Abstract
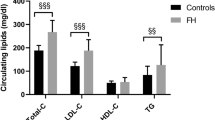
The mechanisms regulating plasma levels of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] are largely unknown. A two- to three-fold increase in Lp(a) levels in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) has implied that LDL receptor activity may be an important factor in determining plasma Lp(a) levels, as it is in determining low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol concentration. Common apolipoprotein E (apoE) variants also affect plasma LDL cholesterol levels. We therefore examined the effect of the common apoE variants on plasma Lp(a) levels in 149 patients with heterozygous FH. Patients with the apoE2 allele (n = 11) had significantly higher plasma levels of LDL cholesterol compared to those with a apoE3E3 phenotype, while patients with the apoE4 isoform had similar levels. However, there was a significant effect of the apoE2 allele in lowering Lp(a) levels, compared to the apoE3E3 group. The median Lp(a) concentration in patients possessing an apoE2 isoform was 13.1 mg/dl below the median, while in those with an apoE4 allele the median Lp(a) levels were 4.13 mg/dl higher. There was a marked inverse correlation between plasma Lp(a) and LDL cholesterol concentration in the FH patients carrying the apoE2 allele. Our data imply that difference in Lp(a) levels observed between FH patients with different apoE isoforms does not result from altered clearance of Lp(a) via the LDL receptor pathway, and suggest that apoE mediated hepatic up-take, or conversion, of remnant particles may be determining Lp(a) production rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- apo:
-
apoprotein
- CHD:
-
coronary heart disease
- FH:
-
familial hypercholesterolaemia
- HDL:
-
high-density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
low-density lipoprotein
- Lp(a):
-
lipoprotein(a)
References
Black IW, Wilcken DEL (1992) Decreases in apolipoprotein(a) after renal transplantation: implications for lipoprotein(a) metabolism. Clin Chem 38:353–357
Boerwinkle E, Menzel HJ, Kraft HG, Utermann G (1989) Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein traint. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Gen 82:73–78
Boerwinkle E, Leffert CC, Lin J, Lackner C, Chiesa G, Hobbs HH (1992) Apolipoprotein(a) gene accounts for greater that 90% of the variation in plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations. J Clin Invest 90:52–60
Carlson LA, Hamsten A, Asplund A (1989) Pronounced lowering of serum levels of lipoprotein Lp(a) in hyperlipidaemic subjects treated with nicotinic acid. J Intern Med 226:271–276
Davignon J, Gregg RE, Sing CF (1988) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 8:1–21
de Knijff P, Kaptein A, Boomsma D, Princen HMG, Frants R, Havekes L (1991) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism effect plasma levels of lipoprotein(a). Atherosclerosis 90:169–174
Demant T, Bedford D, Packard CJ, Shepherd J (1991) Influence of apolipoprotein E polymorphism on apolipoprotein B-100 metabolism in normolipidaemic subjects. J Clin Invest 88:1490–1501
Eto M, Watanabe K, Chonan N, Ishii K (1988) Familial hypercholesterolaemia and apolipoprotein E4. Atherosclerosis 72:123–128
Friedewald WT, Levy R, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1989) Familial hypercholesterolemia. In: Scriver CR et al. (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1215–1250
Hazzard WR, Albers JJ, Baron P, Miller N, Warnick GR, Lewis B (1981) Association of isoapolipoprotein-E3 deficiency with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: implications for lipoprotein physiology. Lancet 1:298–301
Hixon JE, Vernier DT (1990) Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 31:545–548
Hopkins PN, Wu LL, Schumacher MC, Emi M, Hegele RM, Hunt SC, Lalouel J-M, Williams R (1991) Type III dyslipoproteinemia in patients heterozygous for familial hypercholesterolemia and apolipoprotein E2: evidence for gene-gene interaction. Arterioscler Thromb 11:1137–1146
Houlston R, Lewis B, Humphries SE (1991) Polymorphism of the apolipoprotein B and E genes and their possible roles in familial and non-familial combined hyperlipidaemia. Disease Markers 9:319–325
Joven J, Villabona C, Vilella E, Masana L, Alberti R, Vailes M (1990) Abnormalities of lipoprotein metabolism in patients with the nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med 323:578–584
Kannel WB, Dawber TR, Kagan A, Revotskie N, Stokes J (1961) Factors of risk in the development of coronary heart disease-six year follow-up experience. The Framingham Study. Ann Intern Med 55:33–50
Klausen IC, Gerdes LU, Meinertz H, Hansen FA, Faergeman O (1993) Apolipoprotein (a) polymorphism predicts the increase of Lp(a) by pravastatin in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia treated with bile acid sequestration. Eur J Clin Invest 23:240–245
Knight BL, Perombelon YFN, Soutar AK, Wade DP, Seed M (1991) Catabolism of lipoprotein (a) in familial hypercholesterolaemic subjects. Atherosclerosis 87:227–237.
