Abstract
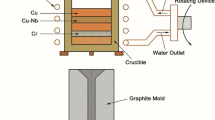
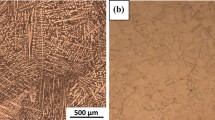
Rapidly solidified Cu2MnAl ribbons were fabricated by the chill-block melt-spinning technique as a function of rotation speed of an iron roller. The rapidly quenched ribbons were relatively ductile, and the total strain at failure for the bend test increased with increasing rotation speed of the roller. The effect of rapid quenching on long-range ordering in Cu2MnAl alloy was studied by X-ray diffraction. The decomposition characteristics during isothermal ageing at temperatures between 350 and 600° C were also examined by X-ray diffraction, magnetization and Vickers hardness measurements. The decomposition reaction at temperatures below 400° C was Cu2MnAl→γ-Cu9Al4+T-Cu3Mn2Al+β-Mn. However, at temperatures between 500 and 600° C, Cu2MnAl decomposed into a new L21 type Cu2MnAl andβ-Mn, and further annealing caused the appearance ofγ-Cu9Al4. The decomposition rate of the rapidly quenched ribbons was faster than that of the water-quenched alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bouchard andG. Thomas,Acta. Metall. 32 (1975) 1485.
M. L. Green andG. Y. Chin,Met. Trans. 6A (1975) 1118.
A. Inoue, T. Masumoto andH. Tomioka,J. Mater. Sci. 19 (1984) 3097.
Y. Sakka, M. Nakamura andK. Hoshimoto,ibid. 24 (1989) 4331.
B. Dubois andD. Chevereau,ibid. 14 (1979) 2296.
T. Yamane, H. Okamoto andJ. Takahashi,Z. Metallkde 71 (1980) 813.
R. Kozubski andJ. Soltys,J. Mater. Sci. 17 (1982) 1441.
Idem, ibid. 18 (1983) 1689.
R. Kozubski, J. Soltys andR. Kuziak,ibid.,18 (1983) 3079.
R. Kozubski andJ. Soltys,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2 (1983) 141.
J. Soltys, M. Stefaniak andJ. Holender,Phil. Mag. B 49 (1984) 151.
D. J. Gaydosh, R. W. Jech andR. H. Titran,J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 4 (1985) 138.
G. E. Dieter, “Mechanical Metallurgy”, 2nd Edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1976) p. 681.
Y. Umakoshi, M. Yamaguchi andT. Yamane,Acta Metall. 32 (1984) 649.
Y. Ono, I. Ohnaka andI. Yamauchi,J. Jpn Inst. Metals 51 (1987) 755 (in Japanese).
J. Soltys,Phys. Status Solidi (a) 63 (1981) 401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakka, Y., Nakamura, M. Mechanical and magnetic properties of the rapidly quenched Cu2MnAl. J Mater Sci 25, 2549–2556 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638057
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00638057