Abstract
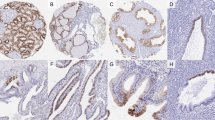
A series of 27 renal cell carcinomas 4 oncocytomas and 7 samples of tumour free kidney parenchyma were analysed immunohistochemically using eight different CD44 isoform-specific monoclonal antibodies. In normal kidney expression of CD44 isoforms (containing variant exons v6, v7/8 and v10) was found predominantly at the distal tubules. The majority of clear cell carcinomas investigated showed expression of variant exons v5, v7/8 and v10, but not v6. Lack of CD44v6 expression was confirmed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis. Carcinomas of the chromophilic cell type were almost completely devoid of CD44 expression, including the standard form CD44s. This study shows that there are statistically significant differences in the CD44 expression pattern of the two major histological subtypes of renal cell carcinomas (clear cell and chromophilic carcinomas). Moreover, the almost complete lack of CD44 expression in chromophilic carcinomas contrasts with carcinomas of other histogenetic origin investigated including stomach, breast and lung which express various CD44 isoforms abundantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolf G, Bodo G, Swetly P (1982) Production of monoclonal antibodies to human IFN-α and their use for analysis of the antigenic composition of various natural interferons. J Cell Physiol Suppl 2:61–68
Allen RW, Trach KA, Hoch JA (1987) Identification of the 37-kDa protein displaying a variable interaction with the erythroid cell membrane as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 262:649–653
Brooks L, Niedobitek G, Agathanggelou A, Farrell P (1995) The expression of variant CD44 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma is unrelated to expression of LMP-1. Am J Pathol 146:1102–1112
Dall P, Heider K-H, Hekele A, Minckwitz G von, Kaufmann M, Ponta H, Herrlich P (1994) Surface protein expression and messenger RNA-splicing analysis of CD44 in uterine cervical cancer and normal cervical epithelium. Cancer Res 54:3337–3341
Fox SB, Fawcett J, Jackson DG (1994) Normal human tissues, in addition to some tumors, express multiple different CD44 isoforms. Cancer Res 54:4539–4546
Friedrichs K, Franke F, Lisboa B-W, Kügler G, Gille I, Terpe H-J, Hölzel F, Maass H, Günthert U (1995) CD44 isoforms correlate with cellular differentiation but not with prognosis in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 55:5424–5433
Günthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S, Zöller M, Haußmann I, Matzku S, Wenzel A, Ponta H, Herrlich P (1991) A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell 65:13–24
Haynes BF, Liao H-X, Patton KL (1991) The transmembrane hyaluronate receptor (CD44): multiple functions, multiple isoforms. Cancer Cells 3:347–350
Heider K-H, Dämmrich J, Skroch-Angel P, Müller-Hermelink H-K, Vollmers HP, Herrlich P, Ponta H (1993) Differential expression of CD44 splice variants in intestinal- and diffuse-type human gastric carcinomas and normal gastric mucosa. Cancer Res 53:4197–4203
Heider K-H, Hofmann M, Horst E, Berg F van den, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST (1993) A human homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44 is expressed in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps. J Cell Biol 120:227–233
Hofmann M, Rudy W, Zöller M, Tölg C, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Günthert U (1991) CD44 splice variants confer metastatic behavior in rats: homologous sequences are expressed in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 51:5292–5297
Kaufmann M, Heider K-H, Sinn H-P, Minckwith G von, Ponta H, Herrlich P (1995) CD44 variant exon epitopes in primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet 345:615–619
Koopman G, Heider K-H, Horst E, Adolf GR, Berg F van den, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST (1993) Activated human lymphocytes and aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphomas express a homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44. J Exp Med 177:897–904
Mayer B, Jauch KW, Günthert U, Figdor CG, Schildberg F, Funke I, Johnson JP (1993) De-novo expression of CD44 and survival in gastric cancer. Lancet 342:1019–1022
Mulder JWR, Kruyt PM, Sewnath M, Oosting J, Seldenrijk CA, Weidema WF, Offerhaus GJ, Pals ST (1994) Expression of exon v6 containing CD44 proteins in human colorectal cancer is associated with unfavorable prognosis in long term follow up. Lancet 344:1470–1472
Screaton GR, Bell MV, Jackson DG, Cornelis FB, Gerth U, Bell JI (1992) Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:12160–12164
Seiter S, Arch R, Reber S, Komitowsky D, Hofman M, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Matzku S, Zöller M (1993) Prevention of tumor metastatis formation by anti-variant CD44. J Exp Med 177:443–455
Stamenkovic I, Amiot M, Pesando JM, Seed B (1989) A lymphocyte molecule implicated in lymph node homing is a member of the cartilage link protein family. Cell 56:1057–1062
Stauder R, Eisterer W, Thaler J, Günthert U (1985) CD44 variant isoforms in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a new independant prognostic factor. Blood 85:2885–2899
Terpe HJ, Tajrobehkar K, Günthert U, Altmannsberger M (1993) Expression of cell adhesion molecules alpha-2, alpha-5 and alpha-6 integrin, E-cadherin, N-CAM and CD44 in renal cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch [A] 422:219–224
Thoenes W, Störkel S, Rumpelt HJ (1986) Histopathology and classification of renal cell tumors (adenomas, oncocytomas and carcinomas). Pathol Res Pract 181:125–143
Tölg C, Hofmann M, Herrlich P, Ponta H (1993) Splicing choice from ten variant exons establishes CD44 variability. Nucleic Acids Res 21:1225–1229
Wielenga VJ, Heider K-H, Offerhaus GJA, Adolf GR, Berg F van den, Ponta H, Herrlich P, Pals ST (1993) Expression of CD44 variant proteins in human colorectal cancer is related to tumor progression. Cancer Res 53:4754–4756
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heider, K.H., Adolf, G.R., Ratschek, M. et al. Expression of CD44 isoforms in human renal cell carcinomas. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 428, 267–273 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196700
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196700