Abstract
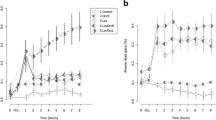
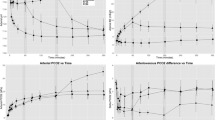
Increased lung vascular permeability leading to increased plasma protein extravasation and accumulation (PPA) is a characteristic feature of acute lung injury. Using a previously described technique, PPA was monitored in the lungs of patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) — an extreme example of acute lung injury in man. An external radiation probe detector was used to monitor the pulmonary accumulation of the plasma protein transferrin radiolabelled in-vivo with 113mIn. Ten patients with ARDS exhibiting increased PPA indices (>1.0x10-3/min) were given an intravenous infusion of terbutaline (7 μg/kg) over 30 min. Of the four patients in whom the post-drug PPA indices remained within the ARDS range, none survived, whilst five of the six patients in whom the post-drug PPA indices were reduced to below 1.0x10-3/min survived. PPA indices prior to the administration of terbutaline were not significantly different between the survivor (n=5) and non-survivor (n=5) groups. There was a significant decrease in the PPA indices following terbutaline in survivors (p<0.01) but not in non-survivors. Thus beta-2-agonists in therapeutic doses can inhibit increased lung vascular permeability in man. These findings may have prognostic and therapeutic implication for beta-2-agonists in ARDS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basran GS, Paul W, Morley J, Turner-Warwick M (1982a) Adrenoceptor-agonist inhibition of the histamine-induced cutaneous response in man. Br J Dermatol 107:Suppl 23;140–142
Basran GS, Morley J, Paul W, Turner-Warwick M (1982b) Evidence in man of synergistic interaction between putative mediators of acute inflammation and asthma. Lancet 1:935–937
Basran GS, McGivern DV (1983) Factors affecting the cutaneous response to intradermal injection of platelet activating factor in man. Br J Pharmacol 80:486P
Basran GS, Byrne AJ, Hardy JG (1985) A non-invasive technique for monitoring lung vascular permeability in man. Nucl Med Commun 6:3–10
Fowler AA, Hamman RF, Good, JT, Benson KN et al. (1983) Adult respiratory distress syndrome: risk with common predispositions. Ann Intern Med 98:593–597
Foy T, Marion J, Brigham KL, Harris TR (1979) Isoproterenol and aminophylline reduce lung capillary filtration during high permeability. J Appl Physiol 46:146–151
Gorin AB, Kohler J, DeNavdo G (1980) Non-invasive measurement of pulmonary transvascular protein flux in normal man. J Clin Invest 66:869–877
Horovitz JH, Carrico CJ, Shires GT (1974) Pulmonary response to major injury. Arch Surg 108:349–355
Majno G, Gilmore V, Leventhal M (1967) On the mechanism of vascular leakage caused by histamine-type mediators. Circ Res 21:833–847
Mizus I, Summer W, Farrukh I, Michael JR, Gurtner GH (1985) Isoproterenol or aminophylline attenuate pulmonary edema after acid lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis 131:256–259
Pepe PE, Hudson LD, Capillo J (1984) Early application of positive end expiratory pressure in ARDS. N Engl J Med 311:281–286
Persson CGA, Ekman M, Erjefalt I (1979) Vascular anti-permeability effects of β-receptor agonists and theophylline in the lung. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 44:216–220
Persson CGA, Erjefalt I, Grega GJ, Svensjo E, (1982) The role of β-receptor agonists in the inhibition of pulonary edema. Ann NY Acad Sci 384:544–556
Petty TL, Fowler AA (1982) Another look at ARDS. Chest 82:98–104
Ryan GB, Majno G (1977) Acute inflammation. Am J Pathol 86:186–276
Staub NC (1978) Pulmonary edema due to increased microvascular permeability to fluid and protein. Circ Res 43:143–151
Svensjo E, Persson CGA, Rutili G (1977) Inhibition of bradykinin induced macromolecular leakage from post-capillary venules by a β2-adrenoreceptor stimulant, terbutaline. Acta Physiol Scand 101:504–506
Svensjo E, Arfors K-E, Raymond RM, Grega GJ (1979) Morphological and physiological correlation of bradykinin-induced macromolecular efflux. Am J Physiol 236:H600-H606
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basran, G.S., Hardy, J.G., Woo, S.P. et al. Beta-2-adrenoceptor agonists as inhibitors of lung vascular permeability to radiolabelled transferrin in the adult respiratory distress syndrome in man. Eur J Nucl Med 12, 381–384 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252194
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252194