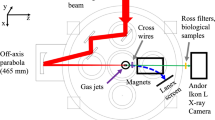
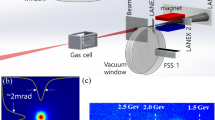
Abstract
The supersonic gas-jet target is an important experimental target for laser wakefield acceleration (LWFA), which has great potential for driving novel radiation sources such as betatron radiation and Compton scattering gamma rays. According to different electron acceleration requirements, it is necessary to provide specific supersonic gas jets with different density profiles to generate electron beams with high quality and high repetition rates. In this study, the interference images and density profiles of different gas-jet targets were obtained through a modified Nomarski interference diagnosis system. The relationships between the gas density and back pressure, nozzle structure, and other key parameters were studied. Targets with different characteristics are conducive to meeting the various requirements of LWFA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.A. Mourou, T. Tajima, S.V. Bulanov, Optics in the relativistic regime. Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 309 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.78.309
T. Tajima, J.M. Dawson, Laser electron accelerator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 267 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.43.267
E. Esarey, C.B. Schroeder, W.P. Leemans, Physics of laser-driven plasma-based electron accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1229 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1229
X. Wang, R. Zgadzaj, N. Fazel et al., Quasi-monoenergetic laser-plasma acceleration of electrons to 2 GeV. Nature Commun. 4, 1988 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2988
A.J. Gonsalves, K. Nakamura, J. Daniels et al., Petawatt laser guiding and electron beam acceleration to 8 GeV in a laser-heated capillary discharge waveguide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 122, 084801 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.122.084801
A. Rousse, K.T. Phuoc, R. Shah et al., Production of a keV X-ray beam from synchrotron radiation in relativistic laser-plasma interaction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 135005 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.135005
S. Corde, K.T. Phuoc, G. Lambert et al., Femtosecond x rays from laser-plasma accelerators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 1–48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1
K.T. Phuoc, S. Corde, R. Shah et al., Imaging electron trajectories in a laser-wakefield cavity using betatron x-ray radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 225002 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.225002
Y. Lu, G. Zhang, J. Zhao et al., Ultra-brilliant GeV betatronlike radiation from energetic electrons oscillating in frequency-downshifted laser pulses. Opt. Express 29, 6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.419761
S.G. Rykovanov, C.G.R. Geddes, J.-L. Vay et al., Quasi-monoenergetic femtosecond photon sources from Thomson Scattering using laser plasma accelerators and plasma channels. J. Phys. B AT Mol. Opt. 47, 23 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-4075/47/23/234013
E. Irani, H. Omidvar, R. Sadighi-Bonabi, Gamma rays transmutation of Palladium by bremsstrahlung and laser inverse Compton scattering. Energ. Convers. Manage. 77, 558 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.78.3091
D. Li, K. Imasaki, K. Horikawa et al., Iodine transmutation through laser compton scattering gamma rays. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 46, 8 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3327/jnst.46.831
H. Xu, H. Wu, G. Fan et al., A new consecutive energy calibration method for X/\( \gamma \) detectors based on energy continuously tunable laser Compton scattering light source. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 28, 121 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-017-0272-1
X. Zhu, M. Chen, S. Weng et al., Extremely brilliant GeV \(\gamma\) -rays from a two-stage laser-plasma accelerator. Sci. Adv. 6, 22 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz7240
C.G.R. Geddes, C. Toth, J. Van Tilborg et al., High-quality electron beams from a laser wakefield accelerator using plasma-channel guiding. Nature 431, 538 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02900
J. Faure, Y. Glinec, A. Pukhov et al., High-charge energetic electron bunch generated by 100 TW laser pulse. Nature 431, 541 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02963
S.P.D. Mangles, C.D. Murphy, Z. Najmudin et al., Particle acceleration using intense laser produced plasmas. Nature 431, 535 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02939
F. Sylla, A. Flacco, S. Kahaly et al., Short intense laser pulse collapse in near-critical plasma. Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 085001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.085001
