Abstract
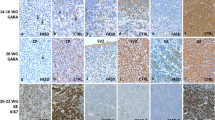
Ethanol induces massive neuroapoptosis in the developing brain. However, whether ethanol-induced neuroapoptosis also involves GABA interneurons remains unknown. Here, we addressed this question in the postnatal days (P) P3-P24 GAD67-GFP mouse hippocampus using cleaved caspase-3 staining, a sensitive measure of ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration combined with DAPI staining to monitor the apoptotic nuclear degradation. We observed that 8 h following ethanol treatment (6 g/kg, intraperiotoneally), significant proportion of GAD67-GFP expressing hippocampal interneurons was stained with cleaved caspase-3 antibodies and displayed chromatin condensation with a formation of the DAPI-stained apoptotic bodies. Maximal number of the cleaved caspase-3 stained interneurons (16.6 % of the total number of GFP expressing neurons and 21.6 % of the total number of caspase-3 stained cells) was observed in the hippocampal slices from P6-9 mice, and minimal damage to interneurons was observed in P3–4 and > P11 mice. While the apoptotic interneurons were found in all hippocampal regions and layers, their highest density was observed in the CA1 region and hilus. Thus, ethanol-induced neuroapoptosis involves hippocampal interneurons that may contribute to the life-long neurobehavioral deficits, increased excitability, and higher incidence of seizures characteristic of the fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikonomidou, C., Bittigau, P., Ishimaru, M. J., Wozniak, D. F., Koch, C., Genz, K., et al. (2000). Ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration and fetal alcohol syndrome. Science, 287, 1056–1060.
Lebedeva, J., Zakharov, A., Ogievetsky, E., Minlebaeva, A., Kurbanov, R., Gerasimova, E., Sitdikova, G., and Khazipov, R. (2015). Inhibition of Cortical Activity and Apoptosis Caused by Ethanol in Neonatal Rats In Vivo. Cereb. Cortex, pii: bhv293 (Epub ahead of print).
Olney, J. W. (2014). Focus on apoptosis to decipher how alcohol and many other drugs disrupt brain development. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 2, 81. doi:10.3389/fped.2014.00081.
West, J. R., Hamre, K. M., Cassell, M. D. (1986). Effects of ethanol exposure during the third trimester equivalent on neuron number in rat hippocampus and dentate gyrus. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 10, 190–197.
Tamamaki, N., Yanagawa, Y., Tomioka, R., Miyazaki, J., Obata, K., Kaneko, T. (2003). Green fluorescent protein expression and colocalization with calretinin, parvalbumin, and somatostatin in the GAD67-GFP knock-in mouse. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 467, 60–79.
Olney, J. W., Tenkova, T., Dikranian, K., Muglia, L. J., Jermakowicz, W. J., D’Sa, C., et al. (2002). Ethanol-induced caspase-3 activation in the in vivo developing mouse brain. Neurobiology of Disease, 9, 205–219.
Willingham, M. C. (1999). Cytochemical methods for the detection of apoptosis. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry, 47, 1101–1110.
Lebedeva, Y. A., Zakharova, A. V., Sitdikova, G. F., Zefirov, A. L., Khazipov, R. N. (2016). Ketamine-midazolam anesthesia induces total inhibition of cortical activity in the brain of newborn rats. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, 161, 15–19.
Sitdikova, G., Zakharov, A., Janackova, S., Gerasimova, E., Lebedeva, J., Inacio, A. R., et al. (2014). Isoflurane suppresses early cortical activity. Annals of Clinical Translational Neurology, 1, 15–26.
Jevtovic-Todorovic, V., Hartman, R. E., Izumi, Y., Benshoff, N. D., Dikranian, K., Zorumski, C. F., et al. (2003). Early exposure to common anesthetic agents causes widespread neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain and persistent learning deficits. Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 876–882.
Freund, T., & Buzsaki, G. (1996). Interneurons of the hippocampus. Hippocampus, 6, 345–470.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by INSERM (LIA to RK), the Program of Competitive Growth of Kazan Federal University, and the subsidy allocated to Kazan Federal University for the state assignment in the sphere of scientific activities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Elena Ogievetsky and Nailya Lotfullina contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogievetsky, E., Lotfullina, N., Minlebaeva, A. et al. Ethanol-Induced Apoptosis of Interneurons in the Neonatal GAD67-GFP Mouse Hippocampus. BioNanoSci. 7, 151–154 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0334-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-016-0334-6