Abstract
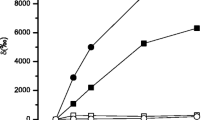
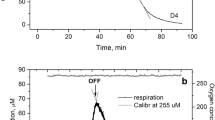
Evidence for host assimilation of 14C-labeled symbiont photosynthates is presented from laboratory studies of the solitary radiolarian Thalassicolla nucleata and the colonial species Collosphaera huxleyi. The amount of 14C-labeled product assimilated in the central capsule of T. nucleata is directly related to the amount of 14C incorporated by the symbionts. In C. huxleyi central capsules, the percentage of 14C-label occurring in the water-soluble fraction is 38% and in the lipid-soluble fraction is 20%, the remainder being in insoluble products. Within the lipid-soluble fraction, a substantial percentage of the 14C activity is associated with the triglyceride and wax ester fractions. The significance of these findings is discussed in relation to the possible physiological role of symbionts in sustaining the host and stabilizing the host-symbiont association.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Anderson, O. R.: Ultrastructure of a colonial radiolarian Collozoum inerme and a cytochemical determination of the role of its zooxanthellae. Tissue Cell 8, 195–208 (1976)
Anderson, O. R.: Fine structure of a symbiont-bearing colonial radiolarian Collosphaera globularis and 14C-isotopic evidence for assimilation of organic substances from its zooxanthellae. J. Ultrastructure Res. 62, 181–189 (1978)
Anderson, O. R.: Radiolaria. In: Biochemistry and physiology of protozoa, Vol. 3, pp. 1–42. Ed. by M. Levandowsky and S. Hutner. New York: Academic Press 1980
Anderson, O. R.: Radiolaria, 370 pp. New York: Springer-Verlag 1983
Anderson, O. R. and M. Botfield: Biochemical and fine structure evidence for cellular specialization in a large Spumellarian radiolarian Thalassicolla nucleata. Mar. Biol. 72, 235–241 (1983)
Brandt, K.: Ueber die morphologische Retentung des chlorophylls Thieren. Arch. Anat. Phys.-Phys., Abth. (1882)
Brandt, K.: Ueber symbiose von Algen und Thieren. Separat Abzug aus Arch. Anat. Phys.-Phys. Abth. 445–454 (1883)
Crossland, C. J., D. J. Barnes, T. Cox and M. Devereux: Compartmentation and turnover of organic carbon in the staghorn coral Acropora formosa. Mar. Biol. 59, 181–187 (1980)
Dorsey, T. E., P. McDonald and O. Roels: A heated biuret-Folin protein assay which gives equal absorbance with different proteins. Anal. Biochem. 78, 156–164 (1977)
Geddes, P.: On the nature and functions of the “yellow cells” of radiolarians and coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. Edinburgh 377 (1882)
Muscatine, L. and E. Cernichiari: Assimilation of photosynthetic products of zooxanthellae by a reef-coral. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 137, 506–523 (1972)
Schmitz, K. and B. P. Kremer: Carbon fixation and analysis of assimilates in a coral dinoflagellate symbiosis. Mar. Biol. 42, 305–313 (1977)
Smith, D., L. Muscatine and D. Lewis: Carbohydrate movement from autotrophs to heterotrophs in parasitic and mutualistic symbiosis. Biol. Rev. 44, 17–90 (1969)
Strickland, J. D. H. and T. Parsons: A practical handbook for seawater analysis. Fish. Res. Bd Can. Bull. 167, 231–234 (1972)
Swanberg, N. R.: The ecology of colonial radiolarians: their colony morphology, trophic interactions and associations, behavior distribution, and the photosynthesis of their symbionts. Woods Hole Oceanogr. Inst., Ph.D. Thesis, 201 pp. 1979
Swanberg, N. R.: The trophic role of colonial radiolaria in oligotrophic oceanic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28, 655–666 (1983)
Swanberg, N. R. and G. R. Harbison: The ecology of Collozoum longiforme, sp. nov. a new colonial radiolarian from the equatorial Atlantic Ocean. Deep-Sea Res. 27, 715–731 (1980)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. I. The assimilation of photosynthesis products of zooxanthellae by two marine coelenterates. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 177, 225–235 (1971a)
Trench, R. K.: The physiology and biochemistry of zooxanthellae symbiotic with marine coelenterates. II. Liberation of fixed 14C by zooxanthellae in vitro. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 177, 237–250 (1971b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S.K. Pierce, College Park
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, O.R., Swanberg, N.R. & Bennett, P. Assimilation of symbiont-derived photosynthates in some solitary and colonial radiolaria. Mar. Biol. 77, 265–269 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395815
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395815