Summary
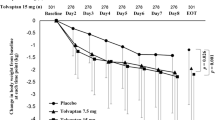
The effects of long-term therapy (70 days) with torasemide (20 mg/day), a new loop diuretic, were compared with those of furosemide (50 mg/day) in a randomized double-blind trial. Both drugs were administered in association with spironolactone (200 mg/day) in 28 nonazotemic cirrhotic patients with controlled ascites. The treatments did not modify creatinine clearance and exhibited a similar effect on body weight, urinary volume, and fractional excretion of uric acid, sodium, and chloride. The effect of torasemide on fractional potassium excretion was lower than that of furosemide. Torasemide showed higher sparing effect than furosemide on calcium, inorganic phosphate, and magnesium excretion and stronger action on free water clearance. No changes in serum parameters were induced by either treatment. Two episodes of hepatic encephalopathy occurred in the torasemide group. In view of its effects on sodium and water excretion and on other urinary parameters, torasemide can represent an alternative tool for the long-term treatment of ascites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achammer I, Hacker W, Glocke M (1988)Efficacy and safety of torasemide in patients with chronic heart failure. Arzneimittelforschung 38:184–187
Ambroes Y, Ronflette I, Dodion L (1986) Diuretic activity, safety and pharmacokinetics of torasemide during chronic treatment in normal subjects. Eur J Pharmacol 31 [Suppl]:1–7
Arroyo V, Epstein M, Gallus G, Gentilini P, Ring-Larsen H, Salerno F (1989) Refractory ascites in cirrhosis: mechanism and treatment. Gastroenterol Int 2:195–207
Broekhuysen J, Deger F, Douchamps J, Ducarne H, Herchueltz A (1986) Torasemide, a new potent diuretic. Doubleblind comparison with furosemide. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 31 [Suppl]:29–34
Burke TJ, Robinson RR, Clapp JR (1972) Determinants of the effect of furosemide on the proximal tubule. Kidney Int 1:12–18
Classen W, Khartabil T, Imm ST, Kindler J (1988) Torasemide for diuretic treatment of advanced chronic renal failure. Arzneimittelforschung 38:209–211
Elia GF, Ferrari C, Degli Antoni A, Penna A, Fiaccadori F (1989) A short-term clinical study of a new loop diuretic, torasemide, in cirrhosis. Ital J Gastroenterol 21:324–328
Epstein M (1988) Diuretic therapy in liver disease. In: Epstein M (ed) The kidney in liver disease, 3rd edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 537–550
Frommer JP, Wesson DE, Eknoyan G (1986) Side effects and complications of diuretic therapy. In: Eknoyan G, Martinez-Maldonado M (eds) The physiological basis of diuretic therapy in clinical medicine. Grime and Stratton, Orlando, pp 293–309
Gerbes AL, Bertheau U, Falkner C, Jungst D, Paumgartner G (1991) Advantages of torasemide vs furosemide in patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites (abstract). Gastroenterology 100: A746
Kult J, Hacker W, Glocke M (1988) Comparison of efficacy and tolerance of different oral doses of torasemide and furosemide in patients with advanced chronic renal failure. Arzneimittelforschung 38:212–214
Laffi G, Marra F, Buzzelli G, Azzena G, Meacci E, De Feo ML, La Villa G, Gentilini P (1991) Comparison of the effects of torasemide and furosemide in nonazotemic cirrhotic patients with ascites: a randomized, double-blind study. Hepatology 13:1101–1105
Lesne M (1988) Comparison of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of torasemide and furosemide in healthy volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung 38:160–163
Perez-Ayuso RM, Arroyo V, Planas R, Gaya J, Bory F, Rimola A, Rivera F, Rodés J (1984) Randomized comparative study of efficacy of furosemide versus spironolactone in non-azotemic cirrhosis with ascites. Gastroenterology 84:961–968
Seldin DW, Eknoyan G, Suky WN, Rector FC jr (1966) Localization of diuretic action from the pattern of water and electrolyte excretion. Ann NY Acad Sci 139:328–343
Spannbrucker N, Achammer I, Metz P, Glocke M (1988) Comparative study on the antihypertensive efficacy of torasemide and indapamide in patients with essential hypertension. Arzneimittelforschung 38:190–193
Spieker C, Zidek W, Hacker W, Schmidt W, Vetter H (1988) Assessment of intracellular sodium and calcium in essential hypertension during diuretic treatment. Arzneimittelforschung 38:188–190
Steele H, Oppenheimer S (1969) Factors affecting urate excretion following diuretic administration in man. Am J Med 47:564–574
Wittner M, Di Stefano A, Wangemann P, Greger R (1991) How do loop diuretics act? Drugs 41 [Suppl 3]: pp 1–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiaccadori, F., Pedretti, G., Pasetti, G. et al. Torasemide versus furosemide in cirrhosis: a long-term, double-blind, randomized clinical study. Clin Investig 71, 579–584 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208486
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208486