Summary
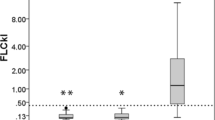
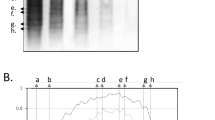
Isoelectric focusing and quantitative estimation of serum and CSF IgG were performed in 85 patients with idiopathic polyneuropathy (IP), subdivided according to the clinical course (acute, subacute, recurrent, chronic). Acute IP very frequently had an increase of oligoclonal and/or polyclonal serum IgG during the progressive phase and blood-CSF barrier damage accompanied by polyclonal IgG intrathecal synthesis during the stationary phase. Polyclonal IgG intrathecal synthesis was also present in several not acute IP and seemed to forecast unfavorable course. Oligoclonal IgG synthesis occurs very rarely within CSF but is a frequent finding in serum of patients with IP. Abnormalities of the IgG serum pattern are neither specific for any clinical course of IP nor of prognostic value. The possible significance of such findings is discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Isoelektrische Fokussierung und quantitative Schätzung von Serum-IgG und Liquor wurden in 85 Patienten mit idiopathischer Polyneuropathie (IP), die schon nach dem klinischen Verlauf (akute, subakute, rückfällige, chronische) unterschiedlich waren, durchgeführt. Akute IP zeigte eine Erhöhung von oligoklonalem und/oder polyklonalem Serum-IgG bei der progressiven Phase. Eine Störung der Blut-Liquor-Schranke mit polyklonaler IgG-intrathekaler Synthese lag auch in verschiedenen nicht akuten IP vor. Sie scheinen einen ungünstigen Verlauf anzuzeigen. Oligoklonale IgG-Synthese ereignet sich sehr selten im Liquor (Blut-Liquor-Schranke), aber sie ist ein häufiger Befund im Serum der Patienten mit IP. Regelwidrigkeiten in der IgG-Zusammensetzung im Serum scheinen weder spezifisch von einem bestimmten klinischen Verlauf der IP abzuhängen, noch von prognostischem Wert zu sein. Die mögliche Bedeutung solcher Befunde wird erörtert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramski, O., Webb, C., Teitalbaum, D., Arnon, R.: Cell mediated immunity to neural antigens in idiopathic polyneuritis and myeloradiculitis. Neurology 25, 1154–1159 (1975)
Arnason, B. G.: Idiopathic polyneuritis (Landry-Guillain-Barré-Strohl syndrome) and experimental allergic neuritis: a comparison. In: Immunological disorders of the nervous system, L. P. Rowland (ed.), pp. 156–177. Baltimore: William and Wilkins 1971
Behan, P. O., Currie, S.: The Landry-Guillain-Barré-Strohl syndrome. In: Clinical neuro-immunology, P. O. Behan, S. Currie (eds.), pp. 81–96. London: Saunders 1978
Bours, J.: The use of protein markers in thin layer isoelectric focusing. Sci. Tools 20, 29–34 (1973)
Castaigne, P., Brunet, P., Mouailhat, F.: Enquete clinique sur les polyradiculonévrites inflammatoires en France. Rev. Neurol. 115, 849–872 (1966)
Chazot, G., Berger, B., Carrier, H., Barbaret, C., Bady, B., Dumas, R., Creyssel, R., Schott, B.: Manifestation neurologiques des gammopathies monoclonales. Rev. Neurol. 132, 195–212 (1976)
Cook, S. D., Dowling, P. C., Murray, M. R., Whitaker, J. N.: Circulating demyelinating factors in acute idiopathic polyneuropathy. Arch. neurol. 24, 136–144 (1971)
Davies, H.: Thin layer isoelectric focusing. In: Isoelectric focusing, J. P. Arbutnott, A. Beeley (eds.), pp. 97–113. London: Butterworths 1973
Delpech, B., Lichtblau, E.: Etude quantitative des immunoglobulins G et de l'albumin du liquide cephalorachidien. Clin. Chim. Acta 37, 15–23 (1972)
Delmotte, P., Demonty, L.: Biochemical findings in multiple sclerosis. II: A detailed study of serum IgG, IgA, IgM levels in 772 multiple sclerosis patients compared with 226 neurological controls. J. Neurol. 211, 135–142 (1976)
Delmotte, P., Gonsette, R.: Biochemical findings in multiple sclerosis. IV: Isoelectric focusing of CSF gamma globulins in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases. J. Neurol. 215, 27–37 (1977)
Dubois-Dalcq, M., Buyse, M., Buyse, G., Gorce, F.: The action of Guillain-Barré syndrome serum on myelin. A tissue culture and electron microscopic analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 13, 67–83 (1971)
Hayamaker, W., Kernohan, J. W.: The Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A clinicopathologic report of fifty fatal cases and a critique of the literature. Medicine 38, 59–140 (1949)
Hinaman, R. C., Magee, K. R.: Guillain-Barré syndrome with a slow progressive onset and persistent elevation of spinal fluid protein. Ann. Inter. Med. 67, 1007–1013 (1967)
Iwashita, H., Inoue, N., Nagamatsu, K.: Polyneuropathy, pigmentation, diabetes mellitus and monoclonal gammopathy. Clin. Neurol. 11, 492–499 (1971)
Jensen, K. G.: Cerebrospinal fluid proteins in neurological diseases. Acta Neurol. Scand. 58, supp. 70, 75–87 (1978)
Kjellin, K. G., Vesterberg, O.: Isoelectric focusing of CSF proteins in neurological diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 23, 199–213 (1974)
Kjellin, K. G., Siden, A.: Cerebrospinal fluid findings on isoelectric focusing in known or probable infections of the nervous system, including Guillain-Barré syndrome. In: Proc. of the 11th World Congress of Neurology, Abs. N. 427, pp. 95–96. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica 1977
