Summary
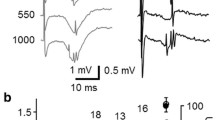
Intracellular recording in the in vitro hippocampal slice was utilized to examine the effects of nimodipine and nifedipine on CA1 pyramidal cell excitability. The excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) elicited by a single stimulus in stratum radiatum was enhanced by nifedipine as evidenced by increases in EPSP amplitude, area and slope. Threshold for synaptically-evoked somatic action potentials was decreased following either nifedipine or nimodipine application, often resulting in spontaneous action potential activity. A secondary, late EPSP-like event appeared in the intracellular recordings during and following bath application of nimodipine, and was associated with burst-like activity in field potential recordings. In accordance with the hydrophobic nature of these compounds, extensive washout in normal Krebs' solution failed to reverse their effects, but nifedipine's actions were photolabile. These results indicate that dihydropyridines can enhance synaptic efficacy in the CA1 region of the hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartus RT, Dean RL, Beer B, Lippa WS (1982) The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 217:408–417
Bono G (1985) In: Nimodipine: pharmacological and clinical properties. Betz E, Deck W, Hoffmeister F (eds) Schattauer, Stuttgart, pp 275–287
Campbell LW, Hao S-Y, Landfield PW (1988) Calcium-dependent inactivation of calcium currents in hippocampal neurons: effects of tetraethylammonium and nimodipine. Soc Neurosci Abstr 14:138
Docherty RJ, Brown DA (1986) Interaction of 1,4-dihydropyridines with somatic Ca currents in hippocampal CA1 neurones of the guinea pig in vitro. Neurosci Lett 70:110–115
Deyo RA, Straube KT, Disterhoft JF (1989) Nimodipine facilitates associative learning in aging rabbits. Science 243:809–811
Glossman H, Ferry DR, Goll A, Steiessnig J, Zernig G (1985) Calcium channels: introduction into their molecular pharmacology. In: Fleckenstein A, van Breemen C, Gross R, Hoffmeister F (eds) Cardiovascular effects of dihydrophine-type calcium antagonits and agonists. Springer, Berlin, pp 113–139
Gurney AM, Nerbonne JM, Lester HA (1985) Photoinduced removal of nifedipine reveals mechanisms of calcium antagonist action on single heart cells. J Gen Physiol 86:353–379
Hock FJ (1987) Drug influences on learning and memory in aged animals and humans. Neuropsychobiology 17:145–160
Itoh E, Kobayashi M, Sugawa M, Noda Y (1987) Age-related decrease in rat brain glucose metabolism and the ameliorating effect of BY-1949 on it. Jp J Pharmacol 43:73
Janis RR, Bellemann P, Sarmiento JG, Triggle DJ (1985) The dihydropyridine receptors. In: Fleckenstein A, Breemen C van, Gross R, Hoffmeister F (eds) Cardiovascular effects of dihydropyridine-type calcium antagonists. Springer, Berlin, pp 140–155
Jones RSG, Heinemann UH (1987) Differential effects of calcium entry blockers on pre- and postsynaptic influx of calcium in the rat hippocampus in vitro. Brain Res 416:257–266
Kamiya H, Sawada S, Yamamoto C (1988) Synthetic w-conotoxin blocks synaptic transmission in the hippocampus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 91:84–88
Kokubun S, Reuter H (1984) Dihydropyridine derivatives prolong the open state of Ca channels in cultured cardiac cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:4824–4827
Miller RJ (1987) Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science 235:46–52
Morgan PF, Tamborska E, Patel J, Marangos PJ (1987) Interactions between calcium channel compounds and adenosine systems in brain of rat. Neuropharmacology 26:693–699
O'Regan MH, Kocsis JD, Waxman SG (1990) Depolarization-dependent actions of dihydropyridines on synaptic transmission in the in vitro rat hippocampus. Brain Res 527:181–191
Phillis JW, O'Regan MH, Walter GA (1988) Effects of nifedipine and felodipine on adenosine and inosine release from the hypoxemic rat cerebral cortex. Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:179–185
Rane SG, Holz GG, Dunlap K (1987) Dihydropyridine inhibition of neuronal calcium current and substance P release. Pflügers Arch 409:361–366
Sanguinetti MC, Kass RS (1984) Photoalteration of calcium channel blockade in the cardiac purkinje fiber. Biophys J 45:873–879
Sanna E, Wright RG, Hanbauer I (1985) Selective localization of 3H-nitredipine recognition sites and voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels in nerve cell bodies of caudate nuclei. Fed Proc Am Soc Exp Biol 45:1008
Scriabine A, Schuurman T, Traber J (1989) Pharmacological basis for the use of nimodipine in central nervous system disorders. FASEB J 3:1799–1806
Tanabe S, Ikeda Y, Shiraki Y, Sakai K (1988) Enhancement of adenosine-induced relaxant responses of the guinea-pig isolated taenia coli and aorta by a novel nootropic agent BY-1949:comparison with dipyridamole. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:582–583
Thompson LT, Deyo RA, Disteroft JF (1989) Effects of nimodipine and other Ca++ channel agents on the activity of single hippocampal pyramidal cells and closely associated interneurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 15:261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: Neuroscience Research Laboratory/127A
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Regan, M.H., Kocsis, J.D. & Waxman, S.G. Nimodipine and nifedipine enhance transmission at the Schaffer collateral CA1 pyramidal neuron synapse. Exp Brain Res 84, 224–228 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231778
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00231778