W. Wang, W. Li, J. Liu et al., High-brightness high-energy electron beams from a laser wakefield accelerator via energy chirp control. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 124801 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.124801
F. Salehi, A.J. Goers, G.A. Hine et al., MeV electron acceleration at 1 kHz with<10 mJ laser pulses. Optics Lett. 42, 2 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.42.000215
D. Guenot, D. Gustas, A. Vernier et al., Relativistic electron beams driven by kHz single-cycle light pulses Nat. Photonics 11, 5 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2017.46
K. Schmida, L. Veisz, Supersonic gas jets for laser-plasma experiments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83, 053304 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4719915
B. Landgraf, M. Schnell, A. Savert et al., High resolution 3D gas-jet characterization. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82, 083106 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3624694
V. Malka, C. Coulaud, J.P. Geindre et al., Characterization of neutral density profile in a wide range of pressure of cylindrical pulsed gas jets. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 71, 2329 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1150619
S. Lorenz, G. Grittani, E. Chacon-Golcher et al., Characterization of supersonic and subsonic gas targets for laser wakefield electron acceleration experiments. Matter. Radiat. Extremes 4, 015401 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5081509
F. Sylla, M. Veltcheva, S. Kahaly et al., Development and characterization of very dense submillimetric gas jets for laser-plasma interaction. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 83, 033507 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3697859
A.M. Hansen, D. Haberberger, J. Katz et al., Supersonic gas-jet characterization with interferometry and Thomson scattering on the OMEGA Laser System. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89, 10C103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5036645
X. Jun, H. Feng, C. Zhong et al., Super-resolution of interference pattern with independent laser beams. Chin. Phys. Lett. 22, 2824 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/22/11/027
X. Yang, A new MachZehnder interferometer to measure light beam dispersion and phase shift. Chin. Phys. Lett. 30, 040701 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/30/4/040701
J. Nejdl, J. VanCura, K. Bohacek et al., Imaging Michelson interferometer for a low-density gas jet characterization. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90, 065107 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5098084
S. Feister, J.A. Nees, J.T. Morrison et al., A novel femtosecond-gated, high-resolution, frequency-shifted shearing interferometry technique for probing pre-plasma expansion in ultra-intense laser experiments. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 11D602 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4886955
Q. Liu, M. Ma, X. Zhang et al., Application of Nomarski interference system in supersonic gas-jet target diagnosis. AIP Adv. 11, 015145 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0027317
G. Pretzier, A new method for numerical Abel-inversion. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung A 46, 639-641 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1515/zna-1991-0715
L.M. Smith, D.R. Keefer, S.I. Sudharsanan, Abel inversion using transform techniques. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 39, 367-373 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4073(88)90101-X
H.A. Lorentz, Ueber die Beziehung zwischen der Fortpflanzungsgeschwindigkeit des Lichtes und der Körperdichte. Ann. Phys. 245, 641–655 (1880). https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.18802450406
L. Lorenz, Ueber die Refractionsconstante. Ann. Phys. 247, 70–103 (1880). https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.18802470905
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Experiment was carried out by Qiu-Shi Liu, Ming-Jiang Ma, Bao-Zhen Zhao, Xiao-Hua Zhang, Xiang-Hao Meng, and Xiao-Na Ban. Data analysis was performed by Qiu-Shi Liu, Bing Guo, Chong Lv, Ji Zhang, Bao-Xian Tian, and Chuang-Ye He. Optical diagnosis system was set up by Qiu-Shi Liu, Ming-Jiang Ma, Zhao Wang, and Xiao-Feng Xi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Qiu-Shi Liu, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work was supported by the Programs for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11975316, 11775312, 12005305 and 61905287) and the Continue Basic Scientific Research Project (Nos. WDJC-2019-02 and BJ20002501).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, QS., Ma, MJ., Zhao, BZ. et al. Effect of multiple parameters on the supersonic gas-jet target characteristics for laser wakefield acceleration. NUCL SCI TECH 32, 75 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-021-00910-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-021-00910-1