Koizumi J, Koizumi I, Uno Y, Inazu A, Kajinami K, Haraki T, Yagi K, Kamon N, Miyamoto S, Takegoshi T, Mabuchi H, Takeda R, Tani N, Takada S (1993) Reduction of lipoprotein(a) by LDL apheresis using a dextran sulfate cellulose column in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 100:65–74
Kostner GM, Gavish D, Leopold B, Bolzano K, Weintraub MS, Breslow JL (1989) HMG CoA reductase inhibitors lower LDL cholesterol without reducing Lp(a) levels. Circulation 80:1313–1319
Kraft H-G, Dieplinger H, Hoye E, Utermann G (1988) Lp(a) phenotyping by immunoblotting with polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. Arteriosclerosis 8:212–216
Kraft HG, Menzel HJ, Hoppichler F, Vogel W, Utermann G (1989) Changes of genetic apolipoprotein phenotypes caused by liver transplantation. J Clin Invest 83:137–142
Krempler F, Kostner G M, Bolzano K, Sandhofer F (1980) Turnover of Lp(a) in man. J Clin Invest 65:1483–1490
Lackner C, Boerwinkle E, Leffert CC, Rahmig T, Hobbs HH (1991) Molecular basis of apolipoprotein(a) isoform size heterogeneity as revealed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Invest 87:2153–2161
Mahley R W, Rall S C (1989) Type III hyperlipoproteinemia (dysbetalipoproteinemia): the role of apolipoprotein E in normal and abnormal lipoprotein metabolism. In; Scriver CR et al (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1195–1213
Mailly F, Moll P, Kottke BA, Kamboh MI, Humphries SE, Ferrell RE (1992) Estimation of the frequency of isoformgenotype discrepancies at the apolipoprotein E locus in heterozygotes for the isoforms. Genet Epidemiol 9:239–248
Mbewu AD, Durrington PN (1990) Lipoprotein(a): structure, properties and possible involvment in thrombogenesis and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 85:1–14
Mbewu AD, Bhatnagar D, Durrington PN, Hunt L, Ishola M, Arrol S, Mackness M, Lockley P, Miller JP (1991) Serum lipoprotein(a) in patients heterozygous for familial hypercholesterolemia, their relatives, and unrelated control populations. Arterioscler Thromb 11:940–946
Morrisett JD, Guyton JR, Gaubatz JW, Gotto AM Jr (1987) Lipoprotein(a): structure, metabolism, and epidemiology. In: Gotto AM (ed) Plasma lipoproteins: new comprehensive biochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 129–152
Perombelon NYF, Gallagher JJ, Myant NB, Soutar AK, Knight BL (1992) Lipoprotein(a) in subjects with familial defective apolipoprotein B100. Atherosclerosis 92:203–212
Rader DJ, Cain W, Zech LA, Usher D, Jr HBB (1993) Variation in lipoprotein(a) concentrations among individuals with the same apolipoprotein(a) isoform is determined by the rate of lipoprotein(a) production. J Clin Invest 91:443–447
Sandholzer C, Feussner G, Brunzell J, Utermann G (1992) Distribution of apolipoprotein(a) in plasma from patients with lipoprotein lipase deficiency and with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest 90:1958–1965
Seed M, Hoppichler F, Reaveley D, McCarthy S, Thompson GR, Boerwinkle E, Utermann G (1990) Relation of serum lipoprotein(a) concentration and apolipoprotein(a) phenotype to coronary heart disease in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 322:1494–1499
Seed M, O'Connor B, Perombelon N, O'Donnell M, Reaveley D, Knight B (1993) The effect of nicotinic acid and acipimox on lipoprotein(a) concentration and turnover. Atherosclerosis 101:61–68
Steinmetz A, Jakobs C, Motzny S, Kaffarnik H (1989) Differential distribution of apolipoprotein E isoforms in human plasma lipoproteins. Arteriosclerosis 9:405–411
Thiery J, Armstrong VW, Schleef J, Creutzfeldt C, Creutzfeldt W, Seidel D (1988) Serum lipoprotein Lp(a) concentrations are not influenced by an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor. Klin Wochenschr 66:462–463
Thompson GR, Seed M, Niththyananthan S, McCarthy S, Thorogood M (1989) Genotypic and phenotypic variation in familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis 9:I-75–80
Utermann G, Menzel HJ, Kraft HG, Duba HC, Kemmler HG, Seitz C (1987) Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes: Inheritance and relation to Lp(a)-lipoprotein concentration in plasma. J Clin Invest 80:458–465
Utermann G, Hoppichler F, Dieplinger H, Seed M, Thompson G, Boerwinkle E (1989) Defects in the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene affect lipoprotein(a) levels: Multiplicative interaction of two gene loci associated with premature atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:4171–4174
White ALRainwater DLLanford RE (1993) Intracellular maturation of apolipoprotein(a) and assembly of lipoprotein(a) in primary baboon hepatocytes. J Lipid Res 34:509–517
Wiklund O, Angelin B, Olofsson S-O, Eriksson M, Fager G, Berglund L, Bondjers G (1990) Apolipoprotein(a) and ischaemic heart disease in familial hypercholesterolaemia. Lancet 335:1360–1363
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindahl, G., Mailly, F., Humphries, S. et al. Apolipoprotein E phenotype and lipoprotein(a) in familial hypercholesterolaemia implication for lipoprotein(a) metabolism. Clin Investig 72, 631–638 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227457
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227457