Abstract
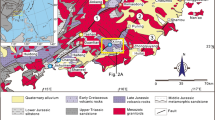
The Olympias Pb-Zn(Au, Ag) sulfide ore deposit, E. Chalkidiki, N. Greece, is hosted by marbles of the polymetamorphic Kerdilia Formation of Paleozoic or older age. The geologic environment of the ore also comprises biotite-hornblende gneisses and amphibolites intruded by Tertiary pegmatite-aplite dikes, lamprophyre dikes, the 30-Ma Stratoni granodiorite, and porphyritic stocks. Only limited parts of the deposit display shear folding and brecciation; most of it is undeformed. Microthermometry of fluid inclusions in gangue syn-ore quartz indicates three types of primary and pseudosecondary inclusions: (1) H2O-rich, 1–18 wt.% NaCl equivalent, <3.6 mol% CO2; (2) H2O-CO2 inclusions, <4wt.% NaCl equivalent, with variable CO2 contents, coexisting in both undeformed and deformed ore; (3) aqueous, highsalinity (28–32 wt,% NaCl equivalent) inclusions found only in undeformed ore. Type 2 inclusions are differentiated into two sub-types: (2a) relatively constant CO2 content in the narrow range of 8–15 mol% and homogenization to the liquid phase; (2b) variable CO2 content between 18 and 50 mol% and homogenization to the vapor phase. Type 1 and 2b inclusions are consistent with trapping of two fluids by unmixing of a high-temperature, saline, aqueous, CO2-bearing fluid of possible magmatic origin, probably trapped in type 2a inclusions. Fluid unmixing and concomitant ore mineralization took place at temperatures of 350 ± 30 °C and fluctuating pressures of less than 500 bar, for both undeformed and deformed ores. The wide salinity range of type 1 inclusions probably represents a complex effect of salinity increase, due to fluid unmixing and volatile loss, and dilution, due to mixing with low-salinity meteoric waters. High solute enrichment of the residual liquid, due to extreme volatile loss during unmixing, may account for high salinity type 3 inclusions. The Olympias fluid inclusion salinity-temperature gradients bear similarities to analogous gradients related to Pb-Zn ores formed in “granite”-hosted, low-T distalskarn, skarn-free carbonate-replacement and epithermal environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angus, S., Armstrong, B., De Reuc, K.M. (1976) International thcrmodynamic tables of fluid state 3: carbon dioxide. Pergamon Press, Oxford, 386 pp
Bodnar, R.J., Burnham, C.W., Sterner, S.M. (1985) Synthetic fluid inclusions in natural quartz. III. Determination of phase equilibrium in the system H2O-NaCl to 1000 °C and 1500 bar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 49:1861–1873
Borisenko, A.S. (1977) Study of the salt composition of solutions in gas-liquid inclusions in minerals by the cryometric method. Soviet. Geol. Geophys 18:11–19
Bowers, T.S., Helgeson, H.C. (1983) Calculation of the thermodynamic and geochemical consequences of non ideal mixing in the system H2O-CO2-NaCl on phase relations in geologic systems: equation of state for H2O-CO2-NaCl fluids at high pressures and temperatures. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 47:1247–1275
Brown, P.E. (1989) FLINCOR: a microcomputer program for the reduction and investigation of fluid inclusion data. Am. Mineral. 74:1390–1393
Burnham, C.W. (1979) Magmas and hydrothermal fluids. In: Barnes, H.L. (ed.) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, 2nd ed. Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 71–136
Bussell, M.A., Alpers, C.N., Petersen, U., Shepherd, T.J., Bermudez, C., Baxter, A.N. (1990) The Ag-Mn-Pb-Zn vein, replacement and skarn deposits of Uchucchaeua. Peru: studies of structure, mineralogy, metal zoning, Sr isotopes and fluid inclusions. Econ. Geol. 85:1348–1383
Casadevall, T., Ohmoto, H. (1977) Sunnyside mine, Eureka mining district, San Juan, Colorado: geochemistry of gold and base metal ore deposition in a volcanic environment. Econ. Geol. 72:1285–1320
Collins, P.L.F. (1979) Gas hydrates in CO2-bearing fluid inclusions and the use of freezing data for estimation of salinity. Econ. Geol. 74:1435–1444
Crawford, M.L. (1981) Phase equilibria in aqueous fluid inclusions. Mineralog. Assoc. Canada Short Course Handbook 6:75–100
Diamond, L.W. (1990) Fluid inclusion evidence for P-V-T-X evolution of hydrothermal solutions in late-Alpine gold-quartz veins at Brusson, Val D'Ayas, NW Italian Alps. Am. J. Sci. 290:912–958
Diamond, L.W. (1992) Stability of CO2 clathrate hydrate + CO2 (liquid-)-CO2 vapor + aqueous KCl-NaCl solutions: experimental determination and application to salinity estimates of fluid inclusions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 56:273–280
