Abstract
Predictions of the amplitude of the last three solar cycles have demonstrated the value and accuracy of the group of prediction methods known as the ‘precursor’ techniques. These are based on a correlation between cycle amplitude and phenomena observed on the Sun, or originating from the Sun, during the declining phase of the cycle or at solar minimum. In many cases, precursor predictions make use of the long record of geomagnetic disturbance indices, assuming that these indices are indicative of solar phenomena such as the occurrence of coronal holes.
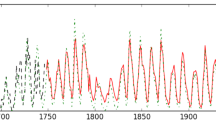
This paper describes a precursor technique for predicting the amplitude of the solar cycle using geomagnetic indices. The technique is accurate — it would have predicted each of the last 11 cycles with a typical error of less than 20 in sunspot number. It has also advantage that a prediction of the lower limit of the amplitude can be made throughout the declining phase, this limit building to a final value at the onset of the new cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, G. M.: 1984, in P. A. Simon, G. R. Heckman, and M. A. Shea (eds.),Proceedings of the Meudon Solar Terrestrial Predictions Workshop, NOAA, Boulder, p. 1.
Kunches, J.: 1993, in J. Hruškaet al. (eds.),Proceedings of the Ottawa Solar Terrestrial Predictions Workshop, NOAA, Boulder, in press.
Gleissberg, W.: 1942,Astrophys. J. 96, 234.
Legrand, J. P. and Simon, P. A.: 1991,Solar Phys. 131, 187.
Martin, S. F. and Harvey, K. L.: 1979,Solar Phys. 64, 93.
Mayaud, P. W.: 1980,Geophysical Monograph Number 22, American Geophysical Union.
Simon, P. A. and Legrand, J. P.: 1992,Solar Phys. 141, 391.
Sýkora, J.: 1992,Solar Phys. 140, 379.
Thompson, R. J.: 1985, IPS Technical Report IPS-TR-85-06, IPS Radio and Space Services, Sydney, Australia.
Thompson, R. J.: 1988,Solar Phys. 117, 279.
Thompson, R. J.: 1993, in J. Hruškaet al. (eds.),Proceedings of the Ottawa Solar Terrestrial Predictions Workshop, NOAA Boulder, in press.
Wilson, P. R.: 1990, in R. J. Thompsonet al. (eds.),Proceedings of the Leura Solar Terrestrial Predictions Workshop, NOAA, Boulder, p. 257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, R.J. A technique for predicting the amplitude of the solar cycle. Sol Phys 148, 383–388 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00645097
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00645097