53
Dardick I, Claude A, Parks WR, Hoppe D, Stinson J, Burns BF, Little J, Brown DL, Dairkee SH (1988) Warthin's tumor: An ultrastructural, immunohistochemical, and fluorescent study of basilar epithelium. Ultrastruct Pathol (In press)
Erlandson RA, Cardon-Cardo C, Higgins PJ (1984) Histogenesis of benign pleomorphic adenoma (mixed tumor) of the major salivary glands. An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Am J Surg Pathol 8:803–820
Eversole LR (1971) Histogenetic classifications of salivary gland tumors. Arch Pathol 92:433–443
Geiger S, Geiger B, Leitmer O, Marshak G (1987) Cytokeratin polypeptides expression in different epithelial elements of human salivary glands. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat] 410:403–414
Kahn HJ, Baumal R, Marks A, Dardick I, Nostrand van AWP (1985) Myoepithelial cells in salivary gland tumors. An immunohistochemical study. Arch Pathol Lab Med 109:190–195
Krepler E, Denk H, Artlieb U, Moll R (1982) Immunohistochemistry of intermediate filament proteins present in pleomorphic adenomas of the human parotid gland: Characterization of different cell types in the same tumor. Differentiation 21:191–199
Lam RMY (1985) An electron microscopic histochemical study of the histogenesis of major salivary gland pleomorphic adenoma. Ultrastruct Pathol 8:207–223
Mitchell D, Ibraham S, Gusterson B (1985) Improved immunohistochemical localization of tissue antigens using modified methacarn fixation. J Histochem Cytochem 33:491–495
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B, Krepler R (1982) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumours and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24
Nakazato Y, Ishida Y, Takahashi K, Suzuki K (1985) Immunohistochemical distribution of S-100 protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein in normal and neoplastic salivary glands. Virchows Arch [Pathol Anat] 405:299–310
Osborn M, Weber K (1983) Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: A novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest 48:372–394
Palmer RM (1986) The identification of myoepithelial cells in human salivary glands. A review and comparison of light microscopical methods. J Oral Pathol 15:221–229
Palmer RM, Lucas RB, Knight J, Gusterson B (1985) Immunocytochemical identification of cell types in pleomorphic adenoma with particular reference to myoepithelial cells. J Pathol 146:213–220
Quinlan RA, Schiller DL, Hatzfeld M, Achtstatter T, Moll R, Jorcano JL, Magin TM, Franke WW (1985) Patterns of expression and organization of cytokeratin intermediate filaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci 455:282–306
Ramaekers FCS, Puto JJG, Moesker O, Kant A, Huysmans A, Haag D, Jap PHK, Herman CJ, Vooijs GP (1983) Antibodies to intermediate filament proteins in the immunohistochemical identification of human tumours: an overview. Histochem J 15:691–713
Regezi JA, Batsakis JG (1977) Histogenesis of salivary gland neoplasms. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 10:297–307
Toto PD, Hsu DJ (1985) Product definition of pleomorphic adenoma of minor salivary glands. J Oral Pathol 14:818–832
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burns, B.F., Dardick, I. & Parks, W.R. Intermediate filament expression in normal parotid glands and pleomorphic adenomas. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 413, 103–112 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749671
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00749671