Summary
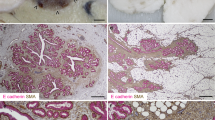
Immunoperoxidase methods were used to localize secretory component, immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin G1 in mammary tissue from dairy cows. In lactating tissue, immunostaining for immunoglobulin A and secretory component was observed primarily in the luminal contents of alveoli. By day 2 of involution, alveolar epithelial cells stained for both immunoglobulin A and secretory component. Staining of alveolar epithelial cells for immunoglobulin A and secretory component continued throughout the period of mammary involution. No staining for secretory component was observed in the interalveolar stromal area. Immunoglobulin G1 immunostaining was localized primarily in the interalveolar areas in lactating tissue, but was localized at the apical and basolateral surface of alveolar cells on day 2 of involution. In contrast to immunoglobulin A, immunoglobulin G1 staining of epithelial cells did not persist and was primarily in the interalveolar areas by day 4. These results suggest that an increased localization of immunoglobulin G1 in bovine mammary epithelial cells may occur transiently in early involution, while an increase in immunoglobulin A and secretory component localization in epithelial cells persists throughout involution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandtzaeg P (1983) The secretory immune system of lactating human mammary glands compared with other exocrine organs. Ann NY Acad Sci 409:353–382
Brantzaeg P (1985) Role of J chain and secretory component in receptor-mediated glandular and hepatic transport of immunoglobulins in man. Scand J Immunol 22:111–146
Guidry AJ, Butler JE, Pearson RE, Weinland BT (1980) IgA, IgGl, IgG2, IgM and BSA in serum and mammary secretion throughout lactation. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 1:329–341
Hurley WL, Rejman JJ (1986) β-Lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin in mammary secretions during the dry period: Parallelism of concentration changes. J Dairy Sci 69:1642–1647
Labib RS, Calvanico NJ, Tomasi TB (1976) Bovine secretory component. Isolation, molecular size and shape, composition, and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem 251:1969–1974
Larson BL (1985) Biosynthesis and cellular secretion of milk. In: Larson BL (ed) Lactation. Iowa State University Press, Ames, pp 129–163
Larson BL, Heary HL, Jr, Devery JE (1980) Immunoglobulin production and transport by the mammary gland. J Dairy Sci 63:665–671
Leary HL, Jr, Larson BL (1982) Intracellular transport of IgGl and IgG2 through the prepartum mammary alveolar cell. J Dairy Sci 65(Suppl 1):82–83
Leary HL, Jr, Larson BL, Nelson DR (1982) Immunohistochemical localization of IgGl and IgG2 in prepartum and lactating bovine mammary tissue. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 3:509–514
Lee CS, Lascelles AK (1970) Antibody-producing cells in antigenically stimulated mammary glands and in the gastro-intestinal tract of sheep. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci 48:525–535
Nickerson SC, Pankey JW, Boddie NT (1984) Distribution, lactation, and ultrastructure of plasma cells in the uninfected, lactating bovine mammary gland. J Dairy Res 51:209–217
Saint-Marie G (1962) A paraffin embedding technique for studies employing immunofluorescence. J Histochem Cytochem 10:250–256
Sasaki M, Larson BL, Nelson DR (1977) Kinetic analyis of the binding of immunoglobulins IgG1 and IgG2 to bovine mammary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 497:160–170
Solari R, Kraehenbuhl J-P (1984) Biosynthesis of the IgA antibody receptor: A model for the transepithelial sorting of a membrane glycoprotein. Cell 36:61–71
Watson DL, Brandon MR, Lascelles AK (1972) Concentrations of immunoglobulin in mammary secretion of ruminants during involution with particular reference to selective transfer of IgG1. Aust J Exp Biol Sci 50:535–539
Welty FK, Smith KL, Schanbacher FL (1976) Lactoferrin concentration during involution of the bovine mammary gland. J Dairy Sci 59:224–231
Wheelock JV, Smith A, Dodd FH, Lyster RLJ (1967) Changes in the quantity and composition of mammary gland secretion in the dry period between lactations. I. The beginning of the dry period. J Dairy Res 34:1–12
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, S., Hurley, W.L., Hegarty, H.M. et al. Immunohistological localization of IgG1, IgA and secretory component in the bovine mammary gland during involution. Cell Tissue Res. 251, 81–86 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215450
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00215450