Drummond, S.E., Ohmoto, H. (1985) Chemical evolution and mineral deposition in boiling hydrothermal systems. Econ. Geol. 80:126–147
Ellis, A.J. (1979) Explored geothermal systems. In: Barnes, H.L. (ed.) Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp. 632–683
Erwood, R.J., Kesler, S.E., Cloke, P.L. (1979) Compositionally distinct, saline hydrothermal solutions, Naica mine, Chihuaua, Mexico. Econ. Geol. 74:95–108
Gehrig, M. (1980) Phasengleichgewichte und pVT-Daten ternaerer mischungen aus Wasser, Kohlendioxid und Natriumchlorid bis 3 kbar und 550 C. Hochschulsammlung Naturwissenschaft, Chemie Band l, Hochschulverlag, Freiburg, 109 pp
Gilg, H.A., Frei, R., Kalogeropoulos, S.I., Nicolaou, M. (1992) Metamorphism and polygenesis of the Madem Lakos polymetallic Sulfide deposit, Greece-a discussion. Econ. Geol. 87:1184–1193
Gilg, H.A. (1993) Geochronology (K-Ar), fluid inclusion, and stable isotope (C,H,O) studies of skarn, porphyry copper, and carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn (Au, Ag) replacement deposits in the Kassandra mining district. Unpub. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, 153 PP
Gilg, H.A., Frei, R. (1994) Chronology of magmatism and mineralization in the Kassandra mining area, Greece. The potentials and limitations of dating hydrothermal ilutes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 58:2107–2122
Godwin, C.I., Watson, P.H., Shen, K. (1986) Genesis of the Lass vein system, Beaverdell silver camp, south-central British Columbia. Can. J. Earth Sci. 23:1615–1626
Haas, J.L., Jr. (1976) Physical properties of the coexisting phases and thermochemical properties of the H2O component in boiling NaCl solutions. US Geol. Survey Bull., 1421-A, 73 pp
Hedenquist, J.W., Henley, R.W. (1985) The importance of CO2 freezing point measurements of fluid inclusions: evidence for geothermal systems and implications for epithermal ore deposition. Econ. Geol. 80:1379–1406
Higgins, N.C. (1985) Wolframite deposition in a hydrothermal vein system: the Grey River tungsten prospect, Newfoundland, Canada. Econ. Geol. 80:1297–1327
Kalogeropoulos, S.I., Bitzios, D., Eliopoulos, D., Veranis, N. (1987) Geological, mineralogical and geochemical study of the Olympias type Pb-Zn (Au, Ag) sulfide ore deposit, E. Chalkidiki, N. Greece. Contribution to its metallogeny. Mineral Dep. Res. 19, I.G.M.E., 36 pp
Kalogeropoulos, S.I., Kilias, S.P. (1989) Oxygen (18O) and carbon (13C) isotopic changes in carbonate rocks and minerals in relation to the Olympias Pb-Zn (Au, Ag) sulfide mineralization, E, Chalkidiki, N. Greece. Contribuion to metallogeny and exploration. Geol. Soc. Greece Bull. 23/2:261–269 (in Greek with English Abstract)
Kalogeropoulos, S.I., Kilias, S.P., Bitzios, D.C., Nicolaou, M., Both, R.A. (1989) Genesis of the Olympias carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn (Au, Ag) sulfide ore deposit, Eastern Chalkidiki Peninsula, N. Greece. Econ. Geol. 84:1210–1234
Kamilli, R.J., Ohmoto, H. (1977) Paragenesis, zoning, fluid inclusion and isotopic studies of the Finlandia vein, Colqui district, central Peru. Econ. Geol. 72:950–982
Kilias, S.P., Kalogeropoulos, S.I. (1989) Physicochemical conditions during sulfide formation of the Olympias carbonatehosted Pb-Zn (Au, Ag) sulfide ore deposit, eastern Chalkidiki Peninsula, N. Greece: evidence from fluid inclusions and arsenopyrite geothermometry. Geol. Soc. Greece Bull. 23/2:271–282 (in Greek with English Abstract)
Kockel, F., Molat, H., Walther, H. (1977) Erlanterung en zur geologiscen Karte der Chalkidiki und angrenzender Gebiete 1∶100 000, Nordgriechenland. Bundesamt. Geowiss. Rohst., Hannover, 119 pp
Kwak, T.A.P. (1986) Fluid inclusions in skarns (carbonate replacement deposits). J. Metam. Geol. 4:363–384
Lynch, J.V.G., Longstaffe, F.J., Nesbitt, B.E. (1990) Stable isotopic and fluid inclusion indications of large-scale hydrothermal paleoflow, boiling, and fluid mixing in the Keno Hill Ag-Pb-Zn district, Yukon Territory, Canada. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 54:1045–1059
Mantzos, L.A. (1989) Geology and lithogeochemistry of the Olympias carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn sulfide deposit, Chalkidiki, Greece. Unpub. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College, University of London, 404 pp
Megaw, P.K.M., Ruiz, J., Titley, S.R. (1988) High-temperature, carbonate-hosted Ag-Pb-Zn (Cu) deposits of Northern Mexico. Econ. Geol. 83:1856–1885
Meinert, L.D. (1987) Skarn zonation and fluid evolution in the Groundhog mine, Central mining district, New Mexico. Econ. Geol. 82:523–545
