Abstract
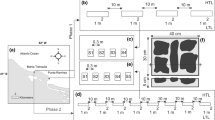
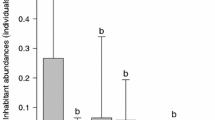
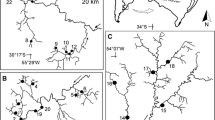
In this study we combine textural and compositional information to characterize the intertidal sediments from three relevant shellfishing banks located in the Rías Altas (Vilarrube, Lombo das Navallas) and Rías Baixas (Playa America) of Galicia (NW Spain). The purpose of this study is to explore the relevance of the sediment characteristics as a key parameter in the decline of commercially exploitable populations of the bivalve Donax trunculus in two of the banks (Lombo das Navallas and Playa América) but not in the other (Vilarrube). The sediments of the three areas show their own distinctive sedimentary characteristics that became defined by their grain size parameters, mineralogical and elemental composition. This is the result of regional land supplies from the erosion of drainage areas and sea cliffs together with the contribution of modern carbonate bioclasts. Notably, the sediments of Vilarrube are characterized by moderately sorted to well sorted fine sand showing little spatial variability. According to our results, sediment texture seems to be a relevant parameter for the settlement and growth of commercial populations of Donax trunculus.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso A, Lorenzo F, Pagés JL (2000) Dinámica litoral y erosión en la ría de El Barquero: factores antrópicos y procesos naturales. Geogaceta 28:7–10
Bernabeu AM, Lersundi-Kanpistegi AV, Vilas F (2012) Gradation from oceanic to estuarine beaches in a ría environment: a case study in the Ría de Vigo. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 102–103:60–69
Blott SJ, Pye K (2001) GRADISTAT: a grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf Process Landf 26:1237–1248
CENTRO DE INVESTIGATIÕNS MARIÑAS (CIMA) Memoria (2014) Conselleria do medio rural e do mar. https://mar.xunta.gal/sites/default/files/fileadmin/arquivos/cima/memorias/cima_memoria_2014_es.pdf
de la Huz R, Lastra M, López J (2002) The influence of sediment grain size on burrowing, growth and metabolism of Donax trunculus L. (Bivalvia: Donacidae). J Sea Res 47:85–95
Delgado I, Alcántara-Carrio J, Alejo I, Alonso I, Louzao M (2002) Influence of hydrodynamics and sedimentary characteristics of Barqueiro ria on Arealonga beach dynamics. J Coast Res SI 36:231–239
Folk RL, Ward WC (1957) Brazos River bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J Sediment Petrol 27:3–26
Freire J, García-Allut A (2000) Socioeconomic and biological causes of management failures in European artisanal fisheries: the case of Galicia (NW Spain). Mar Policy 24:375–384
Grupo Rías Altas (2012) Estudo Integral das Rías Altas. Estudo das rías de Ribadeo, Viveiro, O Barqueiro e Ortigueira Hidrografía, dinámica, bioxeoquímica, sedimentoloxía, ecotoxicoloxía, microbioloxía, patoloxia e bioloxía das zonas de interese marisqueiro Xunta de Galicia Consellería do Medio Rural e do Mar, p 23
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) Past: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9. http://palaeoelectronica.org/2001_1/past/issue1_01.htm
Hulseman J (1966) An inventory of marine carbonate materials. J Sediment Petrol ASCE 36:622–625
La Valle P, Nicoletti L, Finoia MG, Ardizzone GD (2011) Donax trunculus (Bivalvia: Donacidae) as a potential biological indicator of grain-size variations in beach sediment. Ecol Indi. 11:1426–1436
Martí A, García E, Maragayas A (1998) Rachas máximas y temporales de viento en Galicia. Revista Lurralde 21:261–280
Nel R, McLachlan A, Winter DPE (2001) The effect of grain size on the burrowing of two Donax species. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 265:219–238
Rubio B, Vilas F, Nombela MA (2000) La contaminación por metales pesados en las Rías Baixas gallegas: nuevos valores de fondo para la Ría de Vigo (NO de España). J Iber Geol 26:121–149
Sassa S, Watabe Y, Yang S, Kuwae T (2011) Burrowing Criteria and Burrowing Mode Adjustment inBivalves to Varying Geoenvironmental Conditions in Intertidal Flats and Beaches. PLoS ONE 6(9):e25041. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025041
Vilas F, Nombela MA (1985) Las zonas estuarinas de la costa de Galicia y sus medios asociados, NW Península Ibérica. Thalassas 3:7–15
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Xunta de Galicia, Proyecto PGIDT-CIMA 13/08,The authors wish to acknowledge the support from the University of Vigo Marine Research Centre. This study was cofunded by Consellería de Educación e Ordenación Universitaria Xunta de Galicia (Galician Regional Government) and by the European Union. Operative Program ERDF Galicia 2014-2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nombela, M.Á., Diz, P., Couto, E.N. et al. Textural Characteristics might Influence Donax trunculus Shellfishing Banks Exploitability. Thalassas 33, 87–93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-017-0025-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-017-0025-2