Summary
The cochlear nuclei (CN) contain a moderate concentration of norepinephrine (445±20 ng/g tissue) with dopamine levels (46±14 ng/g) that are low and within the precursor range expected for a norepinephrine (NE) terminal system. Lesion and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) experiments indicate that this innervation is bilateral and arises from fusiform and multipolar neurons in the locus coeruleus.
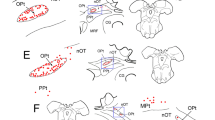
Autoradiographic and fluorescence histochemical experiments demonstrate that locus coeruleus fibers reach the ipsilateral ventral cochlear nuclei via a rostral pathway that projects from the rostral locus coeruleus laterally through the brain stem to the rostral tip of the ventral nuclei. This pathway is located dorsal to the motor and spinal trigeminal nuclei and ventral to the middle cerebellar peduncle. Descending coeruleo-cochlear fibers travel between the fourth ventricle and the vestibular nuclei to enter the acoustic striae. These fibers innervate both the dorsal and ventral nuclei. Contralateral locus fibers reach the CN by crossing in the pontine central gray at the rostral border of the fourth ventricle and by decussating with the fibers of the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus ventral to the medial longitudinal fasciculus. The bilateral locus coeruleus innervation of the cochlear nuclei comprises a highly collateralized network of varicose axons which are not topographically organized. Unlike the cochlear nerve fibers in the CN which form specific projections, the locus coeruleus afferents to these sensory nuclei are diffuse and non-specific.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cant, N.B., Morest, D.K.: Axons from non-cochlear sources in the anteroventral cochlear nucleus of the cat. A study with the rapid Golgi method. Neurosci. 3, 1003–1029 (1978)
Cowan, W.M., Gottlieb, D.I., Hendrickson, A.E., Price, J.L., Woosley, T.A.: The autoradiographic demonstration of axonal connections in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 37, 21–51 (1972)
Coyle, J.T., Henry, D.: Catecholamines in fetal and newborn rat brain. J. Neurochem. 21, 61–67 (1973)
Dahlström, A., Fuxe, K.: Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons. Acta Physiol. Scand. 62, Suppl. 232, 1–55 (1964)
Dahlström, A., Fuxe, K.: Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. II. Experimentally induced changes in the intraneuronal amine levels of the bulbospinal neuron systems. Acta Physiol. Scand. 64, Suppl. 247, 1–36 (1965)
Fuxe, K.: Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. IV. Distribution of monoamine nerve terminals in the central nervous system. Acta Physiol. Scand. 64, Suppl. 247, 39–85 (1965)
Graham, R.C., Karnovsky, M.J.: The early stages of absorpttion of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 14, 291–302 (1966)
Harrison, J.M., Irving, R.: The anterior ventral cochlear nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol. 124, 15–42 (1965)
Harrison, J.M., Irving, R.: The organization of the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 126, 391–403 (1966)
Harrison, J.M., Warr, W.B.: A study of the cochlear nuclei and ascending auditory pathways of the medulla. J. Comp. Neurol. 119, 341–380 (1962)
Held, H.: Die centrale Gehöreleitung. Arch. f. Anat. u. Physiol. Anat. Abt. 201–248 (1893)
Hökfelt, T., Ljungdahl, A.: Modification of the Falck-Hillarp formadehyde fluorescence method using the Vibratome: simple, rapid and sensitive localization of catecholamines in sections of unfixed or formalin fixed brain tissue. Histochemie, 29, 325–339 (1972)
Jones, B.E., Moore, R.Y.: Asceding projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. II. Autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 127, 23–53 (1977)
Kane, E.C.: Synaptic organization in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of the cat: a light and electron microscopic study. J. Comp. Neurol. 155, 301–330 (1974)
Kromer, L.F., Moore, R.Y.: A study of the organization of the locus coeruleus projections to the lateral geniculate nuclei in the albino rat. Neurosci. (in press) (1980)
Kromer, L.F., Moore, R.Y.: Cochlear nuclei innervation by central norepinephrine neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 118, 531–537 (1976)
Laurent, J.-P., Cespuglio, R., Jouvet, M.: Délimitation des voies ascendantes de l'activité pontogeniculo-occipitale chez le chat. Brain Res. 65, 29–52 (1974)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A.: The glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method: a detailed account of the methodology for the visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemie, 39, 97–127 (1974a)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A.: The organization of the ascending catecholamine neuron systems in the rat brain as revealed by the glyoxylic acid fluorescence method. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 412, 1–48 (1974b)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A., Hökfelt, T., Ljungdahl, A.: Application of the glyoxylic acid method to Vibratome sections for the improved visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemie, 35, 31–38 (1973)
Lindvall, O., Björklund, A., Nobin, A., Stenevi, U.: The adrenergic innervation of the rat thalamus as revealed by the glyoxylic acid fluorescence method. J. Comp. Neurol. 154, 317–348 (1974)
Lorén, I., Björklund, A., Lindvall, O.: Magnesium ions in catecholamine fluorescence histochemistry. Application to the cryostat and vibratome techniques. Histochem. 52, 223–239 (1977)
Lorén, I., Björklund, A., Falck, B., Lindvall, O.: The alumimum-formaldehyde (ALFA) method for improved visualization of catecholamines and indolamines (in preparation) (1979)
Lorente de No, R.: The anatomy of the VIII nerve. III. General plan of structure of the primary cochlear nuclei. Laryngoscope (St. Louis) 43, 327–350 (1933)
Lorente de No, R.: Some unresolved problems concerning the cochlear nerve. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. Suppl. 34, 85, 1–28 (1976)
Moore, R.Y., Kromer, L.F.: The organization of central CA neuron systems. In: Neuropharmacology and Behavior, (Haber, B. and Aprison, M. eds.) 55–87, New York: Plenum Press 1978
Olson, L., Fuxe, K.: On the projections from the locus coeruleus noradrenaline neurons: the cerebellar innervation. Brain Res. 28, 165–171 (1971)
Ralston, H.J., Sharp, P.V.: The identification of thalamocortical relay cells in the adult cat by means of retrograde axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. Brain Res. 62, 273–278 (1973)
Ramón y Cajal, S.: Histologie du Système Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vértebrés, pp. 774–838. Paris: A. Maloine 1909
Rasmussen, G.L.: Efferent fibers of cochlear nerve and cochlear nucleus. In: Neural Mechanisms of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems, (Rasmussen, G.L. and Windle, W.E., eds.) pp. 105–115. Springfield, Illinois: C.C. Thomas 1960
Rasmussen, G.L.: Efferent connections of the cochlear nucleus. In: Sensorineural Hearing Processes and Disorders, (Graham, A.B., ed.) pp. 61–75. Boston, Mass.: Little, Brown & Company 1967
Shimizu, N., Ohnishi, S., Satoh, K., Tohyama, M.: Cellular organization of locus coeruleus in the rat as studied by golgi method. Arch. Histol. Jpn. 41, 103–112 (1978)
Swanson, L.W.: The locus coeruleus: a cytoarchitectonic, Golgi and immunohistochemical study in the albino rat. Brain Res. 110, 39–56 (1976)
Swanson, L.W., Hartman, B.K.: The central adrenergic system. An immunofluorescence study of the location of cell bodies and their efferent connections in the rat utilizing dopamine-β-hydroxylase as a marker. J. Comp. Neurol. 163, 467–506 (1975)
Ungerstedt, U.: Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 367, 1–48 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kromer, L.F., Moore, R.Y. Norepinephrine innervation of the cochlear nuclei by locus coeruleus neurons in the rat. Anat Embryol 158, 227–244 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315908
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00315908