Kohn, J.: Benign paraproteinaemia. J. Clin. Pathol. 28, 77–82 (1976)
Lamoreaux, G., Jolicoeur, R., Giard, N., St Hilaire, M., Duplantis, F.: Cerebrospinal fluid proteins in multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system. Neurology 25, 537–546 (1975)
Laterre, E. C., Callawaert, A., Heremans, J. F.: Electrophoretic morphology of gammaglobulins in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system. Neurology 20, 982–990 (1970)
Leneman, F.: The Guillain-Barré syndrome. Arch. Int. Med. 118, 139–144 (1966)
Link, H.: Immunoglobulin abnormalities in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 18, 11–23 (1973)
Link, H.: Demonstration of oligoclonal immunoglobulin G in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Acta Neurol. Scand. 52, 111–120 (1975)
Livrea, P., Zimatore, G. B., Simone, I. L., Lepore, V., Trojano, M., Loreto, M., De Blasi, A., Gennarini, G. F.: Isoelectric focusing and crossed immunoisoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in neurological disorders. Acta Neurol. 33, 501–517 (1978)
Lowenthal, A.: Agar gel electrophoresis in neurology. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1964
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J.: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Masucci, E. F., Kurtzke, J. F.: Diagnostic criteria for the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 13, 483–501 (1971)
Nyland, H., Naess, A.: Lymphocite subpopulations in blood and cerebrospinal fluid from patients with acute Guillain-Barré syndrome. Eur. Neurol. 17, 247–252 (1978)
Osler, L. D., Sidell, A. D.: The Guillain-Barré syndrome. New Engl. J. Med. 262, 964–969 (1960)
Olsson, J. E., Petterson, B.: A comparison between agar gel electrophoresis and cerebrospinal fluid serum quotients of IgG and albumin in neurological diseases. Acta Neurol. Scand. 53, 308–318 (1975)
Prineas, J.: Polyneuropathies of undetermined cause. Acta Neurol. Scand. 46, supp. 44, 1–70 (1970)
Read, D. J., Vanhegan, R. I., Matthews, W. B.: Peripheral neuropathy and benign IgG paraproteinaemia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psych. 41, 215–219 (1978)
Rieder, H. P., Kaeser, H. E., Nusselt, L.: Liquorproteinveränderungen bei Polyneuritis. Schweiz. Med. Wschr. 102, 766–772 (1972)
Rosenberg, R. N., Aung, M. H., Tindall, R. S. A., Molenich, S., Baskin, F., Capra, J. D., Toben, H. R.: Idiopathic polyneuropathy associated with cytotoxic anti-neuroblastoma serum. Neurology 25, 1101–1110 (1975)
Schliep, G., Felgennauer, K.: Serum-CSF protein gradient, the blood-CSF barrier and the local immune response. J. Neurol. 218, 77–96 (1978)
Siden, A., Kjellin, K. G.: Isoelectric focusing of CSF and serum proteins in neurological disorders, combined with benign or malignant proliferations of reticulocytes, limphocytes and plasmocytes. J. Neurol. 216, 251–264 (1977)
Siden, A.: Crossed immunoelectrofocusing of cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulins. J. Neurol. 217, 103–109 (1977)
Siden, A., Kjellin, K. G.: Isoelectric focusing of CSF proteins in known or probable infectious neurological diseases and the Guillain-Barré syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 42, 1–15 (1979)
Soderholm, C., Smyth, J.: Crossed immunoelectric focusing for studies on protein microheterogeneity. In: Progress in isoelectric focusing, P. G. Righetti (ed.), pp. 99–114. Amsterdam: North Holland 1975
Stibler, H.: The normal cerebrospinal fluid proteins identified by means of thin layer isoelectric focusing and crossed immunoelectric focusing. J. Neurol. Sci. 36, 273–288 (1978)
Stibler, H.: Isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid proteins in degenerative diseases of the central nervous system. Ph. D. Thesis. Stockholm: Karolinska Hospital 1978
Tse, K. S., Arbesam, C. E., Tomasi, T. B., Tourville, D.: Demonstration of antimyelin antibodies by immunofluorescence in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 8, 880–887 (1971)
Yonezawa, T., Ishihara, Y., Matsuyama, H.: Studies on experimental allergic peripheral neuritis. I: Demyelinating patterns studied in vitro. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 27, 453–463 (1968)
Vesterberg, O.: Isoelectric focusing of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 257, 11–19 (1972)
Vesterberg, O.: Isoelectric focusing of proteins in thin layer of polyacrylamide gel. Sci. Tools 20, 22–29 (1973)
Whitaker, J. M., Sciabbarasi, B. S., Engel, W. K., Warmolts, J. R., Strober, W.: Serum immunoglobulin and complement (C3) levels. A study in adults with idiopathic chronic polyneuropathies and motor neuron diseases. Neurology 23, 1164–1173 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Livrea, P., Zimatore, G.B., Simone, I.L. et al. Isoelectric focusing and quantitative estimation of cerebrospinal fluid and serum IgG in idiopathic polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 223, 1–12 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313135
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00313135