Nebel, M.L., Hutchinson, R.W., Zartman, R.E. (1991) Metamorphism and polygenesis of the Madem Lakos polymetallic sulfide deposit, Chalkidiki, Greece. Econ. Geol. 86:81–105
Nebel, M.L., Hutchinson, R.W., Zartman, R.E. (1992) Metamorphism and polygenesis of the Madem Lakos polymetallic sulfide deposit, Chalkidiki, Greece a reply. Econ. Geol. 87:1187–1190
Nicolaou, M., Kokonis, I. (1980) Geology and development of Olympias mine, Eastern Chalkidiki, Macedonia, Greece. In: Jones M.J. (ed.) Complex sulfide ores, London Inst. Mining Metallurgy, pp. 260–270
Ohmoto, H., Rye, R.O. (1970) The Bluebell mine, British Columbia, mineralogy, paragenesis, fluid inclusions, and the isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. Econ. Geol. 65:417–437
Pichavant, M., Ramboz, C., Weisbrod, A. (1982) Fluid immiscibility in natural processes: use and misuse of fluid inclusion data. I. Phase equilibria analysis a theoretical and geometrical approach. Chem. Geol. 37:1–27
Potter, R.W., II., Brown, D.L. (1977) The volumetric properties of aqueous sodium chloride solutions from 0 °C to 500 °C at pressures up to 2000 bar based on a regression of available data in the literature. US Geol. Survey Bull. 1421-C, 36 pp
Potter, R.W., II., Clynne, M.A., Brown, D.L. (1978) Freezing point depression of aqueous sodium chloride solutions. Econ. Geol. 73:284–285
Poty, B., Leroy, J., Jachimowicz, L. (1976) Un nouvel appareil pour la mesure de temperatures sous le microscope: I: installation de microthermometrie Chaixmeca. Bull. Mineral. 99:182–186
Ramboz, C., Pichavant, M., Weisbrod, A. (1982) Fluid immiscibility in natural processes: use and misuse of fluid inclusion data in terms of immiscibility. Chem. Geol. 37:29–48
Reed, M.H., Spycher, N.F. (1985) Boiling, cooling and oxidation in epithermal systems: A numerical modeling approach. In: Berger, B.R., Bethke, P.M. (eds.) Geology and geochemistry of epithermal systems, Reviews in Economic Geology 2:249–272
Robert, F., Kelly, W.C. (1987) Ore-forming fluids in Archean goldbearing quartz veins at the Sigma mine, Abitibi greenstone belt, Quebec, Canada. Econ. Geol. 82:1464–1482
Roedder, E. (1984) Fluid inclusions. Mineral. Soc. Am., Reviews in Mineralogy 12:644 pp
Sawkins, F.J. (1964) Lead-zinc ore deposition in the light of fluid inclusions, Providencia mine, Zacatecas, Mexico. Econ. Geol. 59:883–919
Shelton, K.L. (1983) Composition and origin of ore-forming fluids in a carbonate-hosted porphyry copper and skarn deposit: a fluid inclusion and stable isotope study of Mines Gaspe, Quebec. Econ. Geol. 78:387–421
Shepherd, T.J., Rankin, A.H., Alderton, D.H.M. (1985) A practical guide to fluid inclusion studies. In: Shepherd, T.J., Rankin, A.H., Alderton, D.H.M. (eds.). Blackie, New York
Simone, I.S. (1951) Geology and ore deposits of the Zimapan mining district, Mexico. Unpub. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, 237 PP
So, C., Yun, S., Koh, Y. (1993) Mineralogie, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope evidence for the genesis of carbonate-hosted PbZn(-Ag) orebodies of the Taebaek deposit, Republic of Korea. Econ. Geol. 88:855–872
Sourirajan, S., Kennedy, G.S. (1962) The system H2O-NaCl at elevated temperatures and pressures. Am. J. Sci. 260:115–141
Surles, T.L. (1978) Chemical and thermal variations accompanying formation of garnet skarns near Patogonia, Arizona. Unpub. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Arizona, 54 pp
Trommsdorf, V., Skippen, G. (1986) Vapor loss (“Boiling”) as a mechanism for fluid evolution in metamorphic rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 94:317–322
Urusova, M.A. (1975) Phase equilibria and thermodynamic characteristics of solutions in the system H2O-NaCl and NaOH-H2O at 350–550 °C. Geochem. Int. 11:944–950
Woods, T.L., Roedder, E., Bethke, P.M. (1982) Fluid inclusion data on samples from Creede, Colorado, in relation to mineral para genesis. US Geol. Survey Open-File Rept. 82-313, 77 pp
Weast, R.C. (1977) CRC Handbook of chemistry and physics. CRC Press, Cleveland, Ohio
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilias, S.P., Kalogeropoulos, S.I. & Konnerup-Madsen, J. Fluid inclusion evidence for the physicochemical conditions of sulfide deposition in the Olympias carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn(Au, Ag) sulfide ore deposit, E. Chalkidiki peninsula, N. Greece. Mineral. Deposita 31, 394–406 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189187
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00189187