Abstract
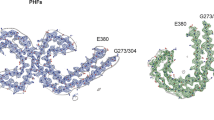
The cytoskeletal abnormalities of cortical neurons in human cerebral cortical dysplasia were compared by immunohistochemical methods to the neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Surgical specimens from cortical resections performed for the treatment of intractable childhood seizures as well as autopsied samples from AD patients were analyzed with different antibodies directed against high- or medium-molecular mass neurofilament epitopes, phosphorylated or non-phosphorylated forms of neurofilaments, ubiquitin, the microtubule-associated protein tau, and paired helical filaments (PHF), a defining feature of AD tangles. A strong abnormal increase in immunoreactivity to the high and medium molecular mass neurofilament epitopes was seen in hypertrophic neurons of cortical dysplasia. These neurofilamentous accumulations of cortical dysplasia as well as AD tangles also displayed immunoreactivity with antibodies also displayed immunoreactivity with antibodies against phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated neurofilament epitopes, tau and ubiquitin. Only the AD tangles, however, were immunoreactive to the antiserum to PHF. These results replicate and extend our previous findings that the neurofibrillary accumulations in cerebral cortical dysplasia share some common antigens with the neurofibrillary tangles of AD but do not demonstrate immunoreactivity to PHF antiserum. The results also suggest that the cytoskeletal abnormalities observed in neurons of cortical dysplasia may result in part from alterations in the level of expression, in phosphorylation state or in transport of cytoskeletal components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bancher C, Brunner C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Jellinger K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Grundke-Iqbal H, Wisniewski HM (1989) Accumulation of abnormally phosphorylated tau precedes the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimers's disease. Brain Res 477: 225–231
Bignami A, Palladini G, Zappella M (1968) Unilateral megalencephaly with nerve cell hypertrophy. An anatomical and quantitative study. Brain Res 9: 103–114
De Rosa MJ, Secor DL, Brown J, Peacock W, Duong T, Fisher RS, Vinters HV (1991) Neuropathology of hemimegalencephaly: morphologic studies from surgically resected specimens. Anat Rec 229: 20A
De Rosa MJ, Farrell MA, Vinters HV (1992) An assessment of the proliferative potential of “balloon cells” in focal cortical resections performed for childhood epilepsy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18: 566–574
De Rosa MJ, Secor DL, Barsom M, Fisher RS, Vinters HV (1992) Neuropathologic findings in surgically treated hemimegalencephaly: immunohistochemical, morphometric, and ultrastructural study. Acta Neuropathol 84: 250–260
Debus E, Weber K, Osborn M (1983) Monoclonal antibodies specific for glial fibrillary acidic (GFA) protein and for each of the neurofilament triplet polypeptides. Differentiation 25: 193–203
Duong T, De Rosa MJ, Vinters HV, Peacock W, Fisher RS (1991) Fibrillary tangles in hemimegalencephaly and Alzheimer's disease share a common antigen determinant. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17: 893
Duong T, Vinters HV, De Rosa MJ, Peacock W, Fisher RS (1991) Neurofilamentous tangles in the human hemimegalencephalic neocortex. Anat Rec 229: 24A
Farrell MA, De Rosa MJ, Curran JG, Secor DL, Cornford ME, Comair YG, Peacock WJ, Shields WD, Vinters HV (1992) Neuropathologic findings in cortical resections (including hemispherectomies) performed for the treatment of intractable childhood epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol 83: 246–259
Eriede R (1989) Developmental neuropathology, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 296–308
Goldman JE, Yen SH (1986) Cytoskeletal protein abnormalities in neurodegenerative diseases. Ann Neurol 19: 209–223
Ihara Y, Abraham C, Selkoe DJ (1983) Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature 304: 727–730
Joachim CL, Morris JH, Selkoe DJ, Kosik KS (1987) Tau epitopes are incorporated in a range of lesions in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 46: 611–622
Leigh PN, Probst A, Dale GE, Power DP, Brion JP, Dodson A, Anderton BH (1989) New aspects of the pathology of neurodegenerative disorders as revealed by ubiquitin antibodies. Acta Neuropathol 79: 61–72
Lichtenberg-Kraag B, Mandelkow E-M, Biernat J, Steiner B, Schröter C, Gustke N, Meyer HE, Mandelkow E (1992) Phosphorylation-dependent epitopes of neurofilament antibodies on tau protein and relationship with Alzheimer tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 5384–5388
Manz HJ, Phillips TM, Rowden G, McCullough DC (1979) Unilateral megalencephaly, cerebral cortex dysplasia, neuronal hypertrophy and heterotopia. Cytomorphometric, fluorimetric cytochemical, and biochemical analyses. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 45: 97–103
Price DL (1986) New perspectives on Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 9: 489–512
Robain O, Floquet C, Heldt N, Rozenberg F (1988) Hemimegalencephaly: a clinicopathologic study of four cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 14: 125–135
Robain O, Chiron C, Dulac O (1989) Electron microscopic and Golgi study in a case of hemimegalencephaly. Acta Neuropathol 77: 664–666
Scott CW, Vulliet PR, Caputo CB (1993) Phosphorylation of tau by proline-directed protein kinase (p34 cdc2/p58 cyclin A) decreases tau-induced microtubule assembly and antibody SMI33 reactivity. Brain Res 611: 237–242
Shaw G, Osborn M, Weber K (1986) Reactivity of a panel of neurofilament antibodies on phosphorylated and dephosphorylated neurofilaments. Eur J Cell Biol 42: 1–9
Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH (1983) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 6126–6130
Taylor DC, Faulkner MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JAN (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Townsend JJ, Nielson SL, Malamud N (1975) Unilateral hemimegalencephaly: hamartoma or neoplasm? Neurology 25: 448–453
Vinters HV, Miller BL, Pardridge WM (1988) Brain amyloid and Alzheimer disease. Ann Intern Med 109: 41–54
Vinters HV, Fisher RS, Cornford ME, Mah V, Secor DL, De Rosa MJ, Comair YG, Peacock WJ, Shields WD (1991) Morphologic substrates of infantile spasms: studies based on surgically resected cerebral tissue. Childs Nerv Syst 8: 8–17
Wiley CA, Love S, Skoglund RR, Lampert PW (1987) Infantile neurodegenerative disease with neuronal accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilaments. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 72: 369–376
Wisniewski K, Jervis GA, Moretz RC, Wisniewski HM (1979) Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles in diseases other than senile and presenile dementia. Ann Neurol 5: 288–294
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIH Training Grant HD 07032 (T.D.), NIH NS28383 (M.J.D., R.S.F., H.V.V.), NIH NS24596 (R.S.F.) and NIH NS26312 (H.V.V.). Ongoing work of the UCLA Pediatric Epilepsy Group is supported by the Milken Family Medical Foundations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duong, T., De Rosa, M.J., Poukens, V. et al. Neuronal cytoskeletal abnormalities in human cerebral cortical dysplasia. Acta Neuropathol 87, 493–503 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294176
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294176