Abstract
The effect of oxygen limitation on the respiration rate of Penicillium chrysogenum was studied. The results show that measurements of critical oxygen tensions within a process that on morphological or on physical grounds exhibits an inhomogenous structure are not likely to resemble the Monod model.
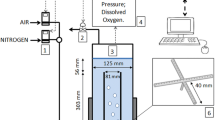
In order to study the effects of short term oxygen starvation on the respiratory capacity of Penicillium chrysogenum, a two compartment fermenter was constructed. This fermenter consists of one well mixed aerobic part (CSTR) and one minor anaerobic part (CPFR). In the latter the circulation time as well as the volume can be varied. After passage of the whole cell culture volume through the anaerobic part, irreversible inhibition of the respiration was observed. This was caused by a circulation time of 5 and 10 min in the plug flow reactor and with a volume of 6% of the stirred tank reactor volume. However, circulation times of 1 and 2 min with an anaerobic zone of 1% of the stirred tank reactor volume did not give any irreversible effects on the respiratory capacity.
This was compared with the results of the previously established model ln(1 — I OUR//100)−1 = kt [1]. The I OUR is the percentage irreversible inhibition of the respiration, t is the anaerobic circulation time and k is a constant. The two compartment fermenter results agree with the earlier model at circulation times of 5 and 10 min, but not with the shorter times, and this suggests that a lag phase exists in the inactivation kinetics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larsson, G.; Enfors, S.-O.: Influence of oxygen starvation on the respiratory capacity of Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 21 (1985) 228–233
Oosterhuis, N. M. G.; Kossen, N. W. F.: Dissolved oxygen concentration profiles in a production scale bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 36 (1984) 546–550
Vardar, F.; Lilly, M. D.: Effect of cycling oxygen concentrations on product formation in penicillin fermentations. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14 (1982) 203–211
Sweere et al.: Proc. 4th European Congress on biotechnology 1 (1987) 180–183
Wang, D., et al.: Fermentation and enzyme technology, pp. 324–326, New York: Wiley & Sons Inc. 1979
Kobayashi, T.; Moo-Young, M.: Backmixing and mass transfer in the design of immobilized-enzyme reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 13 (1971) 893–910
Cleland, N.; Enfors, S.-O.: A biological system for studies on mixing in bioreactors. Bioprocess Engineering 2 (1987) 115–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsson, G., Enfors, S.O. Studies of insufficient mixing in bioreactors: Effects of limiting oxygen concentrations and short term oxygen starvation on Penicillium chrysogenum. Bioprocess Engineering 3, 123–127 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373475
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00373475