Summary
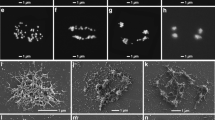
A number of methods are described by the use of which observations were made on the standard coil in the interphase chromosomes of Prorocentrum micans. This is the first algal flagellate in which chromosome spirals have been investigated. The chromosomes were found to have predominantly right-handed helices with an average of just over seven gyres per chromosome after the standard treatment. On the basis of electron microscopical observations it is suggested that the purpose of the spiral is to hold together the many micro-fibrils which make up the chromonema. The spiral is not an artifact.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajer, A.: Cinémicrographic studies on mitosis in endosperm. IV The mitotic contraction stage. Exp. Cell Res. 14, 245–256 (1958).
Baranetzky, J.: Die Kerntheilung in den Pollenmutterzellen einiger Tradescantien. Bot. Z. 38, 283 (1880).
Da Camara, A. S.: Beiträge zur Kenntnis des Spiralbaues der Chromosomen. Z. indukt. Abstamm. Vererb.-Lehre 74, 202–215 (1938).
Cleveland, L. R.: The whole life cycles of chromosomes and their coiling systems. Trans. Amer. Phil. Soc. 39, 1–100 (1949).
—: Photographs of gametogenesis in living cells of Trichonympha. Arch. Protistenk. 105, 497–508 (1962).
Dodge, J. D.: Nuclei, nuclear division and taxonomy in the Dinophyceae. Brit. phycol. Bull. 2, 14–15 (1960).
Dodge, J. D.: The nucleus and nuclear division in the Dinophyceae. Arch. Protistenk. 106 (in the press).
—, and M. B. E. Godward: Experimental evidence for the unusual nature of the Dinophycean nucleus. Brit. phycol. Bull. 2, 102 (1961).
Geitler, L.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen über den feineren Kern- und Chromosomenbau der Cladophoraceen. Planta (Berl.) 25, 530–578 (1936).
Grassé, P.-P., et J. Dragesco: L'ultrasture du chromosome des Péridiniens et ses conséquences génétiques. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 245, 2447–2452 (1957).
Grell, K. G., u K. E., Wohlfarth-Bottermann: Licht- und elektronenmikro-skopische Untersuchungen an dem Dinoflagellaten Amphidinium elegans n. sp. Z. Zellforsch. 47, 7–17 (1957).
Kaufmann, B. P., H., Gay and M. R. McDonald: Organizational patterns within chromosomes. Int. Rev. Cytol. 9, 77–127 (1960).
Kellenberger, E., A. Ryter, and J. Séchaud: Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 4, 671–678 (1958).
Kuwada, Y.: Chromosome structure. A critical review. Cytologia (Tokyo) 10, 213–256 (1939).
Manton, I.: Evidence on spiral structure and chromosome pairing in Osmunda. Phil. Trans. B 230, 179–215 (1939).
—: Comments on chromosome structure. Nature (Lond.) 155, 471 (1945).
—: The spiral structure of chromosomes. Biol. Rev. 25, 486–508 (1950).
—, and J. Smiles: Observations on the spiral structure of somatic chromosomes in Osmunda with the aid of ultra-violet light. Ann. Bot. N. S. 7, 195–212 (1943).
Nebel, B. R.: Chromosome structure in the Tradescantiae. II The direction of coiling of the chromonema. Z. Zellforsch. 16, 285–304 (1932).
Oura, G.: A new method of unravelling the chromonema spirals. Z. wiss. Mikr. 53, 36–37 (1936).
Sakamura, T.: Fixierung von Chromosomen mit siedendem Wasser. Bot. Mag. (Tokyo) 41, 58 (1927).
Sax, K., and L. M. Humphrey: Structure of meiotic chromosomes in microsporogenesis of Tradescantia. Bot. Gaz. 96, 354–362 (1934).
Sinha, J. P.: Cytological and cultural study of some members of Cladophorales and Oedogoniales. Ph. D. thesis, University of London (1958).
Skoczylas, O.: Über die Mitose von Ceratium cornutum und einigen anderen Peridineen. Arch. Protistenk. 103, 193–228 (1958).
Swanson, C. P.: The behaviour of meiotic prophase chromosomes as revealed through the use of high temperatures. Amer. J. Bot. 30, 422–428 (1943).
—: Cytology and Cytogenetics. London: Macmillan 1958.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dodge, J.D. Chromosome structure in the Dinophyceae. Archiv. Mikrobiol. 45, 46–57 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410296